Research shows E.B. White was right in Charlotte's Web
The spider shows the other kind of humble
2014-12-18
(Press-News.org) Before Charlotte the spider spelled the word "humble" in her web to describe Wilbur the pig, she told Templeton the rat that the word meant "not proud."
That's probably what most people say if you put them on the spot. But if you give them time to think about it deeply, like a new study just did, other themes emerge that have a lot to do with learning.
And these intellectual dimensions of humility describe the spider as well or better than the pig.
"Wilbur has many of the dimensions of humility in general: regard for others, not thinking too highly of himself - but highly enough," said Peter Samuelson, the lead study author. "Charlotte shows some of the unique aspects of intellectual humility: curiosity, love of learning, willingness to learn from others."
Samuelson is a psychologist at Fuller Theological Seminary who embarked on a new voyage for academia: a bottom-up exploration of what it really means to be humble. Samuelson teamed up with Brigham Young University psychologist Sam Hardy.
For his part, Hardy utilized a statistical technique called multi-dimensional scaling that made sense of open-ended responses from the 350 study participants recruited from Amazon's "Mechanical Turk."
"This is more of a bottom-up approach, what do real people think about humility, what are the lay conceptions out there in the real world and not just what comes from the ivory tower," Hardy said. "We're just using statistics to present it and give people a picture of that."
Hardy's analysis found two clusters of traits that people use to explain humility. Traits in the first cluster come from the social realm: Sincere, honest, unselfish, thoughtful, mature, etc. The second and more unique cluster surrounds the concept of learning: curious, bright, logical and aware.
Samuelson says the two clusters of humble traits - the social and intellectual - often come as a package deal for people who are "intellectually humble." Because they love learning, they spend time learning from other people.
"In many ways, this is the defining feature of intellectual humility and what makes it distinct from general humility," said Samuelson, who formerly served as a Lutheran pastor prior to his academic career.
The new study appears in The Journal of Positive Psychology.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-18
Auroras are the most visible manifestation of the sun's effect on Earth, but many aspects of these spectacular displays are still poorly understood. Thanks to the joint European Space Agency and NASA's Cluster mission combined with data from a past NASA mission called the Imager for Magnetopause-to-Aurora Global Exploration, or IMAGE, a particular type of very high-latitude aurora has now been explained.
Known as a theta aurora -- because seen from above it looks like the Greek letter theta, an oval with a line crossing through the center -- this type of aurora sometimes ...
2014-12-18
ITHACA, N.Y. - To encode data, today's computer memory technology uses electric currents - a major limiting factor for reliability and shrinkability, and the source of significant power consumption. If data could instead be encoded without current - for example, by an electric field applied across an insulator - it would require much less energy, and make things like low-power, instant-on computing a ubiquitous reality.
A team at Cornell University led by postdoctoral associate John Heron, who works jointly with Darrell Schlom, professor of Industrial Chemistry in the ...
2014-12-18
Scientists from WCS (Wildlife Conservation Society), the Universidad Austral de Chile, the Blue Whale Center, the American Museum of Natural History (AMNH), NOAA, and other organizations are examining molecular clues to answer a big question: how many types of blue whales exist in the waters of the southeastern Pacific?
The answer seems to be two distinct populations, according to a genetic study comparing the blue whales off the southern coast of Chile with those swimming in the waters of Antarctica and other nearby regions. One of the populations could be made up of ...
2014-12-18
By 2050, a majority of U.S. coastal areas are likely to be threatened by 30 or more days of flooding each year due to dramatically accelerating impacts from sea level rise, according to a new NOAA study, published today in the American Geophysical Union's online peer-reviewed journal Earth's Future.
The findings appear in the paper From the Extreme to the Mean: Acceleration and Tipping Points for Coastal Inundation due to Sea Level Rise, and follows the earlier study, Sea Level Rise and Nuisance Flood Frequency Changes around the United States, by the report's co-author, ...
2014-12-18
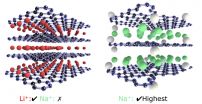
MANHATTAN, KANSAS -- A Kansas State University engineering team has discovered some of graphene oxide's important properties that can improve sodium- and lithium-ion flexible batteries.
Gurpreet Singh, assistant professor of mechanical and nuclear engineering, and Lamuel David, doctoral student in mechanical engineering, India, published their findings in the Journal of Physical Chemistry in the article "Reduced graphene oxide paper electrode: Opposing effect of thermal annealing on Li and Na cyclability."
Graphene oxide is an insulating and defective version of graphene ...
2014-12-18
Many genetic mutations in visual pigments, spread over millions of years, were required for humans to evolve from a primitive mammal with a dim, shadowy view of the world into a greater ape able to see all the colors in a rainbow.
Now, after more than two decades of painstaking research, scientists have finished a detailed and complete picture of the evolution of human color vision. PLOS Genetics is publishing the final pieces of this picture: The process for how humans switched from ultraviolet (UV) vision to violet vision, or the ability to see blue light.
"We ...
2014-12-18
Ibuprofen, a common over-the-counter drug used to relieve pain and fever, could hold the keys to a longer healthier life, according to a study by researchers at the Buck Institute for Research on Aging. Publishing in PLoS Genetics on December 18th, scientists showed that regular doses of ibuprofen extended the lifespan of yeast, worms and fruit flies.
"There is a lot to be excited about," said Brian Kennedy, PhD, CEO of the Buck Institute, who said treatments, given at doses comparable to those used in humans, extended lifespan an average of 15 percent in the model ...
2014-12-18
Many animals may have a previously under-appreciated ability to make up for lost time with more effort, according to new research publishing this week in PLOS Computational Biology.
This capability could help scientists better understand how animals make efficient decisions in changing environments -- and ultimately help ensure the survival of a species.
Researchers from Princeton University challenge the conventional view that animals face a simple trade-off between the speed and the accuracy of their decisions. Adrian de Froment, Daniel Rubenstein and Simon Levin ...
2014-12-18
Most vaccines work by inducing an immune response characterized by neutralizing antibodies against the respective pathogen. An effective HIV vaccine has remained elusive so far, but researchers have continued to make progress, often employing innovative methods. A study published on December 18th in PLOS Pathogens reports that a combination of antibodies from llamas can neutralize (destroy) a wide range of circulating HIV viruses.
After initial disappointment that HIV vaccine candidates were unable to elicit neutralizing antibodies, researchers found that some HIV-infected ...
2014-12-18
COLLEGE STATION -- A common over-the-counter drug that tackles pain and fever may also hold keys to a longer, healthier life, according to a Texas A&M AgriLife Research scientist.
Regular doses of ibuprofen extended the lifespan of multiple species, according to research published in the journal Public Library of Science-Genetics.
"We first used baker's yeast, which is an established aging model, and noticed that the yeast treated with ibuprofen lived longer," said Dr. Michael Polymenis, an AgriLife Research biochemist in College Station. "Then we tried the same process ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Research shows E.B. White was right in Charlotte's Web
The spider shows the other kind of humble