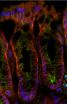
(Press-News.org) LAWRENCE — A study recently published in the journal Carcinogenesis by researchers at the University of Kansas shows a new role for the protein adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) in suppressing colorectal cancer — the second-leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the U.S.
Lead author Kristi Neufeld, associate professor in the Department of Molecular Biosciences and co-leader of the Cancer Biology program at the KU Cancer Center, has spent the better part of her career trying to understand the various activities of APC, a protein whose functional loss is thought to initiate roughly 80 percent of all colon polyps, a precursor to colon cancer. Neufeld, along with her postdoctoral fellow Maged Zeineldin, undergraduate student Mathew Miller and veterinary pathologist Ruth Sullivan, now reports that APC found in a particular subcellular compartment, the nucleus, protects from inflammation as well as tumor development associated with chronic colitis.
Whether APC reaches the nucleus may well affect the ability of intestinal stem cells to produce differentiated cells with specialized functions, Neufeld said.
"It's not widely appreciated, but there is still plenty of cell growth going on in adults, with the colon being a good example," she said. "On average, we shed and replace about 70 pounds of intestinal tissue annually, so you can imagine that this process requires exquisite control to prevent tumor formation."
Regular renewal of the colon lining occurs through stem cells that are capable of constantly dividing. These cells produce descendants that take up specific roles: By secreting mucin, for instance, goblet cells generate a mucus layer that serves as the colon's physical barrier against its many microbial tenants. But if APC can't find its way to the nucleus, Neufeld and her team have noted far fewer goblet cells as one outcome.
"We introduced a specific APC mutation into mice that took away the nuclear zip code, so to speak, leaving APC stuck in the cytoplasm," Neufeld said. The researchers studied this mouse model under conditions that induce ulcerative colitis, a form of inflammatory bowel disease that can be a prelude to colon cancer.
Observing significantly more colon tumors in these mice compared to those with normal APC in the same disease setting, they hypothesized that functional nuclear APC might somehow guard against inflammation and its downstream effects, including tumor development. Now, Neufeld thinks she and her team may have a clue as to how this happens.
"The drop in goblet cell numbers we observed was striking," she said. "We then examined one of the proteins found in mucus, called Muc2, and found that its RNA levels were greatly decreased. If there are fewer goblet cells as a result of APC being unable to reach the nucleus, there will also be less mucus, which could increase the colon's sensitivity to bacteria and other microorganisms in the gut that are capable of promoting inflammation."
Neufeld said while there are still no quick fixes for mutant genes, perhaps tools could be developed to synthetically replace this less-than-ideally thick mucus layer in affected people.
One known function of APC is that it halts cell proliferation: by muzzling the canonical arm of the Wnt signaling pathway, which otherwise instructs cells to go forth and multiply. Neufeld and her group have already shown, using the same mouse model, that APC stationed in the nucleus is necessary to suppress Wnt and its signaling partners — particularly β-catenin, a key target of normal APC. With a role for nuclear APC in controlling goblet cell differentiation now supported, the researchers are probing possible mechanisms to learn if and how Wnt pathway members might be involved.
Comprising 2,843 amino acids, APC is a large protein.
"Rather than being a simple, single-function protein, APC is more like a complex set of moving parts, each doing something different and most still poorly understood," Neufeld said. "I think if the sole purpose of this protein was to target β-catenin for destruction, it wouldn't need to be this large. Our next job is to figure out exactly how goblet cell differentiation is controlled by one or more of APC's many components."
Beyond a slew of mechanistic details, the bigger picture that Neufeld and her group will keep exploring is that some colon cancers could arise from an inflammatory response to bacterial penetration of a thinner-than-normal mucus layer in the gut, resulting from defective APC. The possibilities of just what APC does and doesn't do, and how to compensate for any intestinal glitches related to loss of APC function, present a challenging mystery but also a plentiful harvest for scientists like Neufeld to reap going forward.
INFORMATION:
The National Institutes of Health supported this research.
This news release is based on a story by Alissa Poh that originally appeared at http://www.kucancercenter.org.
Research offers insight into cellular biology of colorectal cancer
2014-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Delivery by drone
2014-08-21
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- In the near future, the package that you ordered online may be deposited at your doorstep by a drone: Last December, online retailer Amazon announced plans to explore drone-based delivery, suggesting that fleets of flying robots might serve as autonomous messengers that shuttle packages to customers within 30 minutes of an order.
To ensure safe, timely, and accurate delivery, drones would need to deal with a degree of uncertainty in responding to factors such as high winds, sensor measurement errors, or drops in fuel. But such "what-if" planning typically ...
Conclusive evidence on role of circulating mesenchymal stem cells in organ injury
2014-08-21
New Rochelle, NY, August 21, 2014--Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are present in virtually every type of human tissue and may help in organ regeneration after injury. But the theory that MSCs are released from the bone marrow into the blood stream following organ damage, and migrate to the site of injury, has long been debated. M.J. Hoogduijn and colleagues provide conclusive evidence to resolve the controversy over the mobilization and migration of MSCs in humans in a new study published in Stem Cells and Development, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., ...
The Lancet: Experimental Ebola drugs must be fairly distributed and tested ethically in clinical trials
2014-08-21
Researchers and health authorities need to ensure that experimental drugs to treat Ebola are distributed fairly, and in the context of randomized controlled trials, according to a new Viewpoint, published in The Lancet today [Thursday 21 August, 2014].
Leading bioethicists Professor Ezekiel Emanuel, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA, and Dr Annette Rid, of King's College London, UK, outline critical ethical principles which need to be adhered to if experimental drugs are to be deployed in the Ebola outbreak, stating that the patients selected to receive ...
Polio: Mutated virus breaches vaccine protection
2014-08-21
Thanks to effective vaccination, polio is considered nearly eradicated. Each year only a few hundred people are stricken worldwide. However, scientists of the University of Bonn, together with colleagues from Gabon, are reporting alarming findings: a mutated virus that was able to resist the vaccine protection to a considerable extent was found in victims of an outbreak in the Congo in 2010. The pathogen could also potentially have infected many people in Germany. The results appear now in the magazine PNAS.
The polio epidemic in the Congo in 2010 was especially serious. ...
Mindfulness-based depression therapy reduces health care visits
2014-08-21
August 21, 2014 (Toronto) – A mindfulness-based therapy for depression has the added benefit of reducing health-care visits among patients who often see their family doctors, according to a new study by the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH) and the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES).
The research showed that frequent health service users who received mindfulness-based cognitive therapy showed a significant reduction in non-mental health care visits over a one-year period, compared with those who received other types of group therapy.
The ...
800 meters beneath Antarctic ice sheet, subglacial lake holds viable microbial ecosystems
2014-08-21
BATON ROUGE – In a finding that has implications for life in other extreme environments, both on Earth and planets elsewhere in the solar system, LSU Associate Professor of Biological Sciences Brent Christner and fellow researchers funded by the National Science Foundation, or NSF, this week published a paper confirming that the waters and sediments of a lake that lies 800 meters (2600 feet) beneath the surface of the West Antarctic ice sheet support "viable microbial ecosystems."
Given that more than 400 subglacial lakes and numerous rivers and streams are thought to ...
Arctic sea ice influenced force of the Gulf Stream
2014-08-21
For AWI geologist Juliane Müller the Fram Strait is a key region in the global oceanic circulation. "On the east side of this passage between Greenland and Svalbard warm Atlantic water flows to the north into the Arctic Ocean while on the west side cold Arctic water masses and sea ice push their way out of the Arctic into the North Atlantic. A considerable portion of the Atlantic water cools here on its way to the north and sinks to deeper layers. The circulation of the water caused in this manner drives the global band of oceanic currents like a giant pump and influences, ...
Water window imaging opportunity
2014-08-21
Ever heard of the water window? It consists of radiations in the 3.3 to 4.4 nanometre range, which are not absorbed by the water in biological tissues. New theoretical findings show that it is possible to develop coherent radiations within the water window. These could be the basis of an optimal technique to obtain a high-contrast image of the biological samples or to be used in high-precision spectroscopy. Now, a new theoretical study identifies the physical mechanism needed to efficiently generate the harmonic radiations—which are multiples of an incoming laser’s frequency—at ...
Study shows steep decline in tooth loss, increase in socioeconomic disparities
2014-08-21
Alexandria, Va., USA – The International and American Associations for Dental Research (IADR/AADR) have published a paper titled "Projections of U.S. Edentulism Prevalence Following Five Decades of Decline." This study, by lead researcher Gary Slade, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, USA, follows edentulism (tooth loss) over the last hundred years and highlights the numbers of people losing teeth and requiring dentures. It is published in the OnlineFirst portion of the IADR/AADR Journal of Dental Research (JDR).
The researchers of this study investigated population ...
Tropical Storm Karina looks like a giant 'number 9' from space
2014-08-21
Despite being the eleventh tropical cyclone of the Eastern Pacific Ocean Hurricane Season, Karina looked like a giant number nine from NASA's Aqua satellite.
Tropical Storm Karina was weakening on August 20 when NASA's Terra satellite passed overhead. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument aboard Terra snapped a visible image of Tropical Storm Karina on August 20 at 19:40 UTC (3:40 p.m. EDT). The MODIS image showed that a thick band of strong thunderstorms spiraled into Karina's center from the southeast. The band of thunderstorms wrapped ...