(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
NOAA's GOES-14 satellite was brought out of storage and put in Super Rapid Scan Operations for GOES-R mode and data of Tropical Storm Lowell from Aug. 19 was animated....
Click here for more information.
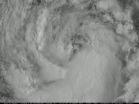
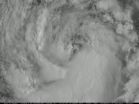
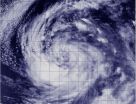
The south side of Tropical Storm Lowell appears to be its toughest side. That is, the side with the strongest thunderstorms, according to satellite imagery from NOAA's GOES-14 and NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellites.
NOAA took its GOES-14 satellite out of storage to simulate how the upcoming GOES-R satellite will work and captured a lot of data on Tropical Storm Lowell on August 19. Those data were used to create an animation that showed a gradual increase in the organization of a band of thunderstorms during the day.
The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Storm Lowell on August 19 at 21:42 UTC (5:42 p.m. EDT). The image showed a thick band of thunderstorms southwest of the center of circulation, wrapping into the center.
At 5 a.m. EDT on Wednesday, August 20, the National Hurricane Center (NHC) noted that curved bands of thunderstorms remained well organized on the south side of the circulation, but strong showers and thunderstorms were lacking to the north of the center.
At the same time, the center of Tropical Storm Lowell was located near latitude 18.7 north and longitude 121.0 west. That's about 775 miles (1,245 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California. Maximum sustained winds remain near 50 mph (85 kph). Lowell was moving toward the northwest near 5 mph (7 kph) and the NHC expects a slow northwest to north-northwest motion during the next day or so.
Forecaster Cangialosi at NHC noted that Lowell is currently over 27C/80.6F waters, and in an atmosphere of fairly low shear and high moisture. Tropical cyclones need waters at least near 26.6C/80F to maintain strength. Since the storm is expected to remain in these favorable conditions for another day and a half, some strengthening is forecast.
INFORMATION:
Text credit: Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA sees Tropical Storm Lowell's tough south side
2014-08-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gene therapy protects mice from lethal heart condition, MU researchers find
2014-08-20
COLUMBIA, Mo. — A new gene therapy developed by researchers at the University of Missouri School of Medicine has been shown to protect mice from a life-threatening heart condition caused by muscular dystrophy.
"This is a new therapeutic avenue," said Yi Lai, Ph.D., the leading author of the study and assistant research professor in the MU School of Medicine's Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology. "This is just a first step, but we hope this could lead to a treatment for people with this devastating heart condition, which is a leading cause of death for ...
Providing futile care in the ICU prevents other patients from receiving critical care
2014-08-20
Providing futile treatment in the intensive care unit sets off a chain reaction that causes other ill patients needing medical attention to wait for critical care beds, according to a study by researchers from UCLA and RAND Health.
The study is the first to show that when unbeneficial medical care is provided, others who might be able to benefit from treatment are harmed, said study lead author Dr. Thanh Huynh, an assistant professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA.
The findings also ...
Novel gene predicts both breast cancer relapse and response to chemotherapy
2014-08-20
Singapore—Scientists have made it easier to predict both breast cancer relapses and responses to chemotherapy, through the identification of a unique gene. The newly found marker could help doctors classify each breast cancer patient and customise a treatment regimen that is more effective. The discovery was a collaborative effort by scientists from A*STAR's Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology (IMCB), and the Cancer Science Institute of Singapore (CSI Singapore) at the National University of Singapore (NUS).
Despite advancements in cancer treatment, breast cancer ...
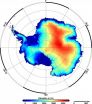
Record decline of ice sheets
2014-08-20
"The new elevation maps are snapshots of the current state of the ice sheets. The elevations are very accurate, to just a few metres in height, and cover close to 16 million km2 of the area of the ice sheets. This is 500,000 square kilometres more than any previous elevation model from altimetry", says lead-author Dr. Veit Helm, glaciologist at the Alfred Wegener Institute in Bremerhaven.
For the new digital maps, the AWI scientists had evaluated all data by the CryoSat-2 altimeter SIRAL. Satellite altimeter measure the height of an ice sheet by sending radar or laser ...
Researchers find security flaws in backscatter X-ray scanners
2014-08-20
A team of researchers from the University of California, San Diego, the University of Michigan, and Johns Hopkins University have discovered several security vulnerabilities in full-body backscatter X-ray scanners deployed to U.S. airports between 2009 and 2013.
In laboratory tests, the team was able to successfully conceal firearms and plastic explosive simulants from the Rapiscan Secure 1000 scanner. The team was also able to modify the scanner operating software so it presents an "all-clear" image to the operator even when contraband was detected. "Frankly, we were ...
Testing the shelf-life of nuclear reactors
2014-08-20
Oxford, August 20, 2014 – Researchers at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Idaho National Laboratory, Idaho Falls and TerraPower based in Bellevue, Washington, have demonstrated the power of high-energy beams of charged particles (ions). The ions can rapidly and consistently damage samples of ferritic-martensitic steel, the material used in certain nuclear reactor components. The significance of the result is that the breakdown closely replicates that seen when high-energy neutrons from a nuclear reactor interact with the material - ...
Chemically extracted acellular allogeneic nerve graft with CNTF for sciatic nerve repair
2014-08-20
Chemically extracted acellular allogeneic nerve, from which Schwann cells, myelin sheath and disintegrating fragments have been removed, reduced postoperative immune rejection. Simultaneously, chemically extracted acellular allogeneic nerve retains neural substrates and base materials, such as the bottom layer of Schwann cells, which can provide a good scaffold in the process of nerve regeneration. Chemically extracted acellular allogeneic nerve, similar to autologous nerve transplantation, can guide nerve regeneration and provide a favorable local environment for neural ...
The channel that relaxes DNA
2014-08-20
VIDEO:
This is a model DNA chain inside a nanochannel that is 100nm wide.
The spontaneous dynamical evolution of the DNA is accompanied by frequent knotting and entanglement at the chain ends....
Click here for more information.
With the widespread use of methods for DNA analysis and manipulation, it's certainly useful to find a way to unravel and relax the strands of this molecule that tends to form tangles spontaneously. One way is to use channels, or rather nano-channels, ...
Test reliably detects inherited immune deficiency in newborns
2014-08-20
A newborn screening test for severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) reliably identifies infants with this life-threatening inherited condition, leading to prompt treatment and high survival rates, according to a study supported by the National Institutes of Health. Researchers led by Jennifer Puck, M.D., of the University of California, San Francisco, also found that SCID affects approximately 1 in 58,000 newborns, indicating that the disorder is less rare than previously thought. The study was funded in part by NIH's National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases ...
Mums trust mums on the net: Australian study
2014-08-20
Facebook groups for mothers are overtaking the traditional mums-and-bubs and playgroup environments as a source of trusted advice, and offers a largely untapped marketing tool for businesses wanting to sell their products, an Australian study has found.
QUT educationalist Dr Rebecca English and marketing expert Dr Raechel Johns from the University of Canberra said word-of-mouth in mothers' groups and communities had fast become a major influence in mothers' buying habits.
The study, Mothers' influencing mothers: the use of virtual discussion boards and their influence ...