(Press-News.org) Underage drinkers are three times more likely to drink alcohol brands that advertise on television programs they watch compared to other alcohol brands, providing new and compelling evidence of a strong association between alcohol advertising and youth drinking behavior.
This is the conclusion of a new study from the Center on Alcohol Marketing and Youth (CAMY) at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and the Boston University School of Public Health that examined whether exposure to brand-specific alcohol advertising on 20 television shows popular with youth was associated with brand-specific consumption among underage drinkers.
Published in Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, it comes on the heels of a study from the same researchers published earlier this month which found underage drinkers are heavily exposed to magazine ads for the alcohol brands they consume.
"Taken together, these studies strengthen the case for a relationship between brand-specific alcohol advertising among underage youth and brand-specific consumption," said lead author Craig Ross, PhD, MBA, president of Virtual Media Resources in Natick, Massachusetts. "As alcohol continues to devastate so many young lives, youth exposure to alcohol advertising should be reduced."
Alcohol is the number one drug among youth and responsible for 4,300 deaths per year, yet alcohol advertising in the U.S. is primarily regulated by the industry itself through a voluntary code which serves as the main vehicle for reducing youth exposure to and appeal of alcohol advertising.
In the current study, researchers surveyed over one thousand youth ages 13-20 recruited from a national Internet panel maintained by Knowledge Networks. All reported consuming at least one drink of alcohol in the past 30 days. The researchers determined all alcohol brands the participants had consumed within the past 30 days, as well as their exposure to alcohol brand advertising on 20 television shows they had watched within the past month.
The researchers found that the relationship between consumption of a brand and advertising exposure for that brand was significant, and that the relationship was strongest at lower levels of exposure. Their results held even after controlling for other factors influencing youth drinking, such as their parents' drinking, whether the youth chose the brand themselves, the brand's average price, and the popularity of the brand among adults.
"There is a link between exposure to brand-specific advertising and youth choices about alcohol, independent of other factors," said study author and CAMY director David Jernigan, PhD.
"The question now becomes what do alcohol advertisers do with this information, given the consequences of alcohol consumption in underage youth," added study co-author Michael B. Seigel, MD, MPH, of the Boston University School of Public Health.
At least 14 long-term studies have found that the more young people are exposed to alcohol advertising and marketing, the more likely they are to drink, or if they are already drinking, to drink more.
INFORMATION:
"The Relationship Between Brand-Specific Alcohol Advertising on Television and Brand-Specific Consumption Among Underage Youth" was written by Craig S. Ross, Emily Maple, Michael Siegel, William DeJong, Timothy S. Naimi, Joshua Ostroff, Alisa A. Padon, Dina L.G. Borzekowski, and David Jernigan.
This research was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health's National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (5R01AA020309).
The Center on Alcohol Marketing and Youth monitors the marketing practices of the alcohol industry to focus attention and action on industry practices that jeopardize the health and safety of America's youth. The Center was founded in 2002 at Georgetown University with funding from The Pew Charitable Trusts and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The Center moved to the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in 2008 and is currently funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. For more information, visit http://www.camy.org.
Brand-specific television alcohol ads predict brand consumption among underage youth
2014-07-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
$15 billion annual public funding system for doctor training needs overhaul, says IOM
2014-07-29
WASHINGTON -- The U.S. should significantly reform the federal system for financing physician training and residency programs to ensure that the public's $15 billion annual investment is producing the doctors that the nation needs, says a new report by the Institute of Medicine. Current financing -- provided largely through Medicare -- requires little accountability, allocates funds independent of workforce needs or educational outcomes, and offers insufficient opportunities to train physicians in the health care settings used by most Americans, the report says.
All ...
A new way to make microstructured surfaces
2014-07-29
A team of researchers has created a new way of manufacturing microstructured surfaces that have novel three-dimensional textures. These surfaces, made by self-assembly of carbon nanotubes, could exhibit a variety of useful properties — including controllable mechanical stiffness and strength, or the ability to repel water in a certain direction.
"We have demonstrated that mechanical forces can be used to direct nanostructures to form complex three-dimensional microstructures, and that we can independently control … the mechanical properties of the microstructures," says ...
NASA sees warmer cloud tops as Tropical Storm Hernan degenerates
2014-07-29
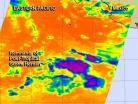
Tropical Storm Hernan degenerated into a remnant low pressure area on July 29. Infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite revealed cloud tops were warming as the storm weakened.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard Aqua gathered infrared data on a quickly weakening Hernan on July 29 at 5:11 a.m. EDT. The data was then made into a false-colored image at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The AIRS image showed small, fragmented areas of a few powerful thunderstorms with high, cold cloud tops in Tropical Storm Hernan as it continued ...
Superconductivity could form at high temperatures in layered 2-D crystals
2014-07-29
An elusive state of matter called superconductivity could be realized in stacks of sheetlike crystals just a few atoms thick, a trio of physicists has determined.
Superconductivity, the flow of electrical current without resistance, is usually found in materials chilled to the most frigid temperatures, which is impractical for most applications. It's been observed at higher temperatures–higher being about 100 kelvin or minus 280 degrees below zero Fahrenheit–in copper oxide materials called cuprate superconductors. But those materials are brittle and unsuitable for fabricating ...
Autistic brain less flexible at taking on tasks, Stanford study shows
2014-07-29
The brains of children with autism are relatively inflexible at switching from rest to task performance, according to a new brain-imaging study from the Stanford University School of Medicine.
Instead of changing to accommodate a job, connectivity in key brain networks of autistic children looks similar to connectivity in the resting brain. And the greater this inflexibility, the more severe the child's manifestations of repetitive and restrictive behaviors that characterize autism, the study found.
The study, which will be published online July 29 in Cerebral Cortex, ...
Diet affects men's and women's gut microbes differently
2014-07-29
The microbes living in the guts of males and females react differently to diet, even when the diets are identical, according to a study by scientists from The University of Texas at Austin and six other institutions published this week in the journal Nature Communications. These results suggest that therapies designed to improve human health and treat diseases through nutrition might need to be tailored for each sex.
The researchers studied the gut microbes in two species of fish and in mice, and also conducted an in-depth analysis of data that other researchers collected ...
Scientists separate a particle from its properties
2014-07-29
Researchers from the Vienna University of Technology have performed the first separation of a particle from one of its properties. The study, carried out at the Institute Laue-Langevin (ILL) and published in Nature Communications, showed that in an interferometer a neutron's magnetic moment could be measured independently of the neutron itself, thereby marking the first experimental observation of a new quantum paradox known as the 'Cheshire Cat'. The new technique, which can be applied to any property of any quantum object, could be used to remove disturbance and improve ...
The quantum Cheshire cat: Scientists separate a particle from its properties
2014-07-29
The Quantum Cheshire Cat: Can a particle be separated from its properties? On July 29, the prestigious journal, Nature Communications, published the results of the first Cheshire Cat experiment, separating a neutron from its magnetic field, conducted by Chapman University in Orange, CA, and Vienna University of Technology.
Chesire Cat"Well! I've often seen a cat without a grin," thought Alice in Wonderland, "but a grin without a cat! It's the most curious thing I ever saw in my life!" Alice's surprise stems from her experience that an object and its property cannot exist ...
The quantum Cheshire cat
2014-07-29
The Cheshire Cat featured in Lewis Caroll's novel "Alice in Wonderland" is a remarkable creature: it disappears, leaving its grin behind. Can an object be separated from its properties? It is possible in the quantum world. In an experiment, neutrons travel along a different path than one of their properties – their magnetic moment. This "Quantum Cheshire Cat" could be used to make high precision measurements less sensitive to external perturbations.
At Different Places at Once
According to the law of quantum physics, particles can be in different physical states at ...
Major turtle nesting beaches protected in 1 of the UK's far flung overseas territories
2014-07-29
But on the remote UK overseas territory of Ascension Island, one of the world's largest green turtle populations is undergoing something of a renaissance.
Writing in the journal Biodiversity and Conservation, scientists from the University of Exeter and Ascension Island Government Conservation Department report that the number of green turtles nesting at the remote South Atlantic outpost has increased by more than 500 per cent since records began in the 1970s. As many as 24,000 nests are now estimated to be laid on the Island's main beaches every year, making it the second ...