Perceived hatred fuels conflicts between Democrats and Republicans, Israelis and Palestinians
Intractability of historic conflicts driven by 'motive attribution asymmetry'; financial incentives can spur greater empathy
2014-10-21
(Press-News.org) What makes human conflict intractable – and how can psychological research resolve historic disagreements? A new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences by a team of researchers from The New School for Social Research, Northwestern University and Boston College demonstrates how seemingly unsolvable political and ethnic conflicts are fueled by asymmetrical perceptions of opponents' motivations – and that these tensions can be relieved by providing financial incentives to better understand what drives an adversary group.
"This research demonstrates a fundamental cognitive bias driving [historic] conflict intractability," write researchers Jeremy Ginges, Assistant Professor of Psychology at The New School, Adam Waytz, Assistant Professor of Management & Organizations at Northwestern, and Liane Young, Assistant Professor of Psychology at Boston College. "Understanding this bias and how to alleviate it can contribute to conflict resolution on a global scale."
The researchers executed a set of three experiments to determine how adversarial groups describe their own motivations (ingroup motives) and the motivations of their opponents (outgroup motives). Among both American Democrats and Republicans, and Israelis and Palestinians, the researchers consistently observed "motive attribution asymmetry" – that is, one group's belief that their rivals are motivated by emotions opposite to their own.
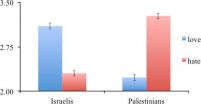
Study One asked 285 American Democrats and Republicans to asses their motives and their opponents' motives for conflict. Democrats reported that they were driven primarily by love of other Democrats rather than hatred of Republicans, but that they believed Republicans were driven more by hatred of Democrats than love for the GOP. Republicans mirrored these beliefs: they reported they were driven by love but Democrats were driven by hatred.
Studies Two and Three found similar attribution asymmetries among a group of 297 Israelis and 1,266 Gaza and West Bank Palestinians: ingroups consistently reported that they were driven by love, while they opponents were driven by hatred.
The researchers then undertook two additional studies to explore how attribution asymmetry affected conflict resolution, and how this effect might be reduced. In Study Four, a survey of 498 Israelis, researchers found a direct correlation between Israelis' belief that Palestinians were motivated by hatred with a belief that Palestinians were unwilling to negotiate and that a win-win agreement was impossible. The study thus suggests that attribution asymmetry impedes conflict resolution.
The researchers' final study sought to explore how motive attribution asymmetry, and thus impediments to resolution, might be reduced. Study Five offered Democrats and Republicans financial incentives for accurately assessing the motivations of their rivals. Once accuracy was incentivized, not only were individuals more likely to attribute love as a primary outgroup motivation, but they were more optimistic about the chances for a win-win resolution to long-running conflicts.
INFORMATION:
The study was supported by Northwestern University, Boston College, the Dispute Resolution Research Center at Kellogg School of Management, the National Science Foundation, and the Office of Naval Research. Read the entire paper at http://bit.ly/1w35aNv.
Founded in 1919, The New School was born out of principles of academic freedom, tolerance, and experimentation. Committed to social engagement, The New School today remains in the vanguard of innovation in higher education, with more than 10,000 undergraduate and graduate students challenging the status quo in design and the social sciences, liberal arts, management, the arts, and media. The New School welcomes thousands of adult learners annually for continuing education courses and calendar of lectures, screenings, readings, and concerts. Through its online learning portals, research institutes, and international partnerships, The New School maintains a global presence. Learn more at http://www.newschool.edu.
EDITOR'S NOTE: READ STUDY at http://bit.ly/1w35aNv
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-21
Boulder, CO, USA — Stegosaurs might be portrayed as lumbering plant eaters, but they were lethal fighters when necessary, according to paleontologists who have uncovered new evidence of a casualty of stegosaurian combat. The evidence is a fatal stab wound in the pubis bone of a predatory allosaur. The wound – in the conical shape of a stegosaur tail spike – would have required great dexterity to inflict and shows clear signs of having cut short the allosaur's life.
"A massive infection ate away a baseball-sized sector of the bone," reports Houston Museum ...
2014-10-21
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Oct. 21, 2014—Scientists at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory have discovered exceptional properties in a garnet material that could enable development of higher-energy battery designs.
The ORNL-led team used scanning transmission electron microscopy to take an atomic-level look at a cubic garnet material called LLZO. The researchers found the material to be highly stable in a range of aqueous environments, making the compound a promising component in new battery configurations.
Researchers frequently seek to improve ...
2014-10-21
Boulder, CO, USA — Washington's coast is so close to the seismically active Cascadia Subduction Zone that if a megathrust earthquake were to occur, a tsunami would hit the Washington shoreline in just 25 minutes.
One coastal community is preparing for such a disaster by starting construction on the nation's first tsunami evacuation refuge, large enough to shelter more than 1,000 people who are within 20-minute walking distance.
The vertical evacuation-refuge will be the roof of the gym of the new school in Grays Harbor County, Washington. The Ocosta Elementary ...
2014-10-21
They may be tiny and stingless but there's nothing sweet and innocent about a species of native Sugarbag bee when it goes to war over a coveted honey-filled hive.
A study by behavioural ecologist Dr Paul Cunningham, from QUT, and molecular biologist Dr James Hereward, from the University of Queensland, published in American Naturalist, found the bees' used their jaws as lethal weapons when they zoomed in on a neighbouring Brisbane hive to boot out the inhabitants and install their own queen to rule.
Dr Cunningham said the attacking bees arrived in a swarm and clashed ...
2014-10-21
This news release is available in German. Stroma cells are derived from connective tissue and may critically influence tumour growth. This knowledge is not new. However, bioanalyst Christopher Gerner and an interdisciplinary team from the University of Vienna and the Medical University of Vienna have developed a novel methodology for investigation. Using modern mass spectrometry, tumour-promoting activities from breast fibroblasts were directly determined from needle biopsy samples. Recently this experimental break-through is published in the renowned Journal of Proteome ...
2014-10-21
Folsom, Calif., (October 21, 2014) – A new animal study published in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease indicates that a diet including walnuts may have a beneficial effect in reducing the risk, delaying the onset, slowing the progression of, or preventing Alzheimer's disease.
Research led by Abha Chauhan, PhD, head of the Developmental Neuroscience Laboratory at the New York State Institute for Basic Research in Developmental Disabilities (IBR), found significant improvement in learning skills, memory, reducing anxiety, and motor development in mice fed a walnut-enriched ...
2014-10-21
When it comes to the brain, "more is better" seems like an obvious assumption. But in the case of synapses, which are the connections between brain cells, too many or too few can both disrupt brain function.
Researchers from Princeton University and the University of California-San Diego (UCSD) recently found that an immune-system protein called MHCI, or major histocompatibility complex class I, moonlights in the nervous system to help regulate the number of synapses, which transmit chemical and electrical signals between neurons. The researchers report in the Journal ...
2014-10-21
Massive black holes spewing out radio-frequency-emitting particles at near-light speed can block formation of new stars in aging galaxies, a study has found.
The research provides crucial new evidence that it is these jets of "radio-frequency feedback" streaming from mature galaxies' central black holes that prevent hot free gas from cooling and collapsing into baby stars.
"When you look into the past history of the universe, you see these galaxies building stars," said Tobias Marriage, assistant professor of physics and astronomy at Johns Hopkins and co-lead author ...
2014-10-21
A new medical imaging method being developed at Rutgers University could help physicians detect cancer and other diseases earlier than before, speeding treatment and reducing the need for invasive, time-consuming biopsies.
The potentially lifesaving technique uses nanotechnology to reveal small cancerous tumors and cardiovascular lesions deep inside the body. It is showing promise in early tests by Rutgers researchers in the schools of engineering and pharmacy.
The Rutgers scientists, who published initial results of their work in the July issue of the journal Nature ...
2014-10-21
Undescended testis is commonly found in newborn boys and usually normalizes spontaneously by the age of six months. In one in a hundred boys, however, at least one testis remains undescended—a condition associated with impaired fertility and a higher risk of testicular cancer in later life. About 3500 boys are affected with this condition in Germany each year. In the currently valid medical guideline for the treatment of undescended testis, early surgery is recommended, i.e., orchidopexy before the child's first birthday, in order to prevent late sequelae. Nonetheless, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Perceived hatred fuels conflicts between Democrats and Republicans, Israelis and Palestinians
Intractability of historic conflicts driven by 'motive attribution asymmetry'; financial incentives can spur greater empathy