(Press-News.org) Tropical Depression 15W intensified during the early morning hours of September 12 and became a tropical storm re-named "Kalmaegi." NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead as the storm intensified.
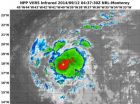
The MODIS instrument, known as the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Storm Kalmaegi approaching the Philippines on Sept. 12 at 4:45 UTC (12:45 a.m. EDT). The image showed tightly-curved bands of thunderstorms over the northern and southern quadrants of the storm that were wrapping into a consolidating low-level center. The consolidation of the center and the banding of thunderstorms are conducive to a strengthening storm, and forecasters expect Kalmaegi to continue strengthening over the next couple of days.
On Friday, September 12 at 0900 UTC (5 a.m. EDT) Tropical Storm Kalmaegi's maximum sustained winds were near 40 knots (46 mph/74 kph). Kalmaegi was centered near 13.8 north latitude and 130.2 east, about 572 nautical miles (658.2 miles/1,059 km) east of Manila, Philippines. Kalmaegi was moving to the west at 14 knots (16.1 mph/25.9 kph).
Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center forecast Kalmaegi to become a typhoon (same thing as a hurricane, but west of the International Date Line) by September 13. Kalmaegi is forecast to cross Luzon, the northern Philippines, from southeast to northwest on September 14 before entering the South China Sea and heading for another landfall south of Hong Kong.
INFORMATION:
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA sees Tropical Storm Kalmaegi swirl toward the Philippines
2014-09-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA-NOAA Suomi NPP sees formation of Tropical Storm Edouard
2014-09-12
The sixth tropical depression of the Atlantic Ocean hurricane season formed in the central Atlantic Ocean yesterday, and today, September 12, it strengthened into Tropical Storm Edouard. NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite flew over Edouard and provided forecasters with an infrared view of what's happening within the strengthening storm.
When Suomi NPP passed over Edouard on September 12 at 04:37 UTC (12:37 a.m. EDT), the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite or VIIRS instrument aboard captured an infrared image of the storm. The infrared data shows temperature, an indicated ...
Worldwide study demonstrates accuracy of genetic analyses
2014-09-12
JACKSONVILLE, Fla., Sept. 12, 2014 — Physicians envision a future in which genomic data from patients is heavily used to manage care — but experts have questioned the accuracy and reliability of these analyses. Now, a study by 150 researchers in 12 countries finds real strength and agreement across RNA genomic sequencing techniques and laboratories — as well as ways to improve what little variability exists to set a new high standard.
The results of the study were published in Nature Biotechnology in three separate research articles.
These results should provide assurance ...
Tropical Storm Odile taken on by 2 NASA satellites
2014-09-12
As Tropical Storm Odile continues to affect Mexico's west coast and stir up dangerous surf, NASA's TRMM and Aqua satellites provided forecasters information on clouds and rainfall in the coast-hugging storm. On September 12, A Tropical Storm Watch remained in effect from Manzanillo to Cabo Corrientes, Mexico.
Tropical Storm Odile formed on September 10, 2014 in the same area where Norbert formed.
Gathering Rainfall and Thunderstorm Height Information
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite flew over tropical storm Odile on September 11, 2014 at ...
CCNY analysis explains rich bird biodiversity in Neotropics
2014-09-12
Applying analyses designed by City College of New York biologist Mike Hickerson, a team of international researchers is challenging a commonly held view that explains how so many species of birds ended up in the Neotropics, an area rich in rain forest extending from Mexico to the southernmost tip of South America. It is home to the most bird species on Earth.
"The unanswered question has been—how did this extraordinary bird diversity originate?" said Dr. Brian Smith, lead author of a paper on the subject published in the journal Nature this week and an assistant curator ...
Fluid mechanics suggests alternative to quantum orthodoxy
2014-09-12
The central mystery of quantum mechanics is that small chunks of matter sometimes seem to behave like particles, sometimes like waves. For most of the past century, the prevailing explanation of this conundrum has been what's called the "Copenhagen interpretation" — which holds that, in some sense, a single particle really is a wave, smeared out across the universe, that collapses into a determinate location only when observed.
But some founders of quantum physics — notably Louis de Broglie — championed an alternative interpretation, known as "pilot-wave theory," which ...
Corn spots: Study finds important genes in defense response
2014-09-12
When corn plants come under attack from a pathogen, they sometimes respond by killing their own cells near the site of the attack, committing "cell suicide" to thwart further damage from the attacker. This cell sacrifice can cause very small, often microscopic, spots or lesions on the plant.
But up until now it's been difficult to understand how the plant regulates this "spotty" defense mechanism because the response is so quick and localized.
Researchers at North Carolina State University have identified a number of candidate genes and cellular processes that appear ...
Experts call for massive global response to tackle Ebola
2014-09-12
AUDIO:
Professor Peter Piot, Director of the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, explains how he co-discovered the Ebola virus in 1976, and gives his views on the current Ebola...
Click here for more information.
The current Ebola outbreak now requires a "rapid response at a massive global scale", according to experts at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine.
Writing an editorial in Science, Professor Peter Piot, co-discoverer of the virus, says that the ...
Stanford-led study assesses the environmental costs and benefits of fracking
2014-09-12
A strange thing happened on the way to dealing with climate change: Advances in hydraulic fracturing put trillions of dollars' worth of previously unreachable oil and natural gas within humanity's grasp.
The environmental costs – and benefits – from "fracking," which requires blasting huge amounts of water, sand and chemicals deep into underground rock formations, are the subject of new research that synthesizes 165 academic studies and government databases. The survey covers not only greenhouse gas impacts but also fracking's influence on local air pollution, earthquakes ...
Piglet health
2014-09-12
Porcine neonatal coccidiosis is a serious parasitic infection of young piglets that severely damages the intestinal mucosa, leading to diarrhoea and reduced nutritional intake. As the infection reduces animal growth, and because secondary infections can result in increased mortality, the disease is responsible for substantial economic losses at affected pig farms.
"The developing immune system of neonatal piglets is not yet mature enough to deal with the parasites. For this reason, an infection shortly after birth results in weakened intestinal tissue with appropriate ...
Moving silicon atoms in graphene with atomic precision
2014-09-12
Richard Feynman famously posed the question in 1959: is it possible to see and manipulate individual atoms in materials? For a time his vision seemed more science fiction than science, but starting with groundbreaking experiments in the late 1980s and more recent developments in electron microscopy instrumentation it has become scientific reality. However, damage caused by the electron beam is often an issue in such experiments.
The present study focused on single-layer graphene with silicon atoms embedded into the lattice, previously created and studied by the collaborators ...