(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR, Mich. — Prostate cancer becomes deadly when anti-hormone treatments stop working. Now a new study suggests a way to block the hormones at their entrance.
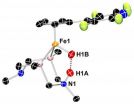
Researchers from the University of Michigan Comprehensive Cancer Center have found that a protein called BET bromodomain protein 4 binds to the hormone androgen receptor downstream of where current therapies work – targeting androgen receptor signaling.
This could mean that when prostate cancer becomes resistant to current treatments, it might remain sensitive to a drug that targets BET bromodomain proteins. Results appear in Nature.
"We think we can target prostate cancer through androgen receptor signaling, rather than directly hitting the androgen receptor. These initial findings suggest the potential that a BET bromodomain inhibitor can work even when prostate cancer becomes resistant to anti-hormone therapies," says senior study author Arul Chinnaiyan, M.D., Ph.D., director of the Michigan Center for Translational Pathology and S.P. Hicks Professor of Pathology at the University of Michigan Medical School.
The researchers used a compound called JQ1, designed to inhibit BET bromodomain proteins, to test the concept in cell lines and mice. They found that JQ1 blocked androgen signaling even when cells no longer responded to current anti-androgen therapies. The JQ1 BET bromodomain inhibitor blocked androgen receptor signaling, which is downstream of the androgen receptor, making it potentially unaffected by the acquired resistance related to hormone signaling.
The researchers also found that BET inhibitors appear to block several transcription factors, including the TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion and MYC, known to drive prostate cancer.
Bromodomain inhibitors have been explored in blood cancers and a rare cancer called NUT midline carcinoma. This is one of the first indications that BET bromodomain inhibitors may be beneficial in a common solid tumor.
A newly formed company, OncoFusion Therapeutics, co-founded by Chinnaiyan and study co-author Shaomeng Wang, Ph.D., will look at developing potential BET bromodomain inhibitors to attack prostate cancer.
"BET bromodomain represents one of the most exciting targets in epigenetics," Chinnaiyan says. "Developing new ways to treat castration-resistant prostate cancer is critical to improving survival for this disease."
INFORMATION:
Additional authors: Irfan A. Asangani, Vijaya L. Dommeti, Xiaoju Wang, Rohit Malik, Marcin Cieslik, June Escara-Wilke, Kari Wilder-Romans, Sudheer Dhanireddy, Carl Engelke, Mathew K. Iyer, Xiaojun Jing, Yi-Mi Wu, Xuhong Cao, Felix Y. Feng, from U-M; Rendong Yang and Zhaohui S. Qin, from Emory University
Funding: Prostate Cancer Foundation, National Cancer Institute grants CA111275 and CA69568, Doris Duke Charitable Foundation, American Cancer Society, A. Alfred Taubman Institute
Disclosure: Chinnaiyan and Wang are co-founders of OncoFusion Therapeutics, which is developing novel BET bromodomain inhibitors. Chinnaiyan, Wang and the University of Michigan have equity interest in OncoFusion.
Reference: Nature, DOI: 10.1038/nature13229, published online April 23, 2014
Resources:
U-M Cancer AnswerLine, 800-865-1125
U-M Comprehensive Cancer Center, http://www.mcancer.org
Clinical trials at U-M, http://www.mcancer.org/clinicaltrials
mCancerTalk blog, http://uofmhealthblogs.org/cancer
New target for prostate cancer resistant to anti-hormone therapies
BET bromodomain inhibitors look promising for castration-resistant prostate cancer
2014-04-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Quality control guidelines for genomics studies
2014-04-23
Sequencing an entire human genome is faster and cheaper than ever before, leading to an explosion of studies comparing the genomes of people with and without a given disease. Often clinicians and researchers studying genetic contributions to a certain disease encounter variations that appear to be responsible, only to find other people with the same mutation who don't have the disease or who are affected to a lesser degree.
How do doctors pinpoint the genetic changes that really cause disease? An open-access policy paper to be published Wednesday in Nature proposes guidelines ...
Picky male black widow spiders prefer well-fed virgins
2014-04-23
New University of Toronto Scarborough research shows that male black widow spiders prefer their female mates to be well-fed virgins – a rare example of mate preference by male spiders.
The study, authored by UTSC post-doc Emily MacLeod and Maydianne Andrade, a professor in UTSC's Department of Biological Sciences, found in both controlled field studies and the wild that males overwhelmingly chose to mate with well-fed, unmated females. They also found male black widows can tell whether a potential mate is well-fed and unmated by pheromones released by females.
"This ...
Halving hydrogen
2014-04-23
RICHLAND, Wash. -- Like a hungry diner ripping open a dinner roll, a fuel cell catalyst that converts hydrogen into electricity must tear open a hydrogen molecule. Now researchers have captured a view of such a catalyst holding onto the two halves of its hydrogen feast. The view confirms previous hypotheses and provides insight into how to make the catalyst work better for alternative energy uses.
This study is the first time scientists have shown precisely where the hydrogen halves end up in the structure of a molecular catalyst that breaks down hydrogen, the team reported ...
Increased infrastructure required for effective oil spill response in US Arctic
2014-04-23
WASHINGTON – A changing climate is increasing the accessibility of U.S. Arctic waters to commercial activities such as shipping, oil and gas development, and tourism, raising concern about the risk of oil spills. A new report from the National Research Council says that a full suite of proven oil response tools is needed to address potential oil spills in U.S. Arctic waters, but not all of them are readily available. While much is known about both oil behavior and response technologies in ice-covered environments, there are areas where additional research would enable ...
On the defensive
2014-04-23
People diagnosed with Huntington's disease, most in their mid-thirties and forties, face a devastating prognosis: complete mental, physical, and behavioral decline within two decades. "Mutant" protein clusters, long blamed for the progression of the genetic disease, have been the primary focus of therapies in development by pharmaceutical companies. But according to new research from Prof. Gerardo Lederkremer and Dr. Julia Leitman of Tel Aviv University's Department of Cell Research and Immunology, in collaboration with Prof. Ulrich Hartl of the Max Planck Institute for ...
ASTRO issues guideline on the role of postoperative radiation therapy for endometrial cancer
2014-04-23
Fairfax, Va., April 23, 2014— The American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) has issued a new guideline, "The Role of Postoperative Radiation Therapy for Endometrial Cancer: An ASTRO Evidence-Based Guideline," that details the use of adjuvant radiation therapy in the treatment of endometrial cancer. The guideline's executive summary is published in the May-June 2014 issue of Practical Radiation Oncology (PRO), the official clinical practice journal of ASTRO. The full-length guideline is available as an open-access article online at http://www.practicalradonc.org.
ASTRO's ...
Conservation priorities released for several protected areas along US-Mexico border
2014-04-23
This news release is available in French and Spanish.
Montreal, 23 April 2014—Today, the CEC released its Conservation Assessment for the Big Bend-Río Bravo Region: A Binational Collaborative Approach to Conservation, which identifies 29 priority conservation areas in a region straddling the United States-Mexico border that includes 11 different protected areas in the states of Texas, Coahuila, and Chihuahua. This region features unique, highly diverse arid and semi-arid habitats inhabited by rare and endangered plants and animals, and provides a vital migratory ...
Novel compound halts cocaine addiction and relapse behaviors
2014-04-23
BUFFALO, N.Y. – A novel compound that targets an important brain receptor has a dramatic effect against a host of cocaine addiction behaviors, including relapse behavior, a University at Buffalo animal study has found.
The research provides strong evidence that this may be a novel lead compound for treating cocaine addiction, for which no effective medications exist.
The UB research was published as an online preview article in Neuropsychopharmacology last week.
In the study, the compound, RO5263397, severely blunted a broad range of cocaine addiction behaviors.
"This ...
NASA sees last vestiges of Tropical Depression Jack
2014-04-23
Tropical Cyclone Jack had weakened to a tropical depression when NASA and JAXA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed above on April 22, 2014 at 1120 UTC/7:20 a.m. EDT.
At that time, TRMM found that Jack was devoid of almost all rainfall near the tropical cyclone's center. Outside the center was a different story, however. That's where TRMM's precipitation radar instrument found rain falling at a rate of over 130mm/hr (about 5.1 inches) in a band of thunderstorms that stretched from east of Jack's center to the south. Some of the thunderstorms even ...
EARTH Magazine: Faking quakes at full scale
2014-04-23
Alexandria, Va. – On a muggy day in mid-July 2009, a lone seven-story condominium complex northwest of Kobe, Japan, was violently shaken by an earthquake. Onlookers watched the 23-unit, wood-frame tower sway and bounce while, inside the building, furniture toppled and plates clattered to the floor. No one was hurt during the highly localized event and there was only minimal damage, in part because the building's wooden skeleton had been augmented to better resist earthquake shaking, but also because the whole event — from the seismicity to the partially furnished building ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists discover a new signaling pathway and design a novel drug for liver fibrosis
High-precision blood glucose level prediction achieved by few-molecule reservoir computing
The importance of communicating to the public during a pandemic, and the personal risk it can lead to
Improving health communication to save lives during epidemics
Antimicrobial-resistant hospital infections remain at least 12% above pre-pandemic levels, major US study finds
German study finds antibiotic use in patients hospitalised with COVID-19 appears to have no beneficial effect on clinical outcomes
Targeting specific protein regions offers a new treatment approach in medulloblastoma
$2.7 million grant to explore hypoxia’s impact on blood stem cells
Cardiovascular societies propel plans forward for a new American Board of Cardiovascular Medicine
Hebrew SeniorLife selected for nationwide collaborative to accelerate system-wide spread of age-friendly care for older adults
New tool helps identify babies at high-risk for RSV
Reno/Sparks selected to be part of Urban Heat Mapping Campaign
Advance in the treatment of acute heart failure identified
AGS honors Dr. Rainier P. Soriano with Dennis W. Jahnigen Memorial Award at #AGS24 for proven excellence in geriatrics education
New offshore wind turbines can take away energy from existing ones
Unprecedented research probes the relationship between sleep and memory in napping babies and young children
Job losses help explain increase in drug deaths among Black Americans
Nationwide, 32 local schools win NFL PLAY 60 grants for physical activity
Exposure to noise – even while in the egg – impairs bird development and fitness
Vitamin D availability enhances antitumor microbes in mice
Conservation actions have improved the state of biodiversity worldwide
Corporate emission targets are incompatible with global climate goals
Vitamin D alters mouse gut bacteria to give better cancer immunity
Escape the vapes: scientists call for global shift to curb consumer use of disposable technologies
First-of-its-kind study definitively shows that conservation actions are effective at halting and reversing biodiversity loss
A shortcut for drug discovery
Food in sight? The liver is ready!
Climate change could become the main driver of biodiversity decline by mid-century
Voluntary corporate emissions targets not enough to create real climate action
Curiosity promotes biodiversity
[Press-News.org] New target for prostate cancer resistant to anti-hormone therapiesBET bromodomain inhibitors look promising for castration-resistant prostate cancer