Radiation costs vary among Medicare patients with cancer
2015-08-11
(Press-News.org) Cost of radiation therapy among Medicare patients varied most widely because of factors unrelated to a patient or that person's cancer, report University of California, San Diego School of Medicine researchers in the Journal of Oncology Practice.
Year of diagnosis, location of treatment, clinic type and individual radiation provider accounted for 44 to 61 percent of the variation in cost for patients with breast, lung and prostate cancer therapies, according to the study published August 11 online. Factors associated with the patient or patient's tumor accounted for less than 3 percent of the variation in the cost of radiation therapy.
"We found that variability in Medicare reimbursement for radiotherapy does not depend on individual characteristics of patients or their cancers," said James Murphy, MD, assistant professor at UC San Diego School of Medicine and radiation therapist at Moores Cancer Center at UC San Diego Health. "Rather, reimbursement was tied to the provider, geography and technology used to treat patients. This strongly suggests inefficiency within the current Medicare reimbursement framework for radiation therapy."
Up to two-thirds of patients with cancer receive radiation therapy. Researchers focused on breast, prostate and lung cancers because they represent the most common malignancies treated with radiotherapy.
The cost of radiation therapy was estimated from Medicare reimbursements for outpatient radiation treatment. The total cost of radiation therapy for the 55,288 patients in the study was estimated to be more than $831 million.
"Understanding why costs vary for radiation therapy helps policy makers evaluate the efficiency of the current fee-for-service Medicare reimbursement system. Such insights are likely to shape policy reforms in the near-future," said Anthony Paravati, MD, first author of the study.
The authors acknowledge that the study does not consider the relationship between cost of radiotherapy and quality of care, therefore higher cost radiation could lead to higher quality radiation. The link between cost and quality of care represents a future research question the authors hope to answer.
INFORMATION:
Co-authors of this study also include Isabel Boero, Daniel Triplett, Lindsay Hwang, Rayna Matsuno, and Loren Mell of UC San Diego; and Beibei Xu of UC San Diego and Peking University in Beijing.
Funding for this research came, in part, from the National Institutes of Health (TL1TR00098 and KL2 RR031978).
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-11
Birds of a feather may flock together, but that doesn't mean they share a genetic background. Though birds were first classified into groups primarily based on appearance, research forthcoming in The Auk: Ornithological Advances by Brett Benz of the American Museum of Natural History, Mark Robbins of the University of Kansas Biodiversity Institute, and Kevin Zimmer of the Los Angeles County Museum of Natural History demonstrates that this method isn't necessarily accurate: in a group of very similar-looking South American woodpecker species, genetic analysis has now shown ...
2015-08-11
The immune system not only responds to infections and other potentially problematic abnormalities in the body, it also contains a built-in brake in the form of regulatory T cells, or Tregs. Tregs ensure that inflammatory responses don't get out of hand and do damage. In autoimmune diseases, sometimes these Treg cells don't act as they should.
A new study led by Songtao Shi of the University of Pennsylvania has demonstrated how Tregs can themselves be regulated, by an unexpected source: hydrogen sulfide, a gas produced by the body's muscle cells and one often associated ...
2015-08-11
MADISON, Wis. -- Graphene, an atom-thick material with extraordinary properties, is a promising candidate for the next generation of dramatically faster, more energy-efficient electronics. However, scientists have struggled to fabricate the material into ultra-narrow strips, called nanoribbons, that could enable the use of graphene in high-performance semiconductor electronics.
Now, University of Wisconsin-Madison engineers have discovered a way to grow graphene nanoribbons with desirable semiconducting properties directly on a conventional germanium semiconductor wafer. ...
2015-08-11
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) -- In findings never before seen in melanoma, a novel combination therapy was found to be highly effective at treating patients with skin metastases, new research from UC Davis has shown.
Led by Emanual Maverakis of the UC Davis Department of Dermatology, the research found that Interleukin (IL)-2 combined with imiquimod and topical retinoid therapy in patients with so-called "in-transit metastases" is a promising therapeutic option.
The findings have been published online first in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology (doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.06.060).
"It's ...
2015-08-11
People infected with the hepatitis C virus are at risk for liver damage, but the results of a new Johns Hopkins study now show the infection may also spell heart trouble.
The findings, described online July 27 in The Journal of Infectious Diseases, emerged from a larger ongoing study of men who have sex with men, many but not all of whom were infected with HIV and followed over time to track risk of infection and disease progression. A subset of the participants had both HIV and hepatitis C, two infections that often occur together.
Even though people infected with ...
2015-08-11
New research from Monash University shows that children are being exposed to thousands of alcohol adverts when watching sport TV, questioning the effectiveness of advertising regulations designed to protect children.
The study, published in the international journal PLOS ONE, found that 87 per cent of all alcohol adverts during the daytime were in sport TV when hundreds of thousands of children were watching. A clause in Australia's advertising regulations allowing alcohol advertising in live sport programming during the day when children are watching appears to be responsible ...
2015-08-11
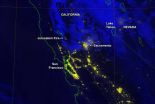
From its orbit around the Earth, the NASA-NOAA Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership satellite or Suomi NPP satellite, captured a night-time image of California's Jerusalem Fire.
InciWeb is an interagency all-risk incident information management system that coordinates with federal, state and local agencies to manage wildfires. According to Inciweb, this fire is burning on lands managed by the U.S. Bureau of Land Management within the Berryessa Snow Mountain National Monument. It is being managed by the Sonoma-Lake-Napa Unit of the California Department of Forestry ...
2015-08-11
MADISON, Wis. -- Human learning is a complex, sometimes mysterious process. Most of us have had experiences where we have struggled to learn something new, but also times when we've picked something up nearly effortlessly.
What if a fusion of computer science and psychology could help us understand more about how people learn, making it possible to design ideal lessons?
That long-range goal is moving toward reality thanks to an effort led by professors in the University of Wisconsin-Madison departments of computer sciences, psychology and educational psychology. Their ...
2015-08-11
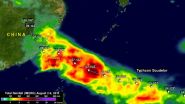
Typhoon Soudelor dropped over two feet of rainfall when it made landfall in China in early August, and soaked Taiwan. NASA estimated that rainfall using data from the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission.
Soudelor formed in the middle of the Pacific Ocean well east of Guam on July 20, 2015. Soudelor became more powerful with peak intensity of about 155 knots (178 mph) reached on August 3, 2015 when the super typhoon was well east of Taiwan over the open waters of the Pacific Ocean.
Soudelor's winds died down a little but rebounded to with over 100 knots (115 ...
2015-08-11
Swine housing has been a hot topic in recent years, not only in the United States, but in many countries, such as Denmark. Due to genetic advancements in recent years, the average litter size in Denmark is 16.6 total born piglets. With increased number of piglets, determining the optimal housing system for both the piglet and sow is critical.
In Denmark, gestation crates were banned in new buildings in 1999 and from all existing units in 2013. As of January 1, 2015, sows are required to be loose housed from time of weaning until seven days before expected parturition ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Radiation costs vary among Medicare patients with cancer