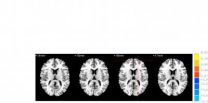
(Press-News.org) Both acupuncture at Waiguan (SJ5) and sham acupuncture can activate/deactivate several brain regions in patients with ischemic stroke, but there are some difference in Brodmann areas 4, 6, 8, Brodmann areas 7, 39, 40, Brodmann areas 18, 19, 22 and Brodmann areas 13, 24, 32, 28. Most studies addressing the specificity of meridians and acupuncture points have focused mainly on the different neural effects of acupuncture at different points in healthy individuals. Dr. Ji Qi and co-workers from School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University in China examined the effects of acupuncture on brain function in a pathological context, and compared the effects between Waiguan and sham points in 16 patients with ischemic stroke. Compared with sham acupuncture, acupuncture at Waiguan in stroke patients inhibited Brodmann area 5 on the healthy side. These findings, published in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 3, 2014), indicated that the altered specificity of sensation-associated cortex (Brodmann area 5) is possibly associated with a central mechanism of acupuncture at Waiguan for stroke patients.INFORMATION:
Article: " Acupuncture at Waiguan and sham points influences activation of functional brain areas of ischemic stroke patients: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study" by Ji Qi1, Junqi Chen2, Yong Huang1, Xinsheng Lai3, Chunzhi Tang3, Junjun Yang4, Hua Chen5, Shanshan Qu1 (1 School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, China; 2 Department of Rehabilitation, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, China; 3 School of Acupuncture-moxibustion and Tuina, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, China; 4 School of Chinese Medicine, Hongkong Baptist University, Hongkong, China; 5 School of Biomedical Engineering, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, China)
Qi J, Chen JQ, Huang Y, Lai XS, Tang CZ, Yang JJ, Chen H, Qu SS. Acupuncture at Waiguan and sham points influences activation of functional brain areas of ischemic stroke patients: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(3):293-300.
Contact: Meng Zhao
eic@nrren.org
86-138-049-98773
Neural Regeneration Research
http://www.nrronline.org/
Acupuncture at Waiguan improves activation of functional brain areas of stroke patients
2014-04-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Physicist demonstrates dictionary definition was dodgy
2014-04-23
It is the defining moment that demonstrates a QUT physicist was correct in pointing out a 99-year-old mistake to one of the world's most authoritative dictionaries.
QUT Senior Lecturer in Physics, Dr Stephen Hughes, sparked controversy over how a humble siphon worked when he noticed an incorrect definition in the prestigious Oxford English Dictionary.
In 2010, eagle-eyed Dr Hughes spotted the mistake, which went unnoticed for 99 years, which incorrectly described atmospheric pressure, rather than gravity, as the operating force in a siphon.
Dr Hughes demonstrated ...
Atorvastatin protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury
2014-04-23
In addition to its lipid-lowering effect, statins exert anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects as well. Statins also provide protection against renal, pulmonary and myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. However, little evidence is available on similar changes in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Therefore, Dr. Qiuyun Tu and colleagues from Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University in China verified that atorvastatin, a commonly used lipid-lowering drug, protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through anti-infammatory and antioxidant effects. ...
Is nuclear power the only way to avoid geoengineering?
2014-04-23
Los Angeles, London (April 23, 2014). "I think one can argue that if we were to follow a strong nuclear energy pathway—as well as doing everything else that we can—then we can solve the climate problem without doing geoengineering." So says Tom Wigley, one of the world's foremost climate researchers, in the current issue of Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, published by SAGE. Refusing to take significant action on climate change now makes it more likely that geoengineering will eventually be needed to address the problem, Wigley explains in an exclusive Bulletin interview. ...
Midlife occupational and leisure-time physical activity limits mobility in old age
2014-04-23
Inverse Effects of Midlife Occupational and Leisure Time Physical Activity on Mobility Limitation in Old Age
Strenuous occupational physical activity in midlife increases the risk of mobility limitation in old age, whereas leisure-time physical activity decreases the risk. This is found in a study which followed up 5,200 public sector employees for 28 years. The study was conducted at the Gerontology Research Center in Finland and the Finnish Institute of Occupational Health.
Heavy physical labor is often repetitive, wears the body and lasts for several hours a day. ...
Fires in the Primorsky Province of Russia
2014-04-23
One of the most influential ecological disturbances is fire. Fire can spread so rapidly and for such far distances that its impact on land is for the most part far greater than any other factor. Less than optimal logging practices in the Primorksy region worsen the problems of human-caused fires in this area. Abandoned fields with dry grasses provide the detritus that can fuel an out of control blaze with a single spark.
In southwest Primorsky Province dry grass has been burned for centuries. This uncontrolled method of managing agricultural areas each year turns the ...
New discovery helps solve mystery source of African lava
2014-04-23
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Floods of molten lava may sound like the stuff of apocalyptic theorists, but history is littered with evidence of such past events where vast lava outpourings originating deep in the Earth accompany the breakup of continents.
New research at Michigan State University shows that the source of some of these epic outpourings, however, may not be as deep as once thought. The results, published in the Journal Geology, show that some of these lavas originated near the surface rather than deep within the mantle.
When geoscientists want to learn more about ...
Non-uniform genetic mutations identified in lung cancers could lead to targeted treatment
2014-04-23
The research, published in the journal Oncotarget, explored tumour heterogeneity – where different cells have different appearances or their own DNA signatures within the same cancer. Such differences could make it difficult to design effective, targeted treatment strategies.
Firstly they confirmed the mutual exclusivity between the EGFR mutation and either the KRAS or BRAF mutation. Secondly, they found that lung cancers driven by the EGFR gene mutation have that specific mutation present uniformly throughout the tumour, regardless of microscopic appearance. In stark ...
ADHD drug may help preserve our self-control resources
2014-04-23
Methylphenidate, also known as Ritalin, may prevent the depletion of self-control, according to research published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Self-control can be difficult — sticking with a diet or trying to focus attention on a boring textbook are hard things to do. Considerable research suggests one potential explanation for this difficulty: Exerting self-control for a long period seems to "deplete" our ability to exert self-control effectively on subsequent tasks.
"It is as if self-control is a limited resource ...
Functional electrical stimulation improves neuronal regeneration after cerebral infarction
2014-04-23
Previous studies have shown that proliferation of endogenous neural precursor cells cannot alone compensate for the damage to neurons and axons. From the perspective of neural plasticity, Dr. Yun Xiang and co-workers from Sun Yat-sen University in China observed the effects of functional electrical stimulation treatment on endogenous neural precursor cell proliferation and expression of basic fibroblast growth factor and epidermal growth factor in the rat brain on the infarct side. The researchers found that functional electrical stimulation can promote endogenous neural ...
Toward unraveling the Alzheimer's mystery
2014-04-23
Getting to the bottom of Alzheimer's disease has been a rapidly evolving pursuit with many twists, turns and controversies. In the latest crook in the research road, scientists have found a new insight into the interaction between proteins associated with the disease. The report, which appears in the journal ACS Chemical Neuroscience, could have important implications for developing novel treatments.
Witold K. Surewicz, Krzysztof Nieznanski and colleagues explain that for years, research has suggested a link between protein clumps, known as amyloid-beta plaques, in the ...