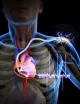
(Press-News.org) Daejeon, Republic of Korea, June 23, 2014--As the number of pacemakers implanted each year reaches into the millions worldwide, improving the lifespan of pacemaker batteries has been of great concern for developers and manufacturers. Currently, pacemaker batteries last seven years on average, requiring frequent replacements, which may pose patients to a potential risk involved in medical procedures.
A research team from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), headed by Professor Keon Jae Lee of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST and Professor Boyoung Joung, M.D. of the Division of Cardiology at Severance Hospital of Yonsei University, has developed a self-powered artificial cardiac pacemaker that is operated semi-permanently by a flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator.
The artificial cardiac pacemaker is widely acknowledged as medical equipment that is integrated into the human body to regulate the heartbeats through electrical stimulation to contract the cardiac muscles of people who suffer from arrhythmia. However, repeated surgeries to replace pacemaker batteries have exposed elderly patients to health risks such as infections or severe bleeding during operations.
The team's newly designed flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator directly stimulated a living rat's heart using electrical energy converted from the small body movements of the rat. This technology could facilitate the use of self-powered flexible energy harvesters, not only prolonging the lifetime of cardiac pacemakers but also realizing real-time heart monitoring.
The research team fabricated high-performance flexible nanogenerators utilizing a bulk single-crystal PMN-PT thin film (iBULe Photonics). The harvested energy reached up to 8.2 V and 0.22 mA by bending and pushing motions, which were high enough values to directly stimulate the rat's heart.
Professor Keon Jae Lee said:
"For clinical purposes, the current achievement will benefit the development of self-powered cardiac pacemakers as well as prevent heart attacks via the real-time diagnosis of heart arrhythmia. In addition, the flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator could also be utilized as an electrical source for various implantable medical devices."
INFORMATION:
This research result was described in the April online issue of Advanced Materials ("Self-Powered Cardiac Pacemaker Enabled by Flexible Single Crystalline PMN-PT Piezoelectric Energy Harvester": http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201400562/abstract).
Youtube link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZWYT2cU_Mog&feature=youtu.be
Self-powered cardiac pacemaker enabled by flexible piezoelectric energy harvester
The first demonstration of a self-powered cardiac pacemaker
2014-06-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Have you been unlucky -- or are you just lazy?
2014-06-23
A new study from the interdisciplinary Interacting Minds Centre at Aarhus University examines the difference between American and Danish attitudes to welfare services. Even though the two countries are traditionally portrayed as being miles apart in this respect, the study concludes that the difference between the ways the two societies are organised is not due to fundamental differences in attitude about when the state should provide financial assistance for citizens.
"The study challenges the conventional wisdom that we Danes are more inclined to play the Good Samaritan ...
New research proves gender bias extraordinarily prevalent in STEM careers
2014-06-23
NEW YORK — With everyone from the federal government to corporate America working to encourage more women to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) fields, you would think the doors would be wide open to women of all backgrounds. A new study from Columbia Business School shows that this could not be further from the truth and that gender bias among hiring managers in STEM fields is extraordinarily prevalent.
"How Stereotypes Impair Women's Careers in Science," written by Ernesto Reuben, assistant professor of management at Columbia Business ...
We can eliminate the major tornado threat in Tornado Alley
2014-06-23
The annually recurring devastating tornado attacks in US Tornado Alley raise an important question: Can we eliminate the major tornado threat in Tornado Alley? Some people may claim that such a question is beyond imagination as people are powerless in facing violent tornadoes. However, according to Professor Rongjia Tao's recent publication in IJMPB, human beings are not powerless on this issue: if we build three east-west great walls in Tornado Alley, we will eliminate major tornado threat there forever. These walls can be built locally at high tornado risk areas to eliminate ...
Not even cell death can stop the alarm
2014-06-23
Even after a cell dies, components of the immune system remain active and continue to fuel inflammatory reactions. An international team of researchers under the direction of scientists from the Institute of Innate Immunity at the University Hospital of Bonn has discovered how this incredible form of communication works. The findings offer potentially novel approaches for therapies against many serious diseases that affect a large part of the population, such as gout, atherosclerosis and Alzheimer's disease. The exciting new results are now published in the renowned journal ...
LED phosphors: Better red makes brighter white
2014-06-23
Chemists at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have developed a novel type of red phosphor material, which significantly enhances the performance of white-emitting LEDs.
In cooperation with Dr. Peter Schmidt of Philips Technologie GmbH in Aachen, a team of researchers led by Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Schnick, who holds the Chair of Inorganic Solid-State Chemistry at LMU Munich, has developed a new material for application in light-emitting diodes (LEDs). "With its highly unusual properties, the new material has the potential to revolutionize the LED market," says ...
Magnetic fields to measure positions of ferromagnetic objects accurately
2014-06-23
Many creatures in nature, including butterflies, newts and mole rats, use the Earth's inherent magnetic field lines and field intensity variations to determine their geographical position. A research team at the University of Minnesota has shown that the inherent magnetic fields of ferromagnetic objects can be similarly exploited for accurate position measurements of these objects. Such position measurement is enabled in this research by showing that the spatial variation of magnetic field around an object can be modeled using just the geometry of the object under consideration. ...
The colon has a safety mechanism that restricts tumor formation
2014-06-23
Colon cancer development starts with the formation of benign tumours called adenomas. It is estimated that between 30% and 50% of people over 50 will develop one of these tumours. These adenomas or polyps are the pre-cancerous lesions that, once they accumulate further genetic mutations over many years, can progress to colon cancer. A team headed by scientists at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) and headed by the ICREA researcher Eduard Batlle has discovered that the colon has a safety mechanism to restrict the formation and growth of adenomas. ...
Researchers discover new genes that promote brain cancer
2014-06-23
La Jolla, Calif., June 22, 2014, A new collaborative study carried out by researchers at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute (Sanford-Burnham), UC San Diego, the German Cancer Research Center, the University of Heidelberg (Germany), and 33 other research institutions has identified two oncogenes, called GFI1 and GFI1B, that drive the development of medulloblastoma, the most common malignant brain tumor in children.
The findings, published June 22 in Nature, suggest that GFI1 and GFI1B are worthy gene candidates for molecular-targeted therapy.
"Using state-of-the-art ...
Vitamin D can lower weight, blood sugar via the brain
2014-06-23
CHICAGO, IL—Women with type 2 diabetes and high cholesterol are less likely than their male peers to reach treatment goals to lower their "bad" cholesterol, or low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, despite access to cholesterol-lowering medication, a Canadian study finds. The results were presented on Saturday at the joint meeting of the International Society of Endocrinology and the Endocrine Society: ICE/ENDO 2014 in Chicago.
Although other research has shown a similar gender gap in reduction of LDL cholesterol among adults with diabetes, the new study found that ...
Low number of taste buds linked to older age, higher fasting blood sugar
2014-06-23
CHICAGO, IL—A study finds that the number of taste buds we have on our tongue decreases as we get older, and that the lower the number of taste buds, the more likely for fasting blood glucose (sugar) levels to be higher than normal. The results were presented Sunday at the joint meeting of the International Society of Endocrinology and the Endocrine Society: ICE/ENDO 2014 in Chicago.
Because high fasting blood sugar level is a main characteristic of diabetes, the study findings suggest that the number of taste buds plays a role in glucose metabolism—how the body uses ...