(Press-News.org) NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured an image of the birth of the Eastern Pacific Ocean's twenty-first tropical depression, located far south of Acapulco, Mexico.
NOAA's GOES-West satellite gathered infrared data on newborn Tropical Depression 21E (TD 21E) and that data was made into an image by NASA/NOAA's GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. At 1200 UTC (9 a.m. EDT), the GOES-West image showed that thunderstorms circled the low-level center and extended northeast of the center indicating that southwesterly wind shear was affecting the storm.
At 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC), maximum sustained winds were near 35 mph (55 kph) and some slow strengthening is forecast during the next 48 hours. TD 21E was centered near latitude 11.5 north and longitude 100.9 west. That's about 380 miles (610 km) south of Acapulco, Mexico. TD 21E was moving west at 6 mph (9 kph) and is expected to turn to the southwest on Friday, Oct. 31, followed by a turn back west on Nov. 1. The estimated minimum central pressure is 1007 millibars.
Forecaster Blake of NHC noted that although the depression is over warm water, southwesterly shear and dry air in the low- to mid-levels are expected to continue for the next day or two which will make any strengthening occur slowly.
The depression is forecast to turn west-southwestward and then southwestward over the next day and a half, and become a tropical storm.
INFORMATION:Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Twenty-first Eastern Pacific tropical depression born on Oct. 30
2014-10-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Reconstruction of a patterned piece of spinal cord in 3-D culture
2014-10-30
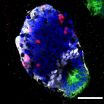
Professor Elly Tanaka and her research group at the DFG Research Center for Regenerative Therapies Dresden - Cluster of Excellence at the TU Dresden (CRTD) demonstrated for the first time the in vitro growth of a piece of spinal cord in three dimensions from mouse embryonic stem cells. Correct spatial organization of motor neurons, interneurons and dorsal interneurons along the dorsal/ventral axis was observed.
This study has been published online by the American journal "Stem Cell Reports" on 30.10.2014.
For many years Elly Tanaka and her research group have been studying ...
Harnessing error-prone chips
2014-10-30
As transistors get smaller, they also grow less reliable. Increasing their operating voltage can help, but that means a corresponding increase in power consumption.
With information technology consuming a steadily growing fraction of the world's energy supplies, some researchers and hardware manufacturers are exploring the possibility of simply letting chips botch the occasional computation. In many popular applications — video rendering, for instance — users probably wouldn't notice the difference, and it could significantly improve energy efficiency.
At ...
Female frogs modify offspring development depending on reproduction date
2014-10-30
Global warming is altering the reproduction of plants and animals, notably accelerating the date when reproduction and other life processes occur. A study by the University of Uppsala (Sweden), including the participation of Spanish researcher Germán Orizaola, has discovered that some amphibians are capable of making their offspring grow at a faster rate if they have been born later due to the climate.
Over recent decades many organisms, both plants and animals, have experienced a notable advance in the date when many of their life processes (like reproduction, migration ...
Could daylight savings time be a risk to diabetics?
2014-10-30
Soon, many will turn back the hands of time as part of the twice-annual ritual of daylight savings time. That means remembering to change the alarm clock next to the bed, which will mean an extra hour of sleep before getting up in the morning.
But for some diabetics who use insulin pumps, Saleh Aldasouqi, associate professor of medicine at Michigan State University, suggests that remembering to change the time on this device should be the priority.
"Some diabetes patients who use insulin pumps may forget to change the clock that is found in these devices," said diabetes ...
Is space tourism safe or do civilians risk health effects?
2014-10-30
Rochelle, NY, October 30, 2014—Several companies are developing spacecraft designed to take ordinary citizens, not astronauts, on short trips into space. "Space tourism" and short periods of weightlessness appear to be safe for most individuals according to a series of articles on space biomedicine published in New Space, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The articles are available free on the New Space website until November 30, 2014.
James Vanderploeg, MD, MPH and colleagues, University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, coauthored ...
NASA sees Cyclone Nilofar looking more like a comet than a tropical cyclone
2014-10-30
Tropical Cyclone Nilofar was closing in on the border between Pakistan and northwestern India on Oct. 30 when NASA's Terra satellite passed overhead from space. Wind shear continued to affect the storm making it appear more like a comet with a tail, than a tropical cyclone.
The MODIS or Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer instrument that flies aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of Nilofar on Oct. 30 at 06:35 UTC (2:35 a.m. EDT). Nilofar was still being affected by southwesterly wind shear, which was blowing the clouds and showers to the northeast. ...
CHEST lung cancer experts present policy statement to CMS Committee on Coverage
2014-10-30
VIDEO:
Dr. Gerard Silvestri gives background on lung cancer screening recommendations.
Click here for more information.
October 30, 2014, Glenview, Illinois -- As the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Committee on Coverage studies the decision to cover lung cancer screening for eligible individuals, today's Online First section of the journal CHEST published Components for High Quality Lung Cancer Screening: American College of Chest Physicians and American Thoracic ...
Clinical practice guidelines address multimodality treatment for esophageal cancer
2014-10-30
Chicago, October 30, 2014 – The Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) has released new clinical practice guidelines for treating cancer of the esophagus and gastroesophageal junction (area where the esophagus meets the stomach).
The guidelines, published in the November 2014 issue of The Annals of Thoracic Surgery, include nine evidence-based recommendations that address issues related to multimodality care, including neoadjuvant therapy (chemotherapy and radiation therapy given prior to surgery). The goal of this therapy is to reduce the extent of cancer before an ...
Molecular tumor markers could reveal new therapeutic targets for lung cancer treatment
2014-10-30
Chicago, October 30, 2014—Analysis of 607 small cell lung cancer (SCLC) lung tumors and neuroendocrine tumors (NET) identified common molecular markers among both groups that could reveal new therapeutic targets for patients with similar types of lung cancer, according to research presented today at the 2014 Chicago Multidisciplinary Symposium in Thoracic Oncology. The Symposium is sponsored by the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO), the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) and ...
Young adults ages 18 to 26 should be viewed as separate subpopulation in policy and research
2014-10-30
WASHINGTON – Young adults ages 18-26 should be viewed as a separate subpopulation in policy and research, because they are in a critical period of development when successes or failures could strongly affect the trajectories of their lives, says a new report from the Institute of Medicine and National Research Council. The committee that wrote the report found that young adults' brains and behaviors continue maturing into their 20s, and they face greater challenges achieving independence than their predecessors did, have lengthened pathways into adulthood, and are ...