Surprise: Baby marmosets learning to 'talk' do listen to adults
2015-08-13
(Press-News.org) This news release is available in Japanese.
As nonhuman primates mature, their vocalizations are thought to be minimally or not at all influenced by caregivers - but a new study reveals that infant marmosets use cues from adults as they develop vocalizations. In a surprise twist then, humans may not be the only primates whose vocal development benefits from early communication. To monitor and measure the vocal development in marmosets, Daniel Takahashi et al. recorded vocalizations between the first day of birth and two months of age, using four well-established acoustic parameters. Recordings were taken during social isolation, as well as during auditory (but not visual) interactions with parents. Adults emit distinct, whistle-like "phees," but infants emit immature sounds such as cries, phee cries, and subharmonic phees. The team sought to determine whether physical maturation or learning from caregivers was the key mechanism behind the transition from immature phees to the sophisticated phees heard in adults. Using a model and validating it by measuring respiratory activity, the team determined that the transition is at least partly caused by more stable respiration as the marmosets physically mature. However, by analyzing the ratio of growth to changes in acoustics across the set of infants, they found that physiological growth does not completely explain the cries-to-phees transition. The team then investigated whether parental responses to infant vocalizations affect the timing of the cries-to-phees transition and found a strong correlation, suggesting that the development of marmoset vocalization is dependent on parental vocal feedback. A Perspective by Daniel Margoliash and Ofer Tchernichovski provides further insights into the role of learned vocalization, both in marmosets and across other species.
INFORMATION:
Article #14: "The developmental dynamics of marmoset monkey vocal production," by D.Y. Takahashi; A.R. Fenley; Y. Teramoto; D.Z. Narayanan; J.I. Borjon; P. Holmes; A.A. Ghazanfar at Princeton University in Princeton, NJ.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
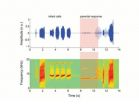
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-13
This news release is available in Japanese.
Amid climate change debates revolving around limited increases in recent global mean surface temperature (GMST) rates, Kevin Trenberth argues that natural climate fluxes - larger than commonly appreciated - can overwhelm background warming, making plateaued rates, or hiatuses, deceiving in significance. After many years of monitoring, it's clear that the GMST can vary from year to year, even decade to decade; these differences, Trenberth argues, are largely a result of internal natural variability. For example, the Pacific ...
2015-08-13
This news release is available in Japanese.
The recently commissioned Gemini Planet Imager has made its first exoplanet discovery: what may be the lowest-mass exoplanet ever directly imaged with a space telescope instrument. Based on available data, the researchers project the planet weighs twice as much as Jupiter - far less than exoplanets directly imaged before, which weighed at least five times Jupiter's mass. The findings from the next-generation Gemini imaging tool pave the way toward a better understanding of how our solar system was formed. In ...
2015-08-13
The Gemini Planet Imager has discovered and photographed its first planet, a methane-enshrouded gas giant much like Jupiter that may hold the key to understanding how large planets form in the swirling accretion disks around stars.
The GPI instrument, which is mounted on the 8-meter Gemini South telescope in Chile, is the size of a small car and was designed, built and optimized for imaging and analyzing the atmospheres of faint Jupiter-like planets next to bright stars, thanks to a device that masks the star's glare.
In December 2104, GPI began searching hundreds of ...
2015-08-13
A Jupiter-like planet within a young system that could serve as a decoder ring for understanding how planets formed around our Sun has been discovered by a team of astronomers from the University of Montreal's Institute of Research on Exoplanets (iREx) in collaboration with an international team of astronomers led by professor Bruce MacInstosh from Stanford University. One of the best ways to learn how our solar system evolved is in fact to look to younger star systems in the early stages of development.
The new planet, called 51 Eridani b, is the first exoplanet discovered ...
2015-08-13
While it may not shock you to learn that children born with disorders of sex development (DSD) face challenges, Concordia University researchers have confirmed that these go far beyond the physical.
In a paper published in the journal Hormone and Metabolic Research, psychology professor William M. Bukowski and his co-authors Elizabeth McCauley and Thomas Mazur examine the potential effects that these disorders can have on children's and adolescents' peer relationships.
The term "disorders of sex development" covers a range of conditions, from physical malformations ...
2015-08-13
Fifteen years ago, an odd mutant fruit fly caught the attention and curiosity of Dr. Ravi Allada, a circadian rhythms expert at Northwestern University, leading the neuroscientist to recently discover how an animal's biological clock wakes it up in the morning and puts it to sleep at night.
The clock's mechanism, it turns out, is much like a light switch. In a study of brain circadian neurons that govern the daily sleep-wake cycle's timing, Allada and his research team found that high sodium channel activity in these neurons during the day turn the cells on and ultimately ...
2015-08-13
For any complex society to function properly, individuals--be they people or social insects--must reliably recognize their friends and family with whom they live and work and readily distinguish those allies from strangers. Ants and other social insects manage this feat of recognition based on chemical pheromones, which are detected via sensors in their antennae. Now researchers reporting August 13 in Cell Reports have discovered that when it comes to assessing body odors, ants really don't miss a thing.
"To our surprise, these very low volatility compounds are not only ...
2015-08-13
A link between malaria and Burkitt's lymphoma was first described more than 50 years ago, but how a parasitic infection could turn immune cells cancerous has remained a mystery. Now, in the August 13 issue of Cell, researchers demonstrate in mice that B cell DNA becomes vulnerable to cancer-causing mutations during prolonged combat against the malaria-causing Plasmodium falciparum.
Individuals who are chronically infected with certain pathogens are at increased risk of developing lymphomas, cancers of the antibody-producing B lymphocytes. For example, Burkitt's lymphoma, ...
2015-08-13
A study from the US National Institutes of Health presents some of the most precise human data yet on whether cutting carbs or fat has the most benefits for losing body fat. In a paper published August 13 in Cell Metabolism, the researchers show how, contrary to popular claims, restricting dietary fat can lead to greater body fat loss than carb restriction, even though a low-carb diet reduces insulin and increases fat burning.
Since 2003, Kevin Hall, PhD--a physicist turned metabolism researcher at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases--has ...
2015-08-13
Irisin, a hormone linked to the positive benefits of exercise, was recently questioned to exist in humans. Two recent studies pointed to possible flaws in the methods used to identify irisin, with commercially available antibodies. In Cell Metabolism on August 13, the Harvard scientists who discovered irisin address this contentious issue by showing that human irisin circulates in the blood at nanogram levels and increases during exercise.
Senior study author Bruce Spiegelman of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard Medical School says that the confusion over irisin ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Surprise: Baby marmosets learning to 'talk' do listen to adults






