(Press-News.org) Fifteen years ago, an odd mutant fruit fly caught the attention and curiosity of Dr. Ravi Allada, a circadian rhythms expert at Northwestern University, leading the neuroscientist to recently discover how an animal's biological clock wakes it up in the morning and puts it to sleep at night.
The clock's mechanism, it turns out, is much like a light switch. In a study of brain circadian neurons that govern the daily sleep-wake cycle's timing, Allada and his research team found that high sodium channel activity in these neurons during the day turn the cells on and ultimately awaken an animal, and high potassium channel activity at night turn them off, allowing the animal to sleep. Investigating further, the researchers were surprised to discover the same sleep-wake switch in both flies and mice.
"This suggests the underlying mechanism controlling our sleep-wake cycle is ancient," said Allada, professor and chair of neurobiology in the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences. He is the senior author of the study. "This oscillation mechanism appears to be conserved across several hundred million years of evolution. And if it's in the mouse, it is likely in humans, too."
Better understanding of this mechanism could lead to new drug targets to address sleep-wake trouble related to jet lag, shift work and other clock-induced problems. Eventually, it might be possible to reset a person's internal clock to suit his or her situation.
The researchers call this a "bicycle" mechanism: two pedals that go up and down across a 24-hour day, conveying important time information to the neurons. That the researchers found the two pedals -- a sodium current and potassium currents -- active in both the simple fruit fly and the more complex mouse was unexpected.
The findings were published today in the Aug. 13 issue of the journal Cell.
"What is amazing is finding the same mechanism for sleep-wake cycle control in an insect and a mammal," said Matthieu Flourakis, the lead author of the study. "Mice are nocturnal, and flies are diurnal, or active during the day, but their sleep-wake cycles are controlled in the same way."
When he joined Allada's team, Flourakis had wondered if the activity of the fruit fly's circadian neurons changed with the time of day. With the help of Indira M. Raman, the Bill and Gayle Cook Professor in the department of neurobiology, he found very strong rhythms: The neurons fired a lot in the morning and very little in the evening.
The researchers next wanted to learn why. That's when they discovered that when sodium current is high, the neurons fire more, awakening the animal, and when potassium current is high, the neurons quiet down, causing the animal to slumber. The balance between sodium and potassium currents controls the animal's circadian rhythms.
Flourakis, Allada and their colleagues then wondered if such a process was present in an animal closer to humans. They studied a small region of the mouse brain that controls the animal's circadian rhythms -- the suprachiasmatic nucleus, made up of 20,000 neurons -- and found the same mechanism there.
"Our starting point for this research was mutant flies missing a sodium channel who walked in a halting manner and had poor circadian rhythms," Allada said. "It took a long time, but we were able to pull everything -- genomics, genetics, behavior studies and electrical measurements of neuron activity -- together in this paper, in a study of two species.
"Now, of course, we have more questions about what's regulating this sleep-wake pathway, so there is more work to be done," he said.
INFORMATION:
The paper is titled "A Conserved Bicycle Model for Circadian Clock Control of Membrane Excitability."
In addition to Allada and Flourakis, other authors of the paper are Elzbieta Kula-Eversole, Tae Hee Han and Indira M. Raman, of Northwestern; Alan L. Hutchison, Aaron R. Dinner and Kevin P. White, of the University of Chicago; Kimberly Aranda and Dejian Ren, of the University of Pennsylvania; Devon L. Moose and Bridget C. Lear, of the University of Iowa; and Casey O. Diekman, of the New Jersey Institute of Technology.
For any complex society to function properly, individuals--be they people or social insects--must reliably recognize their friends and family with whom they live and work and readily distinguish those allies from strangers. Ants and other social insects manage this feat of recognition based on chemical pheromones, which are detected via sensors in their antennae. Now researchers reporting August 13 in Cell Reports have discovered that when it comes to assessing body odors, ants really don't miss a thing.
"To our surprise, these very low volatility compounds are not only ...
A link between malaria and Burkitt's lymphoma was first described more than 50 years ago, but how a parasitic infection could turn immune cells cancerous has remained a mystery. Now, in the August 13 issue of Cell, researchers demonstrate in mice that B cell DNA becomes vulnerable to cancer-causing mutations during prolonged combat against the malaria-causing Plasmodium falciparum.
Individuals who are chronically infected with certain pathogens are at increased risk of developing lymphomas, cancers of the antibody-producing B lymphocytes. For example, Burkitt's lymphoma, ...
A study from the US National Institutes of Health presents some of the most precise human data yet on whether cutting carbs or fat has the most benefits for losing body fat. In a paper published August 13 in Cell Metabolism, the researchers show how, contrary to popular claims, restricting dietary fat can lead to greater body fat loss than carb restriction, even though a low-carb diet reduces insulin and increases fat burning.
Since 2003, Kevin Hall, PhD--a physicist turned metabolism researcher at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases--has ...
Irisin, a hormone linked to the positive benefits of exercise, was recently questioned to exist in humans. Two recent studies pointed to possible flaws in the methods used to identify irisin, with commercially available antibodies. In Cell Metabolism on August 13, the Harvard scientists who discovered irisin address this contentious issue by showing that human irisin circulates in the blood at nanogram levels and increases during exercise.
Senior study author Bruce Spiegelman of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard Medical School says that the confusion over irisin ...
The mechanisms that allow the liver to repair and regenerate itself have long been a matter of debate. Now researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have discovered a population of liver cells that are better at regenerating liver tissue than ordinary liver cells, or hepatocytes. The study, published August 13 in Cell, is the first to identify these so-called "hybrid hepatocytes," and show that they are able to regenerate liver tissue without giving rise to cancer. While most of the work described in the study was done in mouse models, the researchers ...
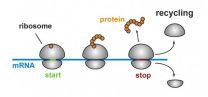
In what appears to be an unexpected challenge to a long-accepted fact of biology, Johns Hopkins researchers say they have found that ribosomes -- the molecular machines in all cells that build proteins -- can sometimes do so even within the so-called untranslated regions of the ribbons of genetic material known as messenger RNA (mRNA).
"This is an exciting find that generates a whole new set of questions for researchers," says Rachel Green, Ph.D., a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator and professor of molecular biology and genetics at the Johns Hopkins University ...
Researchers from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, and their collaborators have developed an experimental, nanoparticle-based vaccine against Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) that can induce potent neutralizing antibodies in vaccinated mice and nonhuman primates. Microscopic particles, known as nanoparticles, are being investigated as potential delivery vehicles for vaccines. The scientists' findings suggest that using a structure-based vaccine design and self-assembling nanoparticles to deliver a viral ...
In a recent study, restricting dietary fat led to body fat loss at a rate 68 percent higher than cutting the same number of carbohydrate calories when adults with obesity ate strictly controlled diets. Carb restriction lowered production of the fat-regulating hormone insulin and increased fat burning as expected, whereas fat restriction had no observed changes in insulin production or fat burning. The research was conducted at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), part of the National Institutes of Health. Results were published ...
Engineers from the University of Sheffield have developed a novel technique to predict when bearings inside wind turbines will fail which could make wind energy cheaper.
The method, published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society A and developed by Mechanical Engineering research student Wenqu Chen, uses ultrasonic waves to measure the load transmitted through a ball bearing in a wind turbine. The stress on wind turbine is recorded and then engineers can forecast its remaining service life.
When a bearing is subject to a load, its thickness is reduced by ...
Black-footed ferrets, a critically endangered species native to North America, have renewed hope for future survival thanks to successful efforts by a coalition of conservationists, including scientists at Lincoln Park Zoo, to reproduce genetically important offspring using frozen semen from a ferret who has been dead for approximately 20 years. The sire, "Scarface," as he is affectionately called by the team, was one of the last 18 black-footed ferrets to exist in the world in the 1980s. Eight kits, including offspring of Scarface, were born recently, significantly increasing ...