(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS – A new study suggests that people who experience migraine in middle age may be more likely to develop Parkinson's disease, or other movement disorders later in life. Those who have migraine with aura may be at double the risk of developing Parkinson's, according to the study published in the September 17, 2014, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
"Migraine is the most common brain disorder in both men and women," said study author Ann I. Scher, PhD, with Uniformed Services University in Bethesda, MD, and a member of the American Academy of Neurology. "It has been linked in other studies to cerebrovascular and heart disease. This new possible association is one more reason research is needed to understand, prevent and treat the condition."
For the study, 5,620 people between the ages of 33 and 65 were followed for 25 years. At the beginning of the study, a total of 3,924 of the participants had no headaches, 1,028 had headaches with no migraine symptoms, 238 had migraine with no aura and 430 had migraine with aura. Later, the investigators assessed whether the participants had any symptoms of Parkinson's or had been diagnosed with Parkinson's or had symptoms of restless legs syndrome (RLS)(also known as Willis-Ekbom disease).
The study found that people with migraine with aura were more than twice as likely to be diagnosed with Parkinson's than people with no headaches. A total of 2.4 percent of those with migraine with aura had the disease, compared to 1.1 percent of those with no headaches. People with migraine with aura had 3.6 the odds of reporting at least four of six parkinsonian symptoms, while those with migraine with no aura had 2.3 times the odds of these symptoms. Overall, 19.7 percent of those with migraine with aura had symptoms, compared to 12.6 percent of those with migraine with no aura and 7.5 percent of those with no headaches. Women with migraine with aura were also more likely to have a family history of Parkinson's disease compared to those with no headaches.
"A dysfunction in the brain messenger dopamine is common to both Parkinson's and RLS, and has been hypothesized as a possible cause of migraine for many years. Symptoms of migraine such as excessive yawning, nausea and vomiting are thought to be related to dopamine receptor stimulation," said Scher. "More research should focus on exploring this possible link through genetic studies.
"While the history of migraine is associated with an increased risk for Parkinson's, that risk is still quite low."
INFORMATION:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Institute on Aging, the Icelandic Heart Association and the Icelandic Parliament.
To learn more about migraine and movement disorders, please visit http://www.aan.com/patients.
The American Academy of Neurology, an association of more than 28,000 neurologists and neuroscience professionals, is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer's disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, brain injury, Parkinson's disease and epilepsy.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit http://www.aan.com or find us on Facebook, Twitter, Google+ and YouTube.
Media Contacts:
Rachel Seroka, rseroka@aan.com, (612) 928-6129
Michelle Uher, muher@aan.com, (612) 928-6120
Migraine in middle age linked to increased risk of Parkinson's, movement disorders later
2014-09-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
For some lung cancer patients, surgery may yield better long-term results
2014-09-17
(September 17, 2014, San Francisco) – Patients with early stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who are otherwise healthy fare better over time if they undergo conventional surgery versus less-invasive radiosurgery to remove their cancer, according to a Yale study. The findings are scheduled to be presented at the 56th annual conference of the American Society for Radiation Oncology in San Francisco. (Abstract # 302; Comparative Effectiveness of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy versus Surgery for Stage I Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.)
The study used Medicare billing records ...
Brain imaging research pinpoints neurobiological basis for key symptoms associated with post-traumatic stress disorder like listlessness and emotional detachment in trauma victims
2014-09-17
NEW YORK, NY, September 17, 2014 - In a novel brain-imaging study among trauma victims, researchers at NYU Langone Medical Center have linked an opioid receptor in the brain -- associated with emotions -- to a narrow cluster of trauma symptoms, including sadness, emotional detachment and listlessness. The study, published online today in the journal JAMA Psychiatry, holds important implications for targeted, personalized treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder, or PTSD, a psychiatric condition affecting more than 8 million Americans that can cause a wide range of debilitating ...
PTSD symptoms associated with increased food addiction
2014-09-17
Bottom Line: Symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) were associated with increased food addiction, especially when individuals had more symptoms or the symptoms occurred earlier in life.
Authors: Susan M. Mason, Ph.D., of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and colleagues.
Background: PTSD is a potentially severe psychiatric condition. A growing body of evidence suggests that PTSD is a risk factor for obesity and obesity-related diseases. Food addiction is not established as a psychiatric diagnosis but may indicate use of food to cope with psychological ...
Vitiligo treatment holds promise for restoring skin pigmentation
2014-09-17
VIDEO:
Henry Lim, M.D., chair of Dermatology, Henry Ford Hospital, highlights the study.
Click here for more information.
DETROIT – A treatment regimen is safe and effective for restoring skin pigmentation in vitiligo patients, according to a Henry Ford Hospital study.
"Our findings offer patients with vitiligo worldwide a renewed hope for a bright future in the treatment of this disfiguring disease," says Henry Lim, M.D., chair of Dermatology at Henry Ford and the study's ...
Combo of phototherapy, drug results in faster repigmentation in vitiligo
2014-09-17
Bottom Line: Patients with the skin depigmentation disease known as vitiligo had faster and better repigmentation after a combination therapy of the implantable drug afamelanotide and narrowband UV-B (NB-UV-B) phototherapy as part of a clinical trial.
Author: Henry W. Lim, M.D., of Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, Mich., and colleagues.
Background: Vitiligo is characterized by white patches of skin and affects 1 percent to 2 percent of the population. The authors report the results of a multicenter randomized clinical trial comparing the safety and effectiveness of the ...
Chromosome buffers hold key to better melanoma understanding
2014-09-17
Buffers that guard against damage to the ends of chromosomes could hold the key to a better understanding of malignant melanoma – the deadliest form of skin cancer – according to new research from the University of Leeds.
The study has uncovered an important new genetic risk factor for melanoma.
It is well known that pigmentation and mole count are the strongest indicators of those most at risk of developing melanoma. For example, paler people should take more care in the sun, as they burn more easily.
It now appears that another risk factor is the length of telomeres, ...
NASA sees Tropical Storm Polo intensifying
2014-09-17
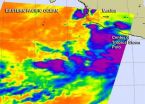
Tropical storm warnings now issued for a portion of the Southwestern coast of Mexico as Polo continues to strengthen. Infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite showed powerful thunderstorms around the center of the storm.
A Tropical Storm Warning is in force for the southwest coast of Mexico from Punta San Telmo to Playa Perula. A Tropical Storm Watch is in force from Punta San Telmo to Zihuatanejo and from Playa Perula to Cabo Corrientes. Rainfall totals of 5 to 10, locally up to 15 inches, can be expected over coastal areas of Michoacan, Colima and Jalisco states ...
NASA sees Hurricane Edouard far from US, but creating rough surf
2014-09-17
Although NASA's Aqua satellite showed that Hurricane Edouard is far from U.S. soil, it is powerful enough that it is creating dangerous swells along the U.S. East Coast.
On Sept. 17, the National Hurricane Center noted "Swells from Edouard will affect portions of the east coast of the United States north of Florida beginning today. These swells will likely cause life-threatening rip current conditions along most of the United States east coast for the next couple of days."
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Hurricane Edouard on Sept. 16 the MODIS instrument captured ...
Shorebird's beak inspires UT Arlington research on water collection
2014-09-17
A UT Arlington engineering professor and his doctoral student have designed a device based on a shorebird's beak that can accumulate water collected from fog and dew.
The device could provide water in drought-stricken areas of the world or deserts around the globe.
Cheng Luo, professor in the Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering Department, and Xin Heng, PhD candidate in the same College of Engineering department, published "Bioinspired Plate-Based Fog Collectors" in the Aug. 25 edition of ACS' (American Chemical Society) Applied Materials & Interfaces journal. ACS also ...
Scripps Research Institute chemists modify antibiotic to vanquish resistant bacteria
2014-09-17
LA JOLLA, CA—September 17, 2014—Scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have devised a new antibiotic based on vancomycin that is powerfully effective against vancomycin-resistant strains of MRSA and other disease-causing bacteria.
The new vancomycin analog appears to have not one but two distinct mechanisms of anti-microbial action, against which bacteria probably cannot evolve resistance quickly.
"This is the prototype of analogues that once introduced will still be in clinical use a generation or maybe even two generations from now," said Dale L. Boger, ...