(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA — More than half of human cancers have abnormally upregulated chemical signals related to lipid metabolism, yet how these signals are controlled during tumor formation is not fully understood.
Youhai Chen, PhD, MD, and Svetlana Fayngerts, PhD, both researchers in the department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine at the Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, and colleagues report that TIPE3, a newly described oncogenic protein, promotes cancer by targeting these pathways.
Lipid second messengers play cardinal roles in relaying and amplifying signals from outside the cell to its interior and outer membrane. One of the best known lipid second messengers is PIP3, which relays signals from hundreds of membrane receptors, including many oncogenic receptors, on the cell surface to PIP3-binding proteins in the cell's interior, which control cell growth, differentiation, migration, transformation, and death.
Therefore, drugs targeting PIP3 – when its function goes awry -- may be effective for treating a variety of diseases, including cancer and inflammatory disorders. TIPE3 belongs to a newly described family of proteins and is a risk factor for human cancer and inflammation, although its mechanisms of action are largely unknown.
Chen and colleagues discovered that TIPE3 is the transfer protein of the second messenger PIP3 and it is hijacked by cancer cells to cause runaway cell division.
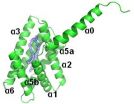
The high-resolution crystal structure of TIPE3 shows a large cavity that captures and transfers PIP3 and its chemical precursor PIP2 to increase their presence on the inner membrane of the cell. This promotes activation of downstream PIP3 effectors that cause cancer.
Importantly, human lung, colon, ovarian, and esophageal cancers have markedly upregulated TIPE3 expression. Knocking down TIPE3 in culture diminishes malignant tumor cell growth and knocking out TIPE3 in mice blocks tumor formation.
"These findings explain why normal cells can control their lipid signals but cancer cells can't, a phenomenon widely recognized, but poorly understood," says Chen. TIPE3 has to be expressed at just the right amount to make sure that the proper signal is transferred, which governs the proper amount of cell division. "Therefore, TIPE3 may represent a new therapeutic target for treating malignant diseases."
The team is now working on strategies to control abnormal TIPE3 expression to treat or prevent cancer.
INFORMATION:
Other contributing authors are Jianping Wu, Camilla L. Oxley, Xianglan Liu, Anastassios Vourekas, Terry Cathopoulis, Zhaojun Wang, Jian Cui, Suxia Liu, Honghong Sun, Mark A. Lemmon, Lining Zhang, Yigong Shi.
This work was funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (AI-077533, AI-050059, GM-085112).
Penn Medicine is one of the world's leading academic medical centers, dedicated to the related missions of medical education, biomedical research, and excellence in patient care. Penn Medicine consists of the Raymond and Ruth Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania (founded in 1765 as the nation's first medical school) and the University of Pennsylvania Health System, which together form a $4.3 billion enterprise.
The Perelman School of Medicine has been ranked among the top five medical schools in the United States for the past 17 years, according to U.S. News & World Report's survey of research-oriented medical schools. The School is consistently among the nation's top recipients of funding from the National Institutes of Health, with $392 million awarded in the 2013 fiscal year.
The University of Pennsylvania Health System's patient care facilities include: The Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania -- recognized as one of the nation's top "Honor Roll" hospitals by U.S. News & World Report; Penn Presbyterian Medical Center; Chester County Hospital; Penn Wissahickon Hospice; and Pennsylvania Hospital -- the nation's first hospital, founded in 1751. Additional affiliated inpatient care facilities and services throughout the Philadelphia region include Chestnut Hill Hospital and Good Shepherd Penn Partners, a partnership between Good Shepherd Rehabilitation Network and Penn Medicine.
Penn Medicine is committed to improving lives and health through a variety of community-based programs and activities. In fiscal year 2013, Penn Medicine provided $814 million to benefit our community.
New cancer drug target involving lipid chemical messengers
2014-09-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Melanoma risk found to have genetic determinant
2014-09-19
(Lebanon, NH 9/18/14)— A leading Dartmouth researcher, working with The Melanoma Genetics Consortium, GenoMEL, an international research consortium, co-authored a paper published today in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute that proves longer telomeres increase the risk of melanoma.
"For the first time, we have established that the genes controlling the length of these telomeres play a part in the risk of developing melanoma," said lead author of the study Mark Iles, PhD, School of Medicine at the University of Leeds (UK).
Telomeres are a part of the genome ...
UChicago-Argonne National Lab team improves solar-cell efficiency
2014-09-19
New light has been shed on solar power generation using devices made with polymers, thanks to a collaboration between scientists in the University of Chicago's chemistry department, the Institute for Molecular Engineering, and Argonne National Laboratory.
Researchers identified a new polymer — a type of large molecule that forms plastics and other familiar materials — which improved the efficiency of solar cells. The group also determined the method by which the polymer improved the cells' efficiency. The polymer allowed electrical charges to move more easily throughout ...
Research predicts possible 6,800 new Ebola cases this month
2014-09-19
Tempe, Ariz. (Sept. 19, 2014) - New research published today in the online journal PLoS Outbreaks predicts new Ebola cases could reach 6,800 in West Africa by the end of the month if new control measures are not enacted.
Arizona State University and Harvard University researchers also discovered through modelling analysis that the rate of rise in cases significantly increased in August in Liberia and Guinea, around the time that a mass quarantine was put in place, indicating that the mass quarantine efforts may have made the outbreak worse than it would have been otherwise. ...
Domestic violence likely more frequent for same-sex couples
2014-09-19
CHICAGO --- Domestic violence occurs at least as frequently, and likely even more so, between same-sex couples compared to opposite-sex couples, according to a review of literature by Northwestern Medicine scientists.
Previous studies, when analyzed together, indicate that domestic violence affects 25 percent to 75 percent of lesbian, gay and bisexual individuals. However, a lack of representative data and underreporting of abuse paints an incomplete picture of the true landscape, suggesting even higher rates. An estimated one in four heterosexual women experience domestic ...
A better way to track emerging cell therapies using MRIs
2014-09-19
Cellular therapeutics – using intact cells to treat and cure disease – is a hugely promising new approach in medicine but it is hindered by the inability of doctors and scientists to effectively track the movements, destination and persistence of these cells in patients without resorting to invasive procedures, like tissue sampling.
In a paper published September 17 in the online journal Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh and elsewhere describe the first human tests of using ...
NASA catches a weaker Edouard, headed toward Azores
2014-09-19
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the Atlantic Ocean and captured a picture of Tropical Storm Edouard as it continues to weaken. The National Hurricane Center expects Edouard to affect the western Azores over the next two days.
NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Tropical Storm Edouard on Sept. 18 at 1:45 p.m. EDT and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument took a visible picture that showed the eye had disappeared and the bulk of clouds pushed east of center.
At 5 a.m. EDT on Sept. 19, Edouard's maximum sustained winds had decreased to near ...
NASA, NOAA satellites show Odile's remnant romp through southern US
2014-09-19
Former Hurricane Odile may be a bad memory for Baja California, but the remnants have moved over New Mexico and Texas where they are expected to bring rainfall there. NASA's TRMM satellite measured Odile's heavy rainfall rates on Sept. 18, and NOAA's GOES-West satellite saw the clouds associated with the former storm continue to linger over the U.S. Southwest on Sept. 19.
The remnants of Hurricane Odile were dropping heavy rain in the area from southern Arizona to western Texas when NASA-JAXA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite flew over on September ...
NASA sees Tropical Storm playing polo with western Mexico
2014-09-19
Tropical Storm Polo is riding along the coast of western Mexico like horses in the game of his namesake. NASA's Aqua satellite saw Polo about 300 miles south-southeast of Baja California on its track north.
NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Polo on Sept. 18 at 4:35 p.m. EDT and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer captured a visible image of the storm that showed that much of the clouds, thunderstorms and showers were west and south of the center of circulation, and away from the coast. That's an indication that easterly wind shear had increased and were pushing ...
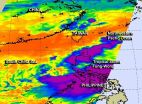
NASA eyes Tropical Storm Fung-Wong move through Northwestern Pacific
2014-09-19
Tropical Storm Fung-Wong continued to affect the Philippines while moving north through the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. NASA's Aqua satellite provided infrared data on the storm's clouds that showed some high, strong thunderstorms with the potential for heavy rainfall over the northern and central regions of the country. The storm is now expected to affect three more countries over the next several days.
The AIRS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite uses infrared light to read cloud top temperatures in tropical cyclones. When Aqua passed over Fung-Wong infrared data ...
Dwindling wind may tip predator-prey balance
2014-09-19
MADISON, Wis. — Bent and tossed by the wind, a field of soybean plants presents a challenge for an Asian lady beetle on the hunt for aphids. But what if the air — and the soybeans — were still?
Rising temperatures and shifting precipitation patterns may get the lion's share of our climate change attention, but predators may want to give some thought to wind, according to a University of Wisconsin Madison zoologist's study, which is among the first to demonstrate the way "global stilling" may alter predator-prey relationships.
"There are all sorts of other things that ...