Recurrence of prostate cancer detected earlier with innovative PSMA-ligand PET/CT
2015-05-04
(Press-News.org) A recent study reported in The Journal of Nuclear Medicine compared use of the novel Ga-68-PSMA-ligand PET/CT with other imaging methods and found that it had substantially higher detection rates of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) in patients with biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Discovering a recurrence early can strongly influence further clinical management, so it is especially noteworthy that this hybrid PSMA-ligand identified a large number of positive findings in the clinically important range of low PSA-values ( END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New climate projections paint bleak future for tropical coral reefs
2015-05-04
ITHACA, N.Y. - As greater atmospheric carbon dioxide boosts sea temperatures, tropical corals face a bleak future. New climate model projections show that conditions are likely to increase the frequency and severity of coral disease outbreaks, reports a team of researchers led by Cornell University scientists, published today (May 4) in Nature Climate Change.
Download study, FAQ and photos: https://cornell.box.com/coral-disease
Conserving coral reefs is crucial to maintaining the biodiversity of our oceans and sustaining the livelihoods of the 500 million people that ...
INFORMS journal study finds double-digit growth for firms creating own online communities
2015-05-04
A new study published in Marketing Science, a journal of the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS), shows double-digit revenue growth for firms that create their own brand-specific online communities.
The study, Social Dollars: The Economic Impact of Customer Participation in a Firm-Sponsored Online Customer Community, is by professors Puneet Manchanda of the University of Michigan, Grant Packard of Wilfrid Laurier University, and Adithya Pattabhiramaiah of the Georgia Institute of Technology.
Engaging consumers through online social ...
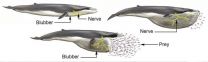
These gigantic whales have nerves like bungee cords
2015-05-04
Nerves aren't known for being stretchy. In fact, "nerve stretch injury" is a common form of trauma in humans. But researchers reporting in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on May 4 have discovered that nerves in the mouths and tongues of rorqual whales can more than double their length with no trouble at all.
"These large nerves actually stretch and recoil like bungee cords," says A. Wayne Vogl of the University of British Columbia. "This is unlike other nerves in vertebrates, where the nerve is of a more fixed length that has enough slack in it to accommodate changes ...
Gigantic whales have stretchy 'bungee cord' nerves
2015-05-04
University of British Columbia (UBC) researchers have discovered a unique nerve structure in the mouth and tongue of rorqual whales that can double in length and then recoil like a bungee cord.
The stretchy nerves explain how the massive whales are able to balloon an immense pocket between their body wall and overlying blubber to capture prey during feeding dives.
"This discovery was totally unexpected and unlike other nerve structures we've seen in vertebrates, which are of a more fixed length," says Wayne Vogl of UBC's Cellular and Physiological Sciences department.
"The ...
Emergency department opioid prescribing
2015-05-04
BOSTON, MA - The Emergency Department (ED) is at the convergence of the opioid epidemic as emergency physicians (EPs) routinely care for patients with adverse effects from opioids, including overdoses and those battling addiction, as well as treating patients that benefit from opioid use. Increasingly, EPs are required to distinguish between patients who are suffering from a condition that warrants opioids to relieve pain, and those who may be attempting to obtain these medications for other purposes, such as abuse or diversion. Overall, opioid pain reliever prescribing ...
Discovery could help reverse glucocorticoid resistance in some young leukemia patients
2015-05-04
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. -- May 4, 2015) Researchers led by St. Jude Children's Research Hospital scientists have identified a mechanism that helps leukemia cells resist glucocorticoids, a finding that lays the foundation for more effective treatment of cancer and possibly a host of autoimmune diseases. The findings appear online today in the scientific journal Nature Genetics.
The research focused on glucocorticoids, a class of steroid hormones. These hormones have been key ingredients in the chemotherapy cocktail that has helped to push long-term survival for the most common ...
Scientists dramatically improve method for finding common genetic alterations in tumors
2015-05-04
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. - May 4, 2015) St. Jude Children's Research Hospital scientists have developed a significantly better computer tool for finding genetic alterations that play an important role in many cancers but were difficult to identify with whole-genome sequencing. The findings appear today in the scientific journal Nature Methods.
The tool is an algorithm called CONSERTING, short for Copy Number Segmentation by Regression Tree in Next Generation Sequencing.
St. Jude researchers created CONSERTING to improve identification of copy number alterations (CNAs) in the ...
Detecting knee-cushion problems early could lead to better treatments
2015-05-04
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- Within the knee, two specialized, C-shaped pads of tissue called menisci perform many functions that are critical to knee-joint health. The menisci, best known as the shock absorbers in the knee, help disperse pressure, reduce friction and nourish the knee. Now, new research from the University of Missouri shows even small changes in the menisci can hinder their ability to perform critical knee functions. The research could provide new approaches to preventing and treating meniscal injuries as well as clues to understanding osteoarthritis; meniscal problems ...
3-D printed trachea among key Mount Sinai research presented at AATS meeting
2015-05-04
(New York -- May 4, 2015) Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai researchers presented several landmark studies at the 2015 American Association for Thoracic Surgery (AATS) meeting in Seattle.
AATS Highlights include:
First Successful 3D Printed Trachea
A team of researchers from Icahn School of Medicine have combined 3D printing technology with human stem cells to create the first successful 3D-printed biologic tracheal graft in an animal model. Using a biocompatible polymer, researchers created a customized 3D-printed tracheal graft seeded with stem cells. The ...
Global decline of large herbivores may lead to an 'empty landscape'
2015-05-04
CORVALLIS, Ore. - The decline of the world's large herbivores, especially in Africa and parts of Asia, is raising the specter of an "empty landscape" in some of the most diverse ecosystems on the planet, according to a newly published study.
Many populations of animals such as rhinoceroses, zebras, camels, elephants and tapirs are diminishing or threatened with extinction in grasslands, savannahs, deserts and forests, scientists say.
An international team of wildlife ecologists led by William Ripple, Oregon State University distinguished professor in the College of ...