(Press-News.org) New research by scientists at the University of Maryland School of Medicine has found that esophageal cancer patients treated with proton therapy experienced significantly less toxic side effects than patients treated with older radiation therapies.
Working with colleagues at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota and the MD Anderson Cancer Center in Dallas, Texas, Michael Chuong, MD, an assistant professor of radiation oncology at the school, compared two kinds of X-ray radiation with proton therapy, an innovative, precise approach that targets tumors while minimizing harm to surrounding tissues.
The researchers looked at nearly 600 patients and found that proton therapy resulted in a significantly lower number of side effects, including nausea, blood abnormalities and loss of appetite. The results were presented on May 22 at the annual conference of the Particle Therapy Cooperative Group, held in San Diego.
"This evidence underscores the precision of proton therapy, and how it can really make a difference in cancer patients' lives," said Dr. Chuong.
Patients with esophageal cancer can suffer a range of side effects, including nausea, fatigue, lack of appetite, blood abnormalities and lung and heart problems. Proton therapy did not make a difference in all of these side effects, but had significant effects on several.
The results have particular relevance for the University of Maryland School of Medicine; this fall the school will open the Maryland Proton Treatment Center (MPTC). The center will provide one of the newest and highly precise forms of radiation therapy available, pencil beam scanning (PBS), which targets tumors while significantly decreasing radiation doses to healthy tissue. This technique can precisely direct radiation to the most difficult-to-reach tumors.
Proton therapy is just one of several new methods for treating cancer. Others include:
Selective Internal Radiation Therapy, a precision modality for treating patients with particularly difficult-to-remove tumors involving the liver such as those from colorectal cancers;
Gammapod, a new, high-precision, noninvasive method of treating early-stage breast cancer;
Thermal Therapies, the use of "heat" in treating a broad spectrum of malignancies.
The treatment works well for many kinds of tumors, including those found in the brain, esophagus, lung, head and neck, prostate, liver, spinal cord and gastrointestinal system. It is also an important option for children with cancer and is expected to become an important option for some types of breast cancer. While most cancer patients are well served with today's state-of-the-art radiation therapy technology, up to 30 percent are expected to have a greater benefit from the new form of targeted proton beam therapy.
Located at the University of Maryland BioPark, the 110,000 square-foot, $200 million center is expected to treat about 2,000 patients a year.
INFORMATION:
About the University of Maryland School of Medicine
The University of Maryland School of Medicine was chartered in 1807 and is the first public medical school in the United States and continues today as an innovative leader in accelerating innovation and discovery in medicine. The School of Medicine is the founding school of the University of Maryland and is an integral part of the 11-campus University System of Maryland. Located on the University of Maryland's Baltimore campus, the School of Medicine works closely with the University of Maryland Medical Center and Medical System to provide a research-intensive, academic and clinically based education. With 43 academic departments, centers and institutes and a faculty of more than 3,000 physicians and research scientists plus more than $400 million in extramural funding, the School is regarded as one of the leading biomedical research institutions in the U.S. with top-tier faculty and programs in cancer, brain science, surgery and transplantation, trauma and emergency medicine, vaccine development and human genomics, among other centers of excellence. The School is not only concerned with the health of the citizens of Maryland and the nation, but also has a global presence, with research and treatment facilities in more than 35 countries around the world.
medschool.umaryland.edu/
May 22, 2015 - Boston, MA - Few professions in the world benefit from the sharing of information as much as meteorology. Nearly all countries around the world realize the value of sharing meteorological data across their borders. This information collaboration is vital to scientific understanding of the atmosphere and the oceans, as well as essential for accurate forecasts and timely warnings of hurricanes, typhoons, and other severe weather.
But what about when one country maintains an active embargo with another country?
That question was answered last year, when ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- It looks like a Slinky suspended in motion.
Yet this photonics advancement -- called a metamaterial hyperlens -- doesn't climb down stairs.
Instead, it improves our ability to see tiny objects.
Described in a research paper published today by the journal Nature Communications, the hyperlens may someday help detect some of the most lethal forms of cancer.
It could also lead to advancements in nanoelectronic manufacturing and boost scientists' ability to examine single molecules -- a development with implications in physics, chemistry, biology and other ...
WASHINGTON, D.C. -- Disaster investigators and emergency personnel may find themselves better able to assess and respond to terrorist attacks and industrial accidents with the aid of a new computational tool that determines the energy from explosions near the Earth's surface. As a first test of the new approach, its developers have analyzed a deadly explosion which reportedly killed dozens of regime soldiers in the Syrian civil war.
Computing the energy yield of an explosion just below, at, or above the ground poses difficult challenges, while deep-underground blasts ...
New York, NY -- May 22, 2015 -- Working with researchers at Zhejiang University in China, Changxi Zheng, assistant professor of computer science at Columbia Engineering, has developed a technique that enables hydrographic printing, a widely used industrial method for transferring color inks on a thin film to the surface of manufactured 3D objects, to color these surfaces with the most precise alignment ever attained. Using a new computational method they developed to simulate the printing process, Zheng and his team have designed a model that predicts color film distortion ...
(NEW YORK - May 22) - By comparing flu viruses to the virus that causes measles, researchers fine-tuned a tool that may enable faster vaccine design, according to a study led by Mount Sinai researchers and published online this week in the journal Cell Reports.
The study results revolve around viruses, which are designed perfectly by evolution to invade human cells, inject viral genes and use human genetic machinery to make copies of them. In an endless back and forth, human immune cells have evolved to recognize and attack viral surface proteins, and viruses to constantly ...
(PARIS, FRANCE) Technique, talk, and talent were three buzzwords at the 2015 EuroPCR congress. As in years past, the conference featured a mix of breaking news, live case demonstrations, oral and poster sessions, debates, and tips-and-tricks tutorials. New study data have been increasingly showcased at EuroPCR and this year's meeting featured over 70 new abstract sessions throughout the four-day meeting, across five interventional tracks.
One of the focus topics at this year's meeting was a spate of recent trials showing a benefit for mechanical thrombectomy in acute ...
URBANA, Ill. - The widespread evolution of herbicide-resistant weeds is costing farmers, especially through decreases in productivity and profitability. Although researchers and industry personnel have made recommendations to slow this evolution, an understanding of the patterns and causes of the resistance has been limited.
Diversifying the herbicide mechanisms of action (MOAs) has been recommended to stop the spread of herbicide-resistant weeds. MOAs refer to the biochemical interaction that affects or disrupts the target site in the weed. Two common methods of diversifying ...
The first definitive summary of the best and safest blood pressure lowering treatments for kidney disease and diabetes patients has been compiled by New Zealand doctor and researcher Associate Professor Suetonia Palmer.
The international relevance of her work for doctors, patients and those who decide which drugs to fund has been demonstrated by the prestigious Lancet medical journal publishing an article on her study in its latest edition.
The University of Otago, Christchurch, researcher together with a global team used innovative statistical analysis to compare hundreds ...
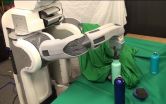
Berkeley -- Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have developed algorithms that enable robots to learn motor tasks through trial and error using a process that more closely approximates the way humans learn, marking a major milestone in the field of artificial intelligence.
They demonstrated their technique, a type of reinforcement learning, by having a robot complete various tasks -- putting a clothes hanger on a rack, assembling a toy plane, screwing a cap on a water bottle, and more -- without pre-programmed details about its surroundings.
"What ...
WASHINGTON, D.C., May 22, 2015 -- Play a flute in Carnegie Hall, and the tone will resonate and fill the space. Play that same flute in the Grand Canyon, and the sound waves will crash against the rock walls, folding back in on each other in sonic chaos. The disparity in acoustics is clear - to the modern listener, the instrument belongs in an auditorium.
"Distinct echoes would be totally unforgivable in today's performance spaces," says Steven J. Waller, an archaeo-acoustician who has studied prehistoric rock art and the acoustics of ancient performance spaces. "But, ...