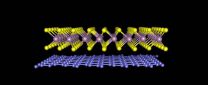
(Press-News.org) LAWRENCE -- Physicists at the University of Kansas have fabricated an innovative substance from two different atomic sheets that interlock much like Lego toy bricks. The researchers said the new material -- made of a layer of graphene and a layer of tungsten disulfide -- could be used in solar cells and flexible electronics. Their findings are published today by Nature Communications.
Hsin-Ying Chiu, assistant professor of physics and astronomy, and graduate student Matt Bellus fabricated the new material using "layer-by-layer assembly" as a versatile bottom-up nanofabrication technique. Then, Jiaqi He, a visiting student from China, and Nardeep Kumar, a graduate student who now has moved to Intel Corp., investigated how electrons move between the two layers through ultrafast laser spectroscopy in KU's Ultrafast Laser Lab, supervised by Hui Zhao, associate professor of physics and astronomy.
"To build artificial materials with synergistic functionality has been a long journey of discovery," Chiu said. "A new class of materials, made of the layered materials, has attracted extensive attention ever since the rapid development of graphene technology. One of the most promising aspects of this research is the potential to devise next-generation materials via atomic layer-level control over its electronic structure."
According to the researchers, the approach is to design synergistic materials by combining two single-atom thick sheets, for example, acting as a photovoltaic cell as well as a light-emitting diode, converting energy between electricity and radiation. However, combining layers of atomically thin material is a thorny task that has flummoxed researchers for years.
"A big challenge of this approach is that, most materials don't connect together because of their different atomic arrangements at the interface -- the arrangement of the atoms cannot follow the two different sets of rules at the same time," Chiu said. "This is like playing with Legos of different sizes made by different manufacturers. As a consequence, new materials can only be made from materials with very similar atomic arrangements, which often have similar properties, too. Even then, arrangement of atoms at the interface is irregular, which often results in poor qualities."
Layered materials such as those developed by the KU researchers provide a solution for this problem. Unlike conventional materials formed by atoms that are strongly bound in all directions, the new material features two layers where each atomic sheet is composed of atoms bound strongly with their neighbors -- but the two atomic sheets are themselves only weakly linked to each other by the so-called van der Waals force, the same attractive phenomenon between molecules that allows geckos to stick to walls and ceilings.
"There exist about 100 different types of layered crystals -- graphite is a well-known example," Bellus said. "Because of the weak interlayer connection, one can choose any two types of atomic sheets and put one on top of the other without any problem. It's like playing Legos with a flat bottom. There is no restriction. This approach can potentially product a large number of new materials with combined novel properties and transform the material science."
Chiu and Bellus created the new carbon and tungsten disulfide material with the aim of developing novel materials for efficient solar cells. The single sheet of carbon atoms, known as graphene, excels at moving electrons around, while a single-layer of tungsten disulfide atoms is good at absorbing sunlight and converting it to electricity. By combining the two, this innovative material can potentially perform both tasks well.
The team used tape to lift a single layer of tungsten disulfide atoms from a crystal and apply it to a silicon substrate. Next, they used the same procedure to remove a single layer of carbon atoms from a graphite crystal. With a microscope, they precisely laid the graphene on top of the tungsten disulfide layer. To remove any glue between the two atomic layers that are unintentionally introduced during the process, the material was heated at about 500 degrees Fahrenheit for a half-hour. This allowed the force between the two layers to squeeze out the glue, resulting in a sample of two atomically thin layers with a clean interface.
Doctoral students He and Kumar tested the new material in KU's Ultrafast Laser Lab. The researchers used a laser pulse to excite the tungsten disulfide layer.
"We found that nearly 100 percent of the electrons that absorbed the energy from the laser pulse move from tungsten disulfide to graphene within one picosecond, or one-millionth of one-millionth second," Zhao said. "This proves that the new material indeed combines the good properties of each component layer."
The research groups led by Chiu and Zhao are trying to apply this Lego approach to other materials. For example, by combining two materials that absorb light of different colors, they can make materials that react to diverse parts of the solar spectrum.
INFORMATION:
The National Science Foundation funded this work.
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori is strongly associated with gastric ulcers and cancer. To combat the infection, researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine and Jacobs School of Engineering developed LipoLLA, a therapeutic nanoparticle that contains linolenic acid, a component in vegetable oils. In mice, LipoLLA was safe and more effective against H. pylori infection than standard antibiotic treatments.
The results are published online Nov. 24 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"Current H. pylori treatments are facing ...
Medford/Somerville, Mass--Researchers in human genetics have known that long nucleotide repeats in DNA lead to instability of the genome and ultimately to human hereditary diseases such Freidreich's ataxia and Huntington's disease.
Scientists have believed that the lengthening of those repeats occur during DNA replication when cells divide or when the cellular DNA repair machinery gets activated. Recently, however, it became apparent that yet another process called transcription, which is copying the information from DNA into RNA, could also been involved.
A Tufts ...
Researchers at the University of Leeds have shed light on a gene mutation linked to autistic traits.
The team already knew that some people with autism were deficient in a gene called neurexin-II. To investigate whether the gene was associated with autism symptoms, the Leeds team studied mice with the same defect.
They found behavioural features that were similar to autism symptoms, including a lack of sociability or interest in other mice.
Dr Steven Clapcote, Lecturer in Pharmacology in the University's Faculty of Biological Sciences, who led the study published ...
Flexible electronics have been touted as the next generation in electronics in various areas, ranging from consumer electronics to bio-integrated medical devices. In spite of their merits, insufficient performance of organic materials arising from inherent material properties and processing limitations in scalability have posed big challenges to developing all-in-one flexible electronics systems in which display, processor, memory, and energy devices are integrated. The high temperature processes, essential for high performance electronic devices, have severely restricted ...
Cancer stem cells are particularly difficult to eradicate and are at the heart of why it is so hard to more effectively treat cancer patients, as the post-treatment survival of cancer stem cells drives tumour recurrence, the systemic spread of cancer and, ultimately, treatment failure.
The researchers, based at the University's Institute of Cancer Sciences and the Cancer Research UK Manchester Institute - both part of the Manchester Cancer Research Centre - investigated the role of mitochondria which produce and release energy within cells. In this context, the new ...
CHICAGO (November 25, 2014) - New research shows providing detainees wash cloths treated with a skin cleanser could reduce the prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) bacteria in U.S. jails. Researchers looked at the effect on transmission of S. aureus of using wash cloths treated with chlorhexidine gluconate (CHG) compared with wash cloths with only plain water in detainees at Dallas County Jail. The study was published in the December issue of Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA). ...
CHICAGO (November 25, 2014) - A new study finds a decrease in an emergent strain of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) that is resistant to last line defense antibiotics. Researchers examined the prevalence of vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA) infections in southeastern Michigan, where the majority of these infections have occurred in the U.S. The study is published in the December issue of Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA).
"Vancomycin is one of the few antimicrobial ...
With research and development costs for many drugs reaching well into the billions, pharmaceutical companies want more than ever to determine whether their drugs already at market have any hidden therapeutic benefits that could warrant putting additional indications on the label and increase production.
Such repurposing of drugs requires evidence of efficacy, and to find candidate drugs for randomized controlled repurposing trials, investigators can use computer simulation and scans of health care billing data, in addition to in vitro and in vivo testing.
A study led ...
Parasites use Trojan horse subterfuge to suppress the immunity of their victims when causing infection, according to a study.
The finding, which shows a new trick parasites can play, paves the way to possible treatments for infectious diseases and allergies.
Scientists have shown that parasites are able to secrete tiny sealed packages of genetic material into the cells of their victims, in order to suppress the immune response to infection.
The packages, known as vesicles, mimic those that are produced naturally in most organisms to carry out everyday functions such ...
(Boston)-- In the largest study of the genetics of memory ever undertaken, an international researcher team including scientists from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM), have discovered two common genetic variants that are believed to be associated with memory performance. The findings, which appear in the journal Biological Psychiatry, are a significant step towards better understanding how memory loss is inherited.
Longer life spans and the increased prevalence of memory impairment and dementia world-wide underscore the critical public health importance of ...