(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. - After hours harvesting forage, managing livestock and milking cows, new Cornell University agricultural economic research shows family members who work on the family dairy farm make $22,000 less annually than comparable hired managers, but are handsomely compensated with "socioemotional" wealth.
"While $22,000 seems like a large penalty, there are nonfinancial rewards they experience working for the family business," said Loren Tauer, professor at Cornell's Charles H. Dyson School of Applied Economics and Management, who with lead author Jonathan Dressler of MetLife's Food and Agribusiness Finance, published "Socioemotional Wealth in the Family Farm," in a forthcoming Agricultural Finance Review.
There are roughly 5,400 dairy farms in New York, large and small. "Family members like to work for the family farm, as it brings prestige and satisfaction by working with siblings, cousins and parents," explains Tauer. "The socioemotional part is that these family members feel an attachment to the dairy farm. It's a warm and fuzzy feeling."
Further, Dressler explained that socioemotional aspects of running a dairy farm "create a sense of pride and belonging, as collectively each family member is contributing an effort toward a common family goal."
Dressler and Tauer examined dairy farm income in 1999 through 2008 and showed that New York farm manager median salaries varied widely from $41,884 in 1999, to $64,466 in 2004 to $74,986 in 2005, all adjusted for inflation to 2008 dollars. While the family farm managers were paid on average about $22,000 less, family members were compensated in other ways, such as with equity in the family business, which includes land values and the value of the operation - all of which have risen over time.
For family farms, Dressler and Tauer estimated a 5 percent current return to equity and asset appreciation of 10 percent, for a total return to equity of 15 percent. With "sweat equity," Tauer explains, children eventually inherit farms or are given an opportunity to purchase farms at a low estimate of the farms' value. That future ownership opportunity and the chance to work with family members offset reduced annual compensation.
INFORMATION:
Cornell University has television, ISDN and dedicated Skype/Google+ Hangout studios available for media interviews.
Compounds found in purple potatoes may help kill colon cancer stem cells and limit the spread of the cancer, according to a team of researchers.
Baked purple-fleshed potatoes suppressed the growth of colon cancer tumors in petri dishes and in mice by targeting the cancer's stem cells. Colon cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the U.S. and responsible for more than 50,000 deaths annually, according to the American Cancer Society.
Attacking stem cells is an effective way to counter cancer, according to Jairam K.P. Vanamala, associate professor ...
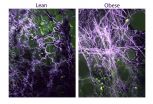
ITHACA, N.Y. - Women who are obese have a higher risk and a worse prognosis for breast cancer, but the reasons why remain unclear. A Cornell study published this month in Science Translational Medicine explains how obesity changes the consistency of breast tissue in ways that are similar to tumors, thereby promoting disease.
The study of mice and women shows obesity leads to a stiffening of a meshwork of material that surrounds fat cells in the breast, called the extracellular matrix, and these biomechanical changes create the right conditions for tumor growth.
The findings ...
A new study conducted by the Media Insight Project, a collaboration between the American Press Institute and The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research, found that while the similarities to the rest of their generation are numerous, there are some distinct differences in the way that Hispanic and African American Millennials use technology to access news and information. The source of their information is one area of difference: these young adults are more likely to use YouTube and Instagram for news than Millennials in general, though all groups rely ...
Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) scientists have discovered how the most common genetic defect in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis kills nerve cells. Their study suggests that the pores that allow molecules into and out of a cell's nucleus get jammed, a finding that could speed the search for other genes that promote this fatal illness.
In people who have amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), the motor neurons that operate the muscles deteriorate. Over time, the disease deprives patients of the ability to walk, swallow, and breathe, and they usually die within three ...
A study led by researchers from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and the University of California, Los Angeles has demonstrated a new, efficient way to accelerate positrons, the antimatter opposites of electrons. The method may help boost the energy and shrink the size of future linear particle colliders - powerful accelerators that could be used to unravel the properties of nature's fundamental building blocks.
The scientists had previously shown that boosting the energy of charged particles by having them "surf" a wave of ionized ...
They're among the most powerful tools for shedding new light on cancer growth and evolution, but mathematical models of the disease for years have faced an either/or stand off.
Though models have been developed that capture the spatial aspects of tumors, those models typically don't study genetic changes. Non-spatial models, meanwhile, more accurately portray tumors' evolution, but not their three-dimensional structure.
A collaboration between Harvard, Edinburgh, and Johns Hopkins Universities including Martin Nowak, Director of the Program for Evolutionary Dynamics ...
New insight into methanotrophs, bacteria that can oxidise methane, may help us develop an array of biotechnological applications that exploit methane and protect our environment from this potent greenhouse gas.
Publishing in Nature, scientists led by Newcastle University have provided new understanding of how methanotrophs are able to use large quantities of copper for methane oxidation.
They have identified a new family of copper storage proteins called Csp that are present in a range of bacteria. These proteins store metal in a way that has not been seen previously ...
It's not a huge mystery why Los Angeles experiences earthquakes. The city sits near a boundary between two tectonic plates -- they shift, we shake. But what about places that aren't along tectonic plate boundaries?
For example, seismicity on the North American plate occurs as far afield as southern Missouri, where earthquakes between 1811 and 1812 estimated at around magnitude 7 caused the Mississippi River to flow backward for hours.
Until now, the cause of that seismicity has remained unclear.
While earthquakes along tectonic plate boundaries are caused by motion ...
The Pacific Northwest is abundantly dotted with wildfires in Washington, Oregon, Idaho and Montana. There are over 27 fires listed in the Inciweb database for the state of Washington. The largest active fire listed is the Okanogan Complex Fire which is currently at 256,567 acres and has 1,250 personnel working the fire. This fire began as a lightning strike on August 15, 2015. It is only 10% contained at present. Governor Inslee's request for a federal Emergency Declaration to provide additional resources to cover some of the costs related to multiple wildfires burning ...
Mostly untouched for 100 years, 15 Roman-era Egyptian mummy portraits and panel paintings were literally dusted off by scientists and art conservators from Northwestern University and the Phoebe A. Hearst Museum of Anthropology as they set out to investigate the materials the painters used nearly 2,000 years ago.
What the researchers discovered surprised them, because it was hidden from the naked eye: the ancient artists used the pigment Egyptian blue as material for underdrawings and for modulating color -- a finding never before documented. Because blue has to be manufactured, ...