INFORMATION:
View a video of blood flow simulation here: http://youtu.be/rc2pQvoeNfM
Engineers develop novel ultrasound technology to screen for heart conditions
2014-10-29
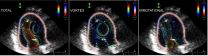
(Press-News.org) Engineers at the University of California, San Diego have determined for the first time the impact of a ring-shaped vortex on transporting blood flow in normal and abnormal ventricles within the human heart. They worked with cardiologists at the Non-Invasive Cardiology Laboratory at Gregorio Marañon Hospital, in Madrid, Spain.
In order to make the study possible, researchers have developed a novel ultrasound technology that makes screening cheaper and much easier, making it possible to reach a large number of people and even infants. Intra-ventricular flow imaging is currently done with MRI scans, which is expensive and not suitable for patients with implanted devices such as pacemakers.
The findings could have an impact on the tests and measurements that physicians rely on to diagnose and treat two heart conditions: hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, in which the heart muscle becomes abnormally thick, and non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy, in which the heart's ability to pump blood decreases as the organ's main pumping chamber, the left ventricle, is enlarged and its muscle thinned.
Nearly one million Americans suffer from either one of these conditions.
So far, physicians only take into consideration the geometry of the left ventricle and the thickness and contractility of its walls when they assess how the heart fills itself with blood. But the way the blood flows into the heart's chambers is important too, researchers argue. "This isn't like toothpaste coming out of a tube," said Juan Carlos del Alamo, professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at the Jacobs School of Engineering at UC San Diego, who led a multidisciplinary team for this study, together with postdoctoral researcher Pablo Martinez-Legazpi and Dr. Javier Bermejo's group of cardiologists at Gregorio Marañon Hospital.
They reported their findings in the Oct. 21 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
"We are trying to shape the view of diastolic dysfunction to include flow patterns as a mechanism that modulates the chamber's resistance to filling—in addition to the wall's own stiffness," said del Alamo.
People suffering from hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathies often don't show symptoms of the condition until it's too late— making early screening of paramount importance. When patients are not diagnosed early, these conditions have unfavorable prognosis— worse than a number of cancers—with most of the patients dying within five years.
For this study, the team of cardiologists recruited 60 subjects, including 20 patients with non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy; 20 patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; and 20 healthy subjects as a control group.
All subjects underwent comprehensive 2D echocardiographic exams. Then, engineers processed the images with methods typically used to create flow simulations for the aeronautical and naval industries, capturing the blood flow inside each subject's hearts.
Researchers found that the ring-shaped vortex helps to allocate about 15 percent of the blood flow within the left ventricle in healthy patients; roughly 20 percent in patients with non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy; but only about 5 percent for patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
"It is always difficult to determine if the heart is filling properly," del Alamo explained. "This new method will bring physicians a step closer to doing so." Treatment therapy for cardiomyopathies often includes devices implantation, such as pacemakers, to regulate blood flow within the heart. The data from these new imaging modalities could be instrumental, helping physicians to properly set up the devices, optimizing blood flow.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
HPV infections in women eradicated by AHCC, Japanese mushroom extract
2014-10-29
VIDEO:
AHCC (Active Hexose Correlated Compound) is a natural immune-modulating compound derived from a unique fraction of specially-cultured medicinal mushroom mycelia which has been clinically shown to strengthen the body's immune...
Click here for more information.
(October 29, 2014, Beaverton, OR) New research presented at the Society for Integrative Oncology (SIO) 11th International Conference in Houston, TX showed for the first time that it is possible to eliminate HPV ...
Penn vet professor investigates parasite-schizophrenia connection
2014-10-29
Many factors, both genetic and environmental, have been blamed for increasing the risk of a diagnosis of schizophrenia. Some, such as a family history of schizophrenia, are widely accepted. Others, such as infection with Toxoplasma gondii, a parasite transmitted by soil, undercooked meat and cat feces, are still viewed with skepticism.
A new study by Gary Smith, professor of population biology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania's School of Veterinary Medicine, used epidemiological modeling methods to determine the proportion of schizophrenia cases that ...
Clean smell doesn't always mean clean air
2014-10-29
Some of the same chemical reactions that occur in the atmosphere as a result of smog and ozone are actually taking place in your house while you are cleaning. A researcher in Drexel's College of Engineering is taking a closer look at these reactions, which involve an organic compound -called limonene- that provides the pleasant smell of cleaning products and air fresheners. His research will help to determine what byproducts these sweet-smelling compounds are adding to the air while we are using them to remove germs and odors.
Secondary organic aerosols (SOAs) are microscopic ...
NIST 'combs' the atmosphere to measure greenhouse gases
2014-10-29
By remotely "combing" the atmosphere with a custom laser-based instrument, researchers from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), in collaboration with researchers from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), have developed a new technique that can accurately measure—over a sizeable distance—amounts of several of the major "greenhouse" gases implicated in climate change.
The technique potentially could be used in several ways to support research on atmospheric greenhouse gases. It can provide accurate data to support ...
Liberal or conservative? Reactions to disgust are a dead giveaway
2014-10-29
The way a person's brain responds to a single disgusting image is enough to reliably predict whether he or she identifies politically as liberal or conservative. As we approach Election Day, the researchers say that the findings reported in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on October 30 come as a reminder of something we all know but probably don't always do: "Think, don't just react."
P. Read Montague of Virginia Tech says he was initially inspired by evidence showing that an individual's political affiliation is almost as heritable as height. Montague and his ...
New technology on the way to aid cancer suffers who lose their hair after chemotherapy
2014-10-29
Cancer suffers who lose their hair as a consequence of chemotherapy will benefit from a major research project that will improve the scalp cooling technology that prevents hair loss.
The research is being now underway and is being pioneered by global scalp cooling manufacturing company, Paxman Coolers, of Fenay Bridge, Huddersfield, in conjunction with the biology department of the University of Huddersfield.
The research will be led by key researcher Omar Hussain, who has a background in the pharmacology of cancer treatment, which he will use towards his PhD.
Omar ...
EEG test to help understand and treat schizophrenia
2014-10-29
Researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have validated an EEG test to study and treat schizophrenia. The findings, published in two separate studies, offer a clinical test that could be used to help diagnose persons at risk for developing mental illness later in life, as well as an approach for measuring the efficacies of different treatment options.
One of the studies, reported online Oct. 23 in Schizophrenia Research, shows that schizophrenia patients don't register subtle changes in reoccurring sounds as well as others and that this deficit ...
Decades of research: Effectiveness of phone counseling for cancer patients still unknown
2014-10-29
Increasingly, cancer care respects the fact that a patient's body is only part of the system that requires treatment. Over a third of cancer patients experience psychosocial distress – the mental health consequences of their conditions. And, increasingly, care providers are exploring phone- and internet-based interventions to help cancer patients navigate mental health challenges. A University of Colorado Cancer Center study recently published in the journal Psycho-Oncology asks an important question: after decades of use and study, can we definitely show that remote ...
Supersonic laser-propelled rockets
2014-10-29
WASHINGTON, Oct. 29, 2014—Scientists and science fiction writers alike have dreamt of aircrafts that are propelled by beams of light rather than conventional fuels. Now, a new method for improving the thrust generated by such laser-propulsion systems may bring them one step closer to practical use.
The method, developed by physicists Yuri Rezunkov of the Institute of Optoelectronic Instrument Engineering, Russia and Alexander Schmidt of the Ioffe Physical Technical Institute in Saint Petersburg, Russia is described today in The Optical Society's (OSA) journal Applied ...
Can plants edge out petroleum as raw material for textiles and plastics?
2014-10-29
Your next pair of spandex pants could be made out of corn — or, more precisely, from dextrose derived from corn. This option is part of a new wave, albeit a small one, of consumer goods that are being produced from plants rather than petroleum-based materials. But a complete transition to a biobased economy won't be easy, according to an article in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society.
Melody M. Bomgardner, a senior editor at C&EN, notes that a range of companies, from start-up firms to industrial giants, have ...