(Press-News.org) Montréal, October 2, 2014 – Scientists at the IRCM discovered a mechanism that promotes the progression of medulloblastoma, the most common brain tumour found in children. The team, led by Frédéric Charron, PhD, found that a protein known as Sonic Hedgehog induces DNA damage, which causes the cancer to develop. This important breakthrough will be published in the October 13 issue of the prestigious scientific journal Developmental Cell. The editors also selected the article to be featured on the journal's cover.
Sonic Hedgehog belongs to a family of proteins that gives cells the information needed for the embryo to develop properly. It also plays a significant role in tumorigenesis, the process that transforms normal cells into cancer cells.
"Our team studied a protein called Boc, which is a receptor located on the cell surface that detects Sonic Hedgehog," explains Lukas Tamayo-Orrego, PhD student in Dr. Charron's laboratory and co-first author of the study. "We had previously shown that Boc is important for the development of the cerebellum, the part of the brain where medulloblastoma arises, so we decided to further investigate its role."
"With this study, we found that the presence of Boc is required for Sonic Hedgehog to induce DNA damage," adds Dr. Charron, Director of the Molecular Biology of Neural Development research unit at the IRCM. "In fact, Boc causes DNA mutations in tumour cells, which promotes the progression of precancerous lesions into advanced medulloblastoma."
"Our study shows that when Boc is inactivated, the number of tumours is reduced by 66 per cent," says Frederic Mille, PhD, co-first author of the article and former postdoctoral fellow in Dr. Charron's research unit. "The inactivation of Boc therefore reduces the development of early medulloblastoma into advanced tumours."
Medulloblastoma ranks among the leading causes of cancer-related mortality in children. Current treatments include surgery, as well as radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Although the majority of children survive the treatment, radiation therapy damages normal brain cells in infants and toddlers and causes long-term harm.
"As a result, many children who undergo these treatments suffer serious side effects including cognitive impairment and disorders," states Dr. Charron. "Our results indicate that Boc could potentially be targeted to develop a new therapeutic approach that would stop the growth and progression of medulloblastoma and could reduce the adverse side effects of current treatments."
INFORMATION:
About the research project
This research project was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Canadian Cancer Society and the Cancer Research Society. Other authors from the IRCM include Martin Lévesque (co-first author), Julie Cardin, Nicolas Bouchard, and Luisa Izzi. The project was also conducted in collaboration with the laboratories of Stefan Pfister in Heidelberg, Germany, and Michael Taylor in Toronto. For more information, please refer to the article summary published online by Developmental Cell: http://www.cell.com/developmental-cell/abstract/S1534-5807(14)00520-6.
About Frédéric Charron
Frédéric Charron obtained his PhD in experimental medicine from McGill University. He is an Associate IRCM Research Professor and Director of the Molecular Biology of Neural Development research unit. Dr. Charron is Associate Research Professor in the Department of Medicine (accreditation in molecular biology) and Adjunct Member in the Department of Neuroscience at the Université de Montréal. He is also Adjunct Professor in the Department of Medicine (Division of Experimental Medicine), the Department of Biology, and the Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology at McGill University. In addition, he is a member of the McGill Integrated Program in Neuroscience, the Montreal Regional Brain Tumor Research Group at the Montreal Neurological Institute, and the Centre of Excellence in Neurosciences (CENUM) at the Université de Montréal. Dr. Charron is a Senior Research Scholar from the Fonds de recherche du Québec – Santé (FRQS). For more information, visit http://www.ircm.qc.ca/charronlab.
About the IRCM
The IRCM is a renowned biomedical research institute located in the heart of Montréal's university district. Founded in 1967, it is currently comprised of 35 research units and four specialized research clinics (cholesterol, cystic fibrosis, diabetes and obesity, hypertension). The IRCM is affiliated with the Université de Montréal, and the IRCM Clinic is associated to the Centre hospitalier de l'Université de Montréal (CHUM). It also maintains a long-standing association with McGill University. The IRCM is funded by the Quebec ministry of Economy, Innovation and Export Trade (Ministère de l'Économie, de l'Innovation et des Exportations).
Despite the legalization of same-sex marriage in 19 states and the District of Columbia and an executive order to prohibit federal contractors from discrimination against lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender employees, LGBT individuals face tremendous hurdles in access to health care and basic human rights. A special report published by The Hastings Center, LGBT Bioethics: Visibility, Disparities, and Dialogue, is a call to action for the bioethics field to help right the wrongs in the ways that law, medicine, and society have treated LGBT people.
The editors are Tia ...
FALLS CHURCH, Va. (October 3, 2014) — A new National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) study, published online in the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene, found that recommended safe handling practices for workers who administer antineoplastic drugs in healthcare settings are not always followed.
Results are derived from the 2011 Health and Safety Practices Survey of Healthcare Workers, the largest federally-sponsored survey of healthcare workers in the U.S., which addresses safety and health practices relative to use of hazardous chemicals. ...
Men who consume more alcohol have a greater risk of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, according to a recent study by Moffitt Cancer Center researchers.
HPV is a common sexually transmitted virus, with more than six million new infections in the United States each year. HPV causes genital warts in both men and women and is a contributing factor to a number of different cancers in women, including cervical, vaginal and anal cancers. More recent studies have shown that HPV can also cause penile, anal and oropharyngeal cancer in men. However, there is limited data regarding ...
A snaking, extended filament of solar material currently lies on the front of the sun-- some 1 million miles across from end to end. Filaments are clouds of solar material suspended above the sun by powerful magnetic forces. Though notoriously unstable, filaments can last for days or even weeks.
NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, which watches the sun 24 hours a day, has observed this gigantic filament for several days as it rotated around with the sun. If straightened out, the filament would reach almost across the whole sun, about 1 million miles or 100 times ...
In response to the rise of drug-resistant pathogens, doctors are routinely cautioned against overprescribing antimicrobials. But when a patient has a confirmed bacterial infection, the advice is to treat aggressively to quash the infection before the bacteria can develop resistance.
A new study questions the accepted wisdom that aggressive treatment with high drug dosages and long durations is always the best way to stem the emergence and spread of resistant pathogens. The review of nearly 70 studies of antimicrobial resistance, which was authored by researchers at Princeton ...
Two NASA satellites captured data on Typhoon Phanfone as it continues to strengthen as it moves through the Northwestern Pacific Ocean.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite flew over Typhoon Phanfone on Oct. 2, 2014 at 0939 UTC (5:39 a.m. EDT). The rainfall pattern observed using TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) and Precipitation Radar (PR) data showed that Phanfone was much better organized than a day earlier. This precipitation analysis revealed that intensifying typhoon Phanfone had formed a large eye. The heaviest rainfall was shown falling at a ...
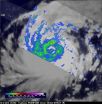
NASA's Terra satellite spotted the birth of Tropical Storm Vongfong in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean on Oct. 3. Vongfong is the nineteenth tropical storm of the Northwestern Pacific typhoon season.
The MODIS or Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer instrument that flies aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Storm Vongfong on Oct. 3 at 00:30 UTC (Oct. 2 at 8:30 p.m. EDT). At the time of the image, the center of Tropical Storm Vongfong was located just to the northeast of Pohnpei, one of four states in the Federated States of Micronesia. ...
Tropical Storm Simon is following the path of several other tropical storms that formed in the Eastern Pacific Ocean by crawling northward along the western coastline of Mexico. NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured an infrared image of Simon on Oct. 3 that showed the eastern side of the storm over Mexico.
An infrared image taken from NOAA's GOES-West satellite on Oct .3 at 7:45 a.m. EDT showed strong thunderstorms circling Tropical Storm Simon's center and a fragmented band of thunderstorms in Simon's eastern quadrant bringing rainfall to western Mexico. Simon's center ...
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory have created a new model to more accurately describe the greenhouse gases likely to be released from Arctic peatlands as they warm. Their findings, based on modeling how oxygen filters through soil, suggest that previous models probably underestimated methane emissions and overrepresented carbon dioxide emissions from these regions.
Peatlands, common in the Arctic, are wetlands filled with dead and decaying organic matter. They are the result of millions of years of plants dying and breaking down ...
It has become common for people who have pets to refer to themselves as "pet parents," but how closely does the relationship between people and their non-human companions mirror the parent-child relationship? A small study from a group of Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) researchers makes a contribution to answering this complex question by investigating differences in how important brain structures are activated when women view images of their children and of their own dogs. Their report is being published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
"Pets hold a special ...