(Press-News.org) It has become common for people who have pets to refer to themselves as "pet parents," but how closely does the relationship between people and their non-human companions mirror the parent-child relationship? A small study from a group of Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) researchers makes a contribution to answering this complex question by investigating differences in how important brain structures are activated when women view images of their children and of their own dogs. Their report is being published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
"Pets hold a special place in many people's hearts and lives, and there is compelling evidence from clinical and laboratory studies that interacting with pets can be beneficial to the physical, social and emotional wellbeing of humans," says Lori Palley, DVM, of the MGH Center for Comparative Medicine, co-lead author of the report. "Several previous studies have found that levels of neurohormones like oxytocin – which is involved in pair-bonding and maternal attachment – rise after interaction with pets, and new brain imaging technologies are helping us begin to understand the neurobiological basis of the relationship, which is exciting."
In order to compare patterns of brain activation involved with the human-pet bond with those elicited by the maternal-child bond, the study enrolled a group of women with at least one child aged 2 to 10 years old and one pet dog that had been in the household for two years or longer. Participation consisted of two sessions, the first being a home visit during which participants completed several questionnaires, including ones regarding their relationships with both their child and pet dog. The participants' dog and child were also photographed in each participants' home.
The second session took place at the Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging at MGH, where functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) – which indicates levels of activation in specific brain structures by detecting changes in blood flow and oxygen levels – was performed as participants lay in a scanner and viewed a series of photographs. The photos included images of each participant's own child and own dog alternating with those of an unfamiliar child and dog belonging to another study participant. After the scanning session, each participant completed additional assessments, including an image recognition test to confirm she had paid close attention to photos presented during scanning, and rated several images from each category shown during the session on factors relating to pleasantness and excitement.
Of 16 women originally enrolled, complete information and MR data was available for 14 participants. The imaging studies revealed both similarities and differences in the way important brain regions reacted to images of a woman's own child and own dog. Areas previously reported as important for functions such as emotion, reward, affiliation, visual processing and social interaction all showed increased activity when participants viewed either their own child or their own dog. A region known to be important to bond formation – the substantia nigra/ventral tegmental area (SNi/VTA) – was activated only in response to images of a participant's own child. The fusiform gyrus, which is involved in facial recognition and other visual processing functions, actually showed greater response to own-dog images than own-child images.
"Although this is a small study that may not apply to other individuals, the results suggest there is a common brain network important for pair-bond formation and maintenance that is activated when mothers viewed images of either their child or their dog," says Luke Stoeckel, PhD, MGH Department of Psychiatry, co-lead author of the PLOS ONE report. "We also observed differences in activation of some regions that may reflect variance in the evolutionary course and function of these relationships. For example, like the SNi/VTA, the nucleus accumbens has been reported to have an important role in pair-bonding in both human and animal studies. But that region showed greater deactivation when mothers viewed their own-dog images instead of greater activation in response to own-child images, as one might expect. We think the greater response of the fusiform gyrus to images of participants' dogs may reflect the increased reliance on visual than verbal cues in human-animal communications."
Co-author Randy Gollub, MD, PhD, of MGH Psychiatry adds, "Since fMRI is an indirect measure of neural activity and can only correlate brain activity with an individual's experience, it will be interesting to see if future studies can directly test whether these patterns of brain activity are explained by the specific cognitive and emotional functions involved in human-animal relationships. Further, the similarities and differences in brain activity revealed by functional neuroimaging may help to generate hypotheses that eventually provide an explanation for the complexities underlying human-animal relationships."
The investigators note that further research is needed to replicate these findings in a larger sample and to see if they are seen in other populations – such as women without children, fathers and parents of adopted children – and in relationships with other animal species. Combining fMRI studies with additional behavioral and physiological measures could obtain evidence to support a direct relationship between the observed brain activity and the purported functions.
INFORMATION:
Stoeckel is a clinical neuropsychologist and lecturer on psychology, and Gollub an associate professor of Psychiatry at Harvard Medical School. Additional co-authors of the PLOS ONE report are Eden Evins, MD, MGH Psychiatry, and Steven Niemi, DVM, Harvard University. Support for the study includes National Institutes of Health grants K23DA032612 and K24DA030443 and support from the Charles A. King Trust. The study was facilitated by imaging consult support from Harvard Catalyst.
Massachusetts General Hospital , founded in 1811, is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School. The MGH conducts the largest hospital-based research program in the United States, with an annual research budget of more than $785 million and major research centers in HIV/AIDS, cardiovascular research, cancer, computational and integrative biology, cutaneous biology, human genetics, medical imaging, neurodegenerative disorders, regenerative medicine, reproductive biology, systems biology, transplantation biology and photomedicine.
West Orange, NJ. October 3, 2014. Stroke researchers have confirmed that damage to the right frontal-subcortical network may cause ipsilateral spatial neglect. Among individuals with ipsilateral neglect, a much greater proportion had frontal subcortical damage than anticipated by the investigators – 83% vs the expected 27%. A difference was also seen in spatial bias, ie, the type of spatial errors among this group tended to be 'where' (perceptual-attentional) rather than 'aiming' (motor-intentional) errors. Ipsilesional Neglect: Behavioral and Anatomical Correlates (doi: ...
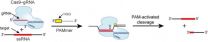
A powerful scientific tool for editing the DNA instructions in a genome can now also be applied to RNA, the molecule that translates DNA's genetic instructions into the production of proteins. A team of researchers with Berkeley Lab and the University of California (UC) Berkeley has demonstrated a means by which the CRISPR/Cas9 protein complex can be programmed to recognize and cleave RNA at sequence-specific target sites. This finding has the potential to transform the study of RNA function by paving the way for direct RNA transcript detection, analysis and manipulation.
A ...
VIDEO:
A software program developed by engineers at Drexel University, called Lineage Editing and Validation (LEVER), allows biologists to tag and track cell proliferation to validate lineage trees.
Click here for more information.
For hundreds of years biologists have studied cells through the lens of a microscope. With a little help from a team of engineers at Drexel University, these scientists could soon be donning 3-D glasses in a home-theater-like lab to take their own ...
FALLS CHURCH, Va. (October 3, 2014) — A new National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) study, published online in the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene, found that recommended safe handling practices for workers who administer antineoplastic drugs in healthcare settings are not always followed.
Results are derived from the 2011 Health and Safety Practices Survey of Healthcare Workers, the largest federally-sponsored survey of healthcare workers in the U.S., which addresses safety and health practices relative to use of hazardous chemicals. ...
Washington, DC—The Endocrine Society today issued a Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) advising against the use of testosterone therapy in healthy women.
The CPG, entitled "Androgen Therapy in Women: A Reappraisal: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline," was published online in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism (JCEM), a publication of the Endocrine Society. The Society updated its 2006 recommendations to address new research concerning testosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) therapy in women as well as advances in testosterone testing ...
Luis Fernando Velásquez-García's group at MIT's Microsystems Technology Laboratories (MTL) develops dense arrays of microscopic cones that harness electrostatic forces to eject streams of ions.
The technology has a range of promising applications: depositing or etching features onto nanoscale mechanical devices; spinning out nanofibers for use in water filters, body armor, and "smart" textiles; or propulsion systems for fist-sized "nanosatellites."
In the latest issue of the IEEE Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, Velásquez-García, his graduate students Eric ...
Cincinnati, OH, October 3, 2014 -- Increasing rates of adolescent obesity and the likelihood that obesity will carry forward into adulthood, have led to various preventive initiatives. It has been suggested that family meals, which tend to include fruits, vegetables, calcium, and whole grains, could be protective against obesity. In a new study scheduled for publication in the Journal of Pediatrics, researchers studied whether frequent family meals during adolescence were protective for overweight and obesity in adulthood.
Jerica M. Berge, PhD, MPH, LMFT, CFLE, and ...
In the field of medicine there has often been a divide between those who focus on modern medicine and those who prefer alternative practices. But pediatrician Sunita Vohra is a firm believer there should be room for both.
A new study from Vohra, a professor in the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry's Department of Pediatrics at the University of Alberta, and a pediatric physician for Clinical Pharmacology with Alberta Health Services, is giving insight into the use of alternative medicines by pediatric cardiac patients and how effective they are seen to be. "We wanted to ...
Tel Aviv — The incidence of type 1 childhood diabetes has been increasing rapidly worldwide. If blood sugar levels aren't well-controlled, juvenile diabetes can affect nearly every organ of a child's body. And while long-term complications of the disease develop gradually, they may become disabling and even life-threatening. The exact cause of juvenile diabetes has eluded scientists, but a new study from Tel Aviv University suggests a likely trigger before birth.
In a recent paper published in Diabetic Medicine, Prof. Zvi Laron, Professor Emeritus of Pediatric Endocrinology ...
A team of researchers, led by the Optoelectronics Research Centre (ORC) at the University of Southampton, has demonstrated a breakthrough technique that offers the first possibility of silicon detectors for telecommunications.
For decades, silicon has been the foundation of the microelectronics revolution and, owing to its excellent optical properties in the near- and mid-infrared range, is now promising to have a similar impact on photonics.
The team's research, reported in the journal Nature Materials, describes engineering the electronic band structure of laser-crystallised ...