Tarantula toxin is used to report on electrical activity in live cells
MBL neurobiology course students contribute to probe's development
2014-10-20
(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
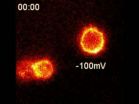
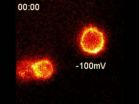
The movie is quantitative imaging of cells with potassium channels, bathed in dilute fluorescent tarantula toxin. Pixel color indicates intensity of tarantula toxin concentration. The circular shapes are cell surfaces,...
Click here for more information.
WOODS HOLE, Mass.--A novel probe that reports on the electrical activity of cells, made by fusing tarantula toxin with a fluorescent compound, is described in a paper today by scientists from the University of California, Davis; the Neurobiology course at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL); and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
The lead authors of the paper are Drew C. Tilley of UC-Davis and the late Kenneth Eum, a Ph.D. candidate at UC-Davis and teaching assistant in the MBL Neurobiology course.
The probe takes advantage of the potent ability of tarantula toxin to bind to electrically active cells, such as neurons, while the cells are in a resting state. The team discovered that a trace amount of toxin combined with a fluorescent compound would bind to a specific subset of voltage-activated proteins (Kv2-type potassium ion channels) in live cells. The probe lights up cell surfaces with this ion channel, and the fluorescent signal dims when the channel is activated by electrical signals.
This is the first time that researchers have been able to visually observe these ion channels "turning on" without first genetically modifying them. All that is required is a means to detect probe location, suggesting that related probes could potentially one day be used to map neural activity in the human brain.
"This is a demonstration, a prototype probe. But the promise is that we could use it to measure the activity state of the electrical system in an organism that has not been genetically compromised," says senior author Jon Sack, an assistant professor in the departments of Physiology and Membrane Biology at UC-Davis. Sack is a faculty member in the MBL Neurobiology course.
Since the probe binds selectively to one of the many different kinds of ion channels, it can help scientists disentangle the function of those specific channels in neuronal signaling. This can, in turn, lead to the identification of drug targets for neurological diseases and disorders.
"We have an incredible diversity of ion channels, and even of voltage-activated ion channels. The real trouble has been determining which ones perform which roles. Which ones turn on and when in normal nervous system functioning? Which are involved in abnormal states or syndromes?" Sack says. "The dream is to be able to see what the different types of ion channels are doing and when, to understand what they contribute to physiology and pathophysiology."
INFORMATION:
Citation:
Tilley DC, Eum KS, Fletcher-Taylor S, Austin DC, Dupré C, Patrón LA, Garcia RL, Yarov-Yarovoy V, Cohen BE, and Sack JT (2014) Chemoselective tarantula toxins report voltage activation of wild-type ion channels in live cells. PNAS doi: http://www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1406876111.
The Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) is dedicated to scientific discovery and improving the human condition through research and education in biology, biomedicine, and environmental science. Founded in Woods Hole, Massachusetts, in 1888, the MBL is a private, nonprofit institution and an affiliate of the University of Chicago.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-20
PULLMAN, Wash.—Researchers led by a Washington State University biologist have found the optimal mechanism by which plants heal the botanical equivalent of a bad sunburn. Their work, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, could lead to the development of crops that can repair the sun's damage more easily, improving yields and profitability.
Helmut Kirchhoff, an assistant professor in WSU's Institute of Biological Chemistry and corresponding author of the PNAS paper, said plants have had to deal with solar damage since the evolution of photosynthesis ...
2014-10-20
PHILADELPHIA — Researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine and School of Engineering at the University of Pennsylvania and The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia have used graphene -- a two-dimensional form of carbon only one atom thick -- to fabricate a new type of microelectrode that solves a major problem for investigators looking to understand the intricate circuitry of the brain.
Pinning down the details of how individual neural circuits operate in epilepsy and other neurological disorders requires real-time observation of their locations, firing patterns, ...
2014-10-20
Hurricane Gonzalo departed from Bermuda leaving power outages, downed trees, and damaged homes and buildings. An on-the ground account of the storm indicated the eye passed over the island. By Oct. 20, post-tropical storm Gonzalo was approaching the United Kindgom, sparking severe weather warnings.
By Sunday, Oct. 19 Gonzalo was affecting eastern Canada. Forecasters expect Gonzalo to hold together over while traveling east across the North Atlantic where it will affect Scotland as an extra-tropical storm on Tuesday, Oct. 21.
Camille Haley was former NASA intern and ...
2014-10-20
Tropical Storm Trudy formed on Saturday, Oct. 17 and by Oct.19 the storm made landfall in southern Mexico and weakened to a remnant low pressure area.
Tropical Storm Trudy formed near the southwestern coast of Mexico during the morning of Oct. 18 triggering warnings and watches. A Hurricane Watch was posted from east of Acapulco to Laguna De Chacahua Mexico and a Tropical Storm Warning was posted for Tecpan De Galeana to Laguna De Chacahua Mexico.
On Sat. Oct. 18 at 8 a.m. EDT, radar from Mexico indicated that the center of Tropical Storm Trudy was located on the coast ...
2014-10-20
VIDEO:
This video shows the movement of Tropical Storm Ana near the Hawaiian Islands from Oct. 17-20.
Click here for more information.
Tropical Storm Ana made a slow track west of the Hawaiian islands over the last couple of days, and by Oct. 20 was moving westward away from the main Hawaiian islands and heading toward the northwest Hawaiian islands. NASA's Terra satellite caught Ana on a flyby on Oct. 19 that showed the storm's clouds blanketing the chain of islands.
The ...
2014-10-20
This NASA satellite image is of the Egyptian River Delta. Actively burning areas, detected by MODIS's thermal bands, are outlined in red. Each hot spot, which appears as a red mark, is an area where the thermal detectors on the MODIS instrument recognized temperatures higher than background. When accompanied by plumes of smoke, as in this image, such hot spots are diagnostic for fire. The location, widespread nature, and number of fires in this image and confirmation from the Ministry of Environment in Egypt. Fires are witnessed every year in October and November, caused ...
2014-10-20
Looking forward in science often requires looking back, evaluating trends to extrapolate future outcomes. A classic case is Moore's Law, which predicts that the density of components on an integrated circuit will double every 24 months. The estimate has helped guide many developments in the computer industry.
In a new study, Rolf Halden, PhD, a researcher at Arizona State University's Biodesign Institute, examines the trajectory of chemicals appearing as emergent threats to human or environmental health.
Halden's meta-analysis of 143,000 peer-reviewed research papers ...
2014-10-20
About 20% of younger siblings of children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) will develop the condition by age 3. A new study by Yale School of Medicine researchers has found that 57% of these younger siblings who later develop the condition already showed symptoms at age 18 months.
Published in the October Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, this is the first large-scale, multi-site study aimed at identifying specific social-communicative behaviors that distinguish infants with ASD from their typically and atypically developing high-risk ...
2014-10-20
ROSEMONT, Ill.—Obesity affects individual patient care, the healthcare system and nearly every organ in the body. People with obesity often have other health problems, including diabetes, heart disease, certain tumors and cancers, and psychiatric disorders. However, the role of obesity in orthopaedic conditions and their treatment is less well-publicized.
According to orthopaedic surgeon William M. Mihalko, MD, PhD, of Campbell Clinic Orthopaedics in Memphis, Tenn., "obesity can accompany a multitude of comorbidities that can have a significant impact on a patient's ...
2014-10-20
Older individuals who are subliminally exposed to positive stereotypes about aging showed improved physical functioning that can last for several weeks, a new study led by the Yale School of Public Health has found.
Researchers used a novel intervention method to examine for the first time whether exposure to positive age stereotypes could weaken negative age stereotypes and their effects over time, and lead to healthier outcomes.
The study, to be published online in an upcoming issue of the journal Psychological Science, consisted of 100 older individuals (average ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Tarantula toxin is used to report on electrical activity in live cells
MBL neurobiology course students contribute to probe's development