(Press-News.org) Maggot infestations, rotting carcasses, unidentifiable gunk in the kitchen sink – how much your brain responds to disgusting images could predict whether you are liberal or conservative.
In a study to be published in an upcoming issue of Current Biology, an international team of scientists led by Virginia Tech reports that the strength of a person's reaction to repulsive images can forecast their political ideology.
"Disgusting images generate neural responses that are highly predictive of political orientation even when those neural responses don't correspond with an individual's conscious reaction to the images," said Read Montague, a Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute professor who led the study. "Remarkably, we found that the brain's response to a single disgusting image was enough to predict an individual's political ideology."
In a brain scanner, participants were shown disgusting images, such as dirty toilets or mutilated carcasses, mixed with neutral and pleasant images, such as landscapes and babies.
Afterward, the subjects took a standard political ideology inventory, answering questions about how often they discuss politics and whether they agreed or disagreed with hot-button topics such as school prayer and gay marriage.
Using functional magnetic resonance imaging, scientists from the Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute – in collaboration with researchers from University College London, Rice University, the University of Nebraska at Lincoln, and Yale University – recorded brain activity of the subjects responding to the images.
Responses to disgusting images could predict, with 95 percent to 98 percent accuracy, how a person would answer questions on the political survey.
The results suggest political ideologies are mapped onto established neural responses that may have served to protect our ancestors against environmental threats, Montague said. Those neural responses could be passed down family lines — it's likely that disgust reactions are inherited.
"We pursued this research because previous work in a twin registry showed that political ideology — literally the degree to which someone is liberal or conservative — was highly heritable, almost as heritable as height," said Montague, who directs the Computational Psychiatry Unit at the Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute.
Conservatives tend to have more magnified responses to disgusting images, but scientists don't know exactly why, Montague said.
The responses could be a callback to the deep, adverse reactions primitive ancestors needed to avoid contamination and disease. To prevent unsavory consequences, they had to learn to separate the canteen from the latrine.
Montague points out that we're not necessarily hardwired to respond on instinct alone. He uses height as an analogy.
"Genetics predetermines height – but not fully," Montague said. "Nutrition, sleep, and starvation can all change someone's ultimate height. But tall people's children tend to be tall, and that's a kind of starting point. If we can begin to understand that some automatic reactions to political issues may be simply that – reactions – then we might take the temperature down a bit in the current boiler of political discourse."
People are unique among animals in their degree of cognitive control. Montague calls it a behavioral superpower.
"People can deny their biological instincts for an idea – think of hunger strikes for political reasons," Montague said. "That requires a high degree of cognitive control, and that's the point."
The takeaway message for Election Day?
"Think, don't just react," Montague said. "But no one needs neuroscience to know that's a good idea."
INFORMATION:
The Wellcome Trust Principal Research Fellowship, the Gatsby Charitable Trust, the National Science Foundation, and the Kane Family Foundation supported the research.
Written by Ashley WennersHerron
Sleep apnea may affect your ability to form new spatial memories, such as remembering where you parked your car, new research led by NYU Langone Medical Center sleep specialists suggests.
The study, published online Oct. 29 in Journal of Neuroscience, demonstrates through the playing of a specific video game that disruption of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep as a consequence of sleep apnea impairs spatial memory in humans even when other sleep stages are intact.
Spatial memory is utilized for everyday tasks, such as remembering the location of a favorite restaurant, ...
Wind shear has kicked in and has been pushing clouds and showers away from Tropical Cyclone Nilofar's center. NASA's Aqua satellite captured an image that showed the effects of the shear on Oct. 29.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an image of Tropical Cyclone Nilofar on Oct. 29 at 09:00 UTC (5 a.m. EDT). Tropical Cyclone Nilofar is moving through the Arabian Sea. The image shows that clouds were being pushed to the northeast of the center of the storm, from strong southwesterly wind shear.
On Oct. 29 at 1500 UTC ...
In the largest study of its kind to date, researchers have used DNA sequencing to uncover dozens of genes that heighten the risk for autism. Joseph Buxbaum, Ph.D., Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, Mark Daly, Ph.D., Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT, and their colleagues examined more than 14,000 DNA samples from affected children, parents and unrelated people. They identified changes in 107 genes that are likely to contribute to the risk for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) – a jump from the nine genes implicated in earlier studies using these ...
Small differences in as many as a thousand genes contribute to risk for autism, according to a study led by Mount Sinai researchers and the Autism Sequencing Consortium (ASC), and published today in the journal Nature.
The new study examined data on several types of rare, genetic differences in more than 14,000 DNA samples from parents, affected children, and unrelated individuals – by far the largest number to date – to dramatically expand the list of genes identified with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
Most of the genes that contribute to autism remain ...
A research group led by Anne Dutrey from the Laboratory of Astrophysics of Bordeaux, France, and the National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS) observed the distribution of dust and gas in a binary star system called GG Tau-A. It was recently discovered that one of GG Tau-A's components is itself a double star. This object is only a few million years old and lies approximately 460 light-years from Earth in the constellation Taurus.
Like a wheel in a wheel, GG Tau-A contains a large, outer disk encircling the entire system as well as an inner disk around the main central ...
Mouse lemurs can live at least eight years in the wild – twice as long as some previous estimates, a long-term longitudinal study finds.
PLOS ONE published the research on brown mouse lemurs (Microcebus rufus) led in Madagascar by biologist Sarah Zohdy, a post-doctoral fellow in Emory University's Department of Environmental Sciences and the Rollins School of Public Health. Zohdy conducted the research while she was a doctoral student at the University of Helsinki.
"It's surprising that these tiny, mouse-sized primates, living in a jungle full of predators that ...
A team led by the Lawrence Livermore scientists has created a new kind of ion channel based on short carbon nanotubes, which can be inserted into synthetic bilayers and live cell membranes to form tiny pores that transport water, protons, small ions and DNA.
These carbon nanotube "porins" have significant implications for future health care and bioengineering applications. Nanotube porins eventually could be used to deliver drugs to the body, serve as a foundation of novel biosensors and DNA sequencing applications, and be used as components of synthetic cells.
Researchers ...
A study led by investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital and the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania has identified a potential target for therapies to treat cocaine addiction. In their study receiving advance online publication in Molecular Psychiatry, the investigators find evidence that changing one amino acid in a subunit of an important receptor protein alters whether cocaine-experienced animals will resume drug seeking after a period of cocaine abstinence. Increasing expression of the enzyme responsible for that change within the ...
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — To understand the extent to which human activities are polluting Earth's atmosphere and oceans, it's important to distinguish human-made pollutants from compounds that occur naturally. A recent study co-authored by a Brown University professor does just that for ammonium, a compound that is produced by human activities like agriculture, as well as by natural processes that occur in the ocean.
The research, based on two years of rainwater samples taken in Bermuda, suggests that ammonium deposited over the open ocean comes almost ...
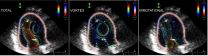
Engineers at the University of California, San Diego have determined for the first time the impact of a ring-shaped vortex on transporting blood flow in normal and abnormal ventricles within the human heart. They worked with cardiologists at the Non-Invasive Cardiology Laboratory at Gregorio Marañon Hospital, in Madrid, Spain.
In order to make the study possible, researchers have developed a novel ultrasound technology that makes screening cheaper and much easier, making it possible to reach a large number of people and even infants. Intra-ventricular flow imaging ...