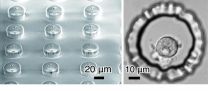
Dead feeder cells support stem cell growth
Discovery suggests simpler method to grow stem cells
2015-04-24
(Press-News.org) Stem cells naturally cling to feeder cells as they grow in petri dishes. Scientists have thought for years that this attachment occurs because feeder cells serve as a support system, providing stems cells with essential nutrients.
But a new study that successfully grew stem cells with dead, or fixed, feeder cells suggests otherwise.
The discovery, described in the Journal of Materials Chemistry B, challenges the theory that feeder cells provide nutrients to growing stem cells. It also means that the relationship between the two cells is superficial, according to Binata Joddar, Ph.D., a biomedical engineer at The University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP).
"We've proved an important phenomenon," said Joddar, who runs UTEP's Inspired Materials and Stem-Cell Based Tissue Engineering Lab. "And it suggests that these feeder cells, which are difficult to grow, may not be important at all for stem cell growth."
In the study, feeder cells were chemically fixed before living stem cells were placed in the same dish. Like organs that are preserved with formaldehyde, this kept the feeder cells' physical appearance the same, but essentially killed them.
Even though the feeder cells were dead, the stem cells still latched on and grew successfully.
The discovery offers a simpler and more cost-effective way to grow stem cells, which has proved difficult over the years.
"Because feeder cells don't need to stay alive in the process, we can store them at room temperature and spend less time cultivating them," Joddar said.
Joddar believes the finding suggests that stem cells may only like the "topology" of feeder cells.
"This makes me think that we use a nanomanufacturing approach to grow stem cells," she said. "We could mimic feeder cells' nanotopology with 3-D printing techniques and skip using feeder cells altogether in the future."
INFORMATION:
Link to paper: http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C4TB01635A
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-04-24
Aid workers who provide shelter following natural disasters, such as hurricanes or earthquakes, should consider long-term archaeological information about how locals constructed their homes in the past, and what they do when they repair and rebuild. Archaeologists and international humanitarian organizations are both involved in recovery, with the former doing this for the past, and the latter for the present. So says Alice Samson of the University of Cambridge in the UK, leader of an archaeological overview of building practices used in the Caribbean 1,400 to 450 years ...
2015-04-24
New research published today in the journal Nature Communications represents a potentially fundamental shift in our understanding of how nerve cells in the brain generate the energy needed to function. The study shows neurons are more independent than previously believed and this research has implications for a range of neurological disorders.
"These findings suggest that we need to rethink the way we look at brain metabolism," said Maiken Nedergaard, M.D., D.M.Sc., co-director of the University of Rochester Center for Translational Neuromedicine and lead author of ...
2015-04-24
(April 15th, 2015) Coeliac disease is one of the most common life-long conditions in Europe, yet many people remain undiagnosed and lengthy diagnostic delays may be putting lives at risk. Today, doctors are being urged to consider testing for Coeliac disease in anyone showing signs and symptoms of the condition and to consider screening everyone in high-risk groups.
A paper published in this month's special Coeliac disease (CD) issue of the UEG Journal assessed the viability of screening for CD in the general population and concluded that screening of first-degree relatives ...
2015-04-24
April 24, 2015 - A simple method of testing "twilight vision" gives reliable results in identifying people who have decreased visual acuity under low light conditions, according to a study in the May issue of Optometry and Vision Science, official journal of the American Academy of Optometry. The journal is published by Wolters Kluwer.
Using filters to test at a light level 100 times lower than for daylight visual acuity testing, vision care professionals can obtain "reliable and repeatable" measurements of twilight vision, report Jason S. Ng, OD, PhD, and colleagues ...
2015-04-24
MAYWOOD, Il. - The recent Great Recession was accompanied by a significant and sustained increase in major depression in U.S. adults, according to a Loyola study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Prevalence of major depression increased from 2.33 percent during the years 2005-2006 to 3.49 percent in 2009-2010 to 3.79 percent in 2011-2012, according to the study by Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine researchers.
Prevalence of less-severe depression increased from 4.1 percent in 2005-2006 to 4.79 percent in 2009-2010, but then declined ...
2015-04-24
Leesburg, VA, April 24, 2015--Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) increases the rate of cancer detection in women with dense breast tissue by as much as 67%, according to new research from the Einstein Medical Center in Philadelphia.
"There are a lot of data showing that screening with DBT increases cancer detection, but much less is known about the effect of density and lesion type on detection rates," said coauthor Caroline Ling. "We found a striking increase in detection among women with dense breasts called back for mass and asymmetry relative to nondense breasts."
The ...
2015-04-24
Functional analysis of a cell, which is the fundamental unit of life, is important for gaining new insights into medical and pharmaceutical fields. For efficiently studying cell functions, it is essential to reconstruct cellular microenvironments by parallel manipulation of single cells. Various cell manipulation techniques including fluidic, optical, and electrical techniques have been developed.
However, all these techniques lack flexibility with respect to changes in the cellular types, number, and places. In addition, the manipulations, which have been conducted in ...
2015-04-24
While seeking targets to attack Huntington's disease, an incurable inherited neurodegenerative disorder, neurobiologists of the research group led by Professor Erich Wanker of the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association found what they were looking for. Using a filtering strategy borrowed from criminologists, the researchers systematically filtered interaction networks of various biological databases. In several steps, they increasingly narrowed down their search until they ultimately found the protein (CRMP1). In subsequent lab experiments ...
2015-04-24
Dropping off a child at kindergarten for the first time can be one of the most memorable yet terrifying experiences of parenthood. Among the many concerns parents face is the worry whether your child will make friends - a key factor, research shows, in reducing anxiety, depression and the likelihood of being bullied.
For parents of children with disabilities, the concern is even greater as four-out-of-10 of their children will enter kindergarten without the social skills necessary to develop close friendships. The response from schools has been to create inclusive classrooms, ...
2015-04-24
A new technique that identifies how genes are controlled could help scientists spot errors in the genetic code which trigger disease, a study suggests.
The method focusses on those parts of DNA - known as enhancer regions - which regulate the activity of genes and direct the production of proteins that have key functions within the body.
Errors in protein production can result in a wide range of diseases in people, researchers say.
The new method could help researchers pinpoint the source of disease-causing mutations in enhancers. Until now, these genetic errors ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Dead feeder cells support stem cell growth
Discovery suggests simpler method to grow stem cells