(Press-News.org) Raloxifene is a U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved treatment for decreasing fracture risk in osteoporosis. While raloxifene is as effective at reducing fracture risk as other current treatments, this works only partially by suppressing bone loss. With the use of wide- and small-angle x-ray scattering (WAXS and SAXS, respectively), researchers carried out experiments at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE's) Advanced Photon Source (APS) at Argonne National Laboratory that revealed an additional mechanism underlying raloxifene action, providing an explanation for how this drug can achieve equivalent clinical benefit.
These data, together with complementary techniques, help define a novel mechanism by which raloxifene increases inherent bone toughness.
In osteoporosis, decreased bone density increases the risk of fracture. All current drugs for treatment of this disease act upon living cells within the bone matrix to either decrease bone resorption, a process by which the mineral components of bone are broken down and released into the bloodstream, or to increase net bone formation during remodeling, a process by which bone is also broken down but then reforms bone. In either case, treatment results in an overall increase in bone density, and therefore a reduction in fracture risk.
While raloxifene is known to mildly suppress bone loss, "It has always been somewhat paradoxical that raloxifene suppresses bone loss less than other osteoporosis therapies, yet reduces fracture risk to about the same level," said David B. Burr of Indiana University School of Medicine and lead author of the Bone article on this research.
To uncover the density-independent mechanism by which raloxifene (marketed as Evista by Eli Lilly and Company) increases bone toughness, researchers in this study from the Indiana University School of Medicine; Purdue University; Indiana University–Purdue University at Indianapolis; the University of California, San Diego; Northwestern University; and Argonne National Laboratory assessed the effect of the drug on devitalized bone cleared of living cells that normally mediate resorption and remodeling.
In these bone samples, raloxifene prolonged the loading that the bone could bear before fracturing, indicating that the drug was acting upon the physical properties of the bone itself. Using ultra-short-echo-time nuclear magnetic resonance, researchers found that raloxifene-mediated water retention within the bone matrix is associated with the observed increase in toughness.
In order to elucidate the mechanism underlying this association, researchers collected WAXS and SAXS diffraction patterns of carbonated hydroxyapatite crystals (cAp), the mineral component of bone that had been subjected to four-point bending. These data, collected at the X-ray Science Division 1-ID x-ray beamline at the Argonne APS, a Department of Energy user facility, allowed the researchers to measure mechanical strains on cAp crystals at a resolution of 1μm and showed that raloxifene increased the amount of physical deformation, or strain, that occurred at the collagen-mineral interface before fracture.
This increased strain between cAp and collagen reduces stresses and may be caused by water-mediated slipping between these components at their interface, increasing the amount of energy the bone can absorb prior to fracture.
"The x-ray diffraction data," Burr said, "allowed us to explain the mechanism by which increases in bound water would improve the fracture properties of bone."
According to Burr, this work uncovers an entirely novel mechanism of action for raloxifene and "paves the way for a new class of drugs to treat osteoporosis, therapies that do not act by altering cellular activity or bone remodeling, but act by directly changing the physical properties of the bone matrix constituents."
INFORMATION: END
Revealing a novel mode of action for an osteoporosis drug
2014-08-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study reveals how Ebola blocks immune system
2014-08-29
Researchers at the Washington University School of Medicine have identified one way the Ebola virus dodges the body's antiviral defenses, providing important insight that could lead to new therapies, in research results published in the journal Cell Host & Microbe.
In work performed at Beamline 19ID at Argonne National Laboratory's Advanced Photon Source, the researchers developed a detailed map of how a non-pathogenic Ebola protein, VP24, binds to a host protein that takes signaling molecules in and out of the cell nucleus.
Their map revealed that the viral protein ...
Argonne scientists pioneer strategy for creating new materials
2014-08-29
Making something new is never easy. Scientists constantly theorize about new materials, but when the material is manufactured it doesn't always work as expected. To create a new strategy for designing materials, scientists at the Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory combined two different approaches at two different facilities to synthesize new materials.
This new strategy gives faster feedback on what growth schemes are best, thus shortening the timeframe to manufacture a new, stable material for energy transport and conversion applications.
A recent ...
Aging Africa
2014-08-29
Boulder, Colorado, USA – In the September issue of GSA Today, Paul Bierman of the University of Vermont–Burlington and colleagues present a cosmogenic view of erosion, relief generation, and the age of faulting in southernmost Africa. By measuring beryllium-10 (10Be) in river sediment samples, they show that south-central South Africa is eroding at the slow rate of about five meters per million years, consistent with rates in other non-tectonically active regions.
By measuring 10Be and aluminum-26 (26Al) in exposed quartzites, Bierman and colleagues find that undeformed ...
Preventing cancer from forming 'tentacles' stops dangerous spread
2014-08-29
EDMONTON, AB – A new study from the research group of Dr. John Lewis at the University of Alberta (Edmonton, AB) and the Lawson Health Research Institute (London, ON) has confirmed that "invadopodia" play a key role in the spread of cancer. The study, published in Cell Reports, shows preventing these tentacle-like structures from forming can stop the spread of cancer entirely.
Roughly 2 in 5 Canadians will develop cancer in their lifetime, and one in four of them will die of the disease. In 2014, it's estimated that nine Canadians will die of cancer every hour. Thanks ...
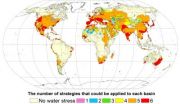
Reducing water scarcity possible by 2050
2014-08-29
Water scarcity is not a problem just for the developing world. In California, legislators are currently proposing a $7.5 billion emergency water plan to their voters; and U.S. federal officials last year warned residents of Arizona and Nevada that they could face cuts in Colorado River water deliveries in 2016.
Irrigation techniques, industrial and residential habits combined with climate change lie at the root of the problem. But despite what appears to be an insurmountable problem, according to researchers from McGill and Utrecht University it is possible to turn the ...
Evidence mounting that older adults who volunteer are happier, healthier
2014-08-29
Toronto, Canada – Older adults who stay active by volunteering are getting more out of it than just an altruistic feeling – they are receiving a health boost!
A new study, led by the Rotman Research Institute at Baycrest Health Sciences and published online this week in Psychological Bulletin, is the first to take a broad-brush look at all the available peer-reviewed evidence regarding the psychosocial health benefits of formal volunteering for older adults.
Lead investigator Dr. Nicole Anderson, together with scientists from Canadian and American academic centres, ...
NASA sees Hurricane Cristobal racing through North Atlantic
2014-08-29
Satellite imagery shows Hurricane Cristobal racing through the North Atlantic on Friday, August 29 while losing its tropical characteristics. An image from NOAA's GOES-East satellite showed Cristobal headed south of Greenland. The previous day, NASA's TRMM satellite saw heavy rainfall occurring in the hurricane.
In a visible image from NOAA's GOES-East satellite on August 29 at 7:45 a.m. EDT, Hurricane Cristobal was moving through the North Atlantic about 500 miles southwest of Greenland. The image was created by the NASA/NOAA GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight ...
CCNY team defines new biodiversity metric
2014-08-29
To understand how the repeated climatic shifts over the last 120,000 years may have influenced today's patterns of genetic diversity, a team of researchers led by City College of New York biologist Dr. Ana Carnaval developed a new biodiversity metric called "phylogeographic endemism."
It quantifies the degree to which the genetic variation within species is restricted in geographical space.
Dr. Carnaval, an assistant professor of biology, and 14 other researchers from institutions in Brazil, Australia and the United States, analyzed the effects of current and past climatic ...
Hydrogen powers important nitrogen-transforming bacteria
2014-08-29
This news release is available in German. Nitrite-oxidizing bacteria are key players in the natural nitrogen cycle on Earth and in biological wastewater treatment plants. For decades, these specialist bacteria were thought to depend on nitrite as their source of energy. An international team of scientists led by Holger Daims, a microbiologist at the University of Vienna, has now shown that nitrite-oxidizing bacteria can use hydrogen as an alternative source of energy. The oxidation of hydrogen with oxygen enables their growth independent of nitrite and a lifestyle outside ...
NASA animation shows Hurricane Marie winding down
2014-08-29
VIDEO:
This video of NOAA's GOES-West satellite imagery from Aug. 26-29 shows Hurricane Marie winding down into a post-tropical storm.
Click here for more information.
NOAA's GOES-West satellite keeps a continuous eye on the Eastern Pacific and has been covering Hurricane Marie since birth. NASA's GOES Project uses NOAA data and creates animations and did so to show the end of Hurricane Marie.
At 5 a.m. EDT (0900 UTC) on Friday, August 29, Marie became a post-tropical storm ...