Oral contraceptives may impact aspects of arthritis in women
2015-08-18
(Press-News.org) New research indicates that use of oral contraceptives may provide benefits for women with inflammatory arthritis.
Among 273 women with early inflammatory arthritis, women who had used oral contraceptives in the past and those who were currently using them reported fewer problems related to how well they can function, their mood, and how active their disease is.
The findings are published in Arthritis Care & Research.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-18
It's known that brain changes are present in drug addicts even when they have been abstinent for a short period of time. Now new research shows that alterations persist in long-term abstinent heroin-depended individuals as well.
Through the use of functional magnetic resonance imaging, investigators analyzed the brains of 30 heroin-addicted individuals after a long period of abstinence (more than 3 years) and compared the results with those of 30 healthy controls.
The team found that in the former heroin users, there was significant dysfunctional activity in the nucleus ...
2015-08-18
The fourth tropical depression of the Atlantic Ocean hurricane season formed today, August 18, 2015 as NASA's Terra satellite passed overhead.
On Aug. 18 at 8:45 a.m. EDT the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of newborn Tropical Depression 4 in the central Atlantic Ocean. The image showed thunderstorms banding around the center of circulation in all quadrants except the northwest.
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) also uses measurements from the Advanced Scatterometer or ASCAT instrument ...
2015-08-18
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed over Typhoon Goni and gathered infrared data that helped identify the strongest part of the storm as the south and eastern quadrants.
The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi satellite captured an infrared image of Goni on August 18 at 4:18 UTC (12:18 a.m. EDT) that showed the strongest thunderstorms with the coldest cloud top temperatures (near -63F/-53C) were in the eastern and southern quadrants.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted that animated enhanced infrared satellite ...
2015-08-18
Irvine, Calif., Aug. 18, 2015 - Researchers from the University of California, Irvine and NASA have uncovered a remarkably strong link between high wildfire risk in the Amazon basin and the devastating hurricanes that ravage North Atlantic shorelines. The climate scientists' findings appear in the journal Geophysical Research Letters near the 10th anniversary of Hurricane Katrina's calamitous August 2005 landfall at New Orleans.
"Hurricane Katrina is indeed part of this story," said James Randerson, Chancellor's Professor of Earth system science at UCI and senior author ...
2015-08-18
CHICAGO--From a food science and technology perspective, sugar (sucrose) plays several roles when it comes to the functional properties in food. In the September issue of Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety published by the Institute of Food Technologists (IFT), authors from the University of Minnesota write about the functional properties of sugar and why they are often added to foods.
1. Taste: Sweetness improves the palatability of many foods. Adding sugar to foods with high nutrient quality may increase the chance they are consumed. In addition, ...
2015-08-18
Strawberries are one of the most economically important fruits worldwide but are easily susceptible to bruising and are highly perishable. A new study in the August issue of the Journal of Food Science, published by the Institute of Food Technologists (IFT) found that edible active coatings (EACs) based on pectin, pullulan and chitosan may improve quality and shelf life of strawberries. Edible coatings protect perishable food products from deterioration and act as a protective cover (Atress, 2010). Pectin is present in the cell walls of many fruits and vegetables; chitosan ...
2015-08-18
One of the striking features of self-organization in biomolecular systems is the capacity of assemblies of filamentous particles for synchronous motion. Physicists of Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich now provide new insights into how such movements are coordinated.
Living matter, which consists largely of diverse polymeric structures assembled from various types of subunits, often exhibits striking behaviors, such as a capacity for self-organization and active motion. On an organismic scale, this type of collective motion is exemplified by the synchronous ...
2015-08-18
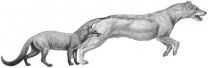
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Old dogs can teach humans new things about evolution. In Nature Communications a new study of North American dog fossils as old as 40 million years suggests that the evolutionary path of whole groups of predators can be a direct consequence of climate change.
"It's reinforcing the idea that predators may be as directly sensitive to climate and habitat as herbivores," said Christine Janis, professor of ecology and evolutionary biology at Brown University, who worked with lead author Borja Figueirido, a former Brown Fulbright postdoctoral ...
2015-08-18
Most of the debate around e-cigarettes has focused on the developed world, but the devices are becoming more widely available in some low- and middle-income countries, where there is even greater potential for impact on public health, say two Stanford University School of Medicine researchers.
"People don't think e-cigarettes will reach the developing world. But they are already being produced in developing countries, and they are cheap. People know they are available," said Andrew Chang, MD, a resident in internal medicine who focuses on global health.
Chang and Michele ...
2015-08-18
Among high school students in Los Angeles, those who had ever used electronic cigarettes were more likely to report initiation of smokable ("combustible") tobacco (such as cigarettes, cigars, and hookah) use over the next year compared with nonusers, according to a study in the August 18 issue of JAMA.
Combustible tobacco, which has well-known health consequences, has long been the most common nicotine-delivering product used. Electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes), which are devices that deliver inhaled aerosol usually containing nicotine, are becoming increasingly popular, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Oral contraceptives may impact aspects of arthritis in women