New fossil skulls reveal insights about penguin brain evolution
2015-08-27
(Press-News.org) When they're not being the stars of various animated movies, penguins are playing an important role in evolutionary studies. Penguins are unique among modern birds in that they 'fly' through the water. Although flightless in air, penguins have a number of adaptations which allow them glide effortlessly through the water. And some of these adaptations are in an unlikely part of their anatomy - their brains. Recent finds of fossil penguins from 35 million year old sediments in Antarctica have begun to shed light on the changes in penguin brains that accompanied their transition to water.
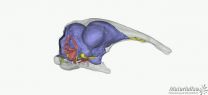
"Comparing multiple species (extinct and living penguins and living birds that both fly and dive), in the way our study does, brings us closer to the answers of two major questions about penguin brain evolution: (1) what major morphological changes have occurred, (2) when did these changes occur?" said lead author Claudia Tambussi. The new finds, which are described in the latest issue of the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, include skulls which are so well-preserved that they could be CT-scanned to analyze their internal structure.
These scans revealed some interesting traits of these early penguins that speak to their transitional nature. Many of these findings have to do with the sensory abilities of these fossil species. For instance, one area, the Wulst, which is associated with complex visual functions, is enlarged. "The Antarctic fossils reveal that the neuroanatomy of penguins was still evolving roughly 30 million years after the loss of aerial flight, with trends such as the expansion of the Wulst and reduction of the olfactory bulbs still in progress", said co-author Daniel Ksepka.
In addition to the increase in visual complexity, and reduction in olfaction, findings in the ear region shed light on the head position and equilibrium-maintaining abilities of the fossil penguins. All together, the findings show that these early penguins had many of the adaptations of living forms, while having a few unique traits not seen in the modern ones. Not only that, but some of these adaptations are found in modern flying birds, attesting to penguins' unique mode of swimming.
Said Ksepka, "Penguins are considered flightless, but when it comes to wing-propelled diving they are essentially practicing underwater flight. The brain morphology reflects this as penguins retain an overall "flight-ready" brain."
INFORMATION:
About the Society of Vertebrate Paleontology
Founded in 1940 by thirty-four paleontologists, the Society now has more than 2,300 members representing professionals, students, artists, preparators, and others interested in VP. It is organized exclusively for educational and scientific purposes, with the object of advancing the science of vertebrate paleontology.
Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology
The Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology (JVP) is the leading journal of professional vertebrate paleontology and the flagship publication of the Society. It was founded in 1980 by Dr. Jiri Zidek and publishes contributions on all aspects of vertebrate paleontology.
Tambussi, C.P., F.J. Degrange, and D.T. Ksepka. 2015. Endocranial Anatomy Of Antarctic Eocene Stem Penguins: Implications For Sensory System Evolution In Sphenisciformes (Aves). Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. DOI:10.1080/02724634.2015.981635 ; http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/02724634.2015.981635#.Vd77SPlViko
AUTHOR CONTACT INFORMATION:
Claudia P. Tambussi
Centro de Investigaciones em Ciencias de la Tierra (Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas-Universidad Nacional de Córdoba)
Avenida Vélez Sársfield 1611, X5016GCA
Córdoba, Argentina
tambussi.claudia@conicet.gov.ar
Federico J. Degrange
Centro de Investigaciones Paleobiológicas
Facultad de Ciencias Exactas Físicas y Naturales, Universidad Nacional de Córdoba
Avenida Vélez Sársfield 299, X5000GCA
Córdoba, Argentina
fjdino@gmail.com
Daniel Ksepka
North Carolina State University
Raleigh, NC, USA
ksepka@gmail.com
OTHER EXPERTS NOT ASSOCIATED WITH STUDY:
Stig Walsh
Senior Curator of Vertebrate Palaeobiology
National Museums Scotland s.walsh@nms.ac.uk
Julia Clarke
Associate Professor
Department of Geological Sciences, Jackson School of Geosciences julia_clarke@jsg.utexas.edu
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-27
More than a cause of a simple infection, viruses are often involved in the development of serious diseases. Such is the case with liver cancer, which often develops in an organ that has been weakened by hepatitis B or C virus. Researchers at Inserm, the Paris Public Hospitals (AP-HP), Paris Descartes University, Paris 13 University (USPC), and Paris Diderot University have just identified the role of a new virus, hitherto unsuspected, in the occurrence of a rare type of liver cancer.
This study, based on follow-up and observation of 193 patients, is published in the 24 ...
2015-08-27
Consumers aren't embracing electric cars and trucks, partly due to the dearth of charging stations required to keep them moving. Even the conservation-minded are hesitant to go electric in some states because, studies show, if fossil fuels generate the electricity, the car is no greener than one powered with an efficient gasoline.
Charging cars by solar cell would appear to be the answer. But most cells fail to meet the power requirements needed to directly charge lithium-ion batteries used in today's all-electric and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles.
Researchers at ...
2015-08-27
New research published in Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica, a journal of the Nordic Federation of Societies of Obstetrics and Gynecology, found that pregnant women in Sweden had inadequate levels of iodine in their diets. Proper iodine nutrition is necessary for neurological development of the fetus.
Iodine is an element that is involved in the production of thyroid hormones. Pregnant and breastfeeding women need about 50% more iodine in the diets, and WHO recommends a total daily iodine intake of 250 μg/d for pregnant and lactating women. Medical evidence ...
2015-08-27
Probiotics show no benefit for preventing or eliminating gastrointestinal colonization with drug-resistant organisms in patients in the intensive care unit compared to standard care, according to new research published online today in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
"Our research suggests that probiotics do not help prevent gastrointestinal colonization with multidrug-resistant organisms in critically ill patients," said Jennie H. Kwon, DO, lead author of the study.
This prospective, randomized ...
2015-08-27
August 27, 2015 - Do you have problems with dry eyes? If so, you're not alone--it's one of the most common reasons for patient visits to eye care professionals. Recent years have seen significant progress in management of patients with dry eyes, according to the September special issue of Optometry and Vision Science, official journal of the American Academy of Optometry. The journal is published by Wolters Kluwer.
"There has been a growing interest among clinicians and patients on treatment and management and origins of the signs and symptoms of dry eye," comments Anthony ...
2015-08-27
This news release is available in French.
Not even close to every person who faces challenges or lives with severe depression commits suicide. Some people are more vulnerable than others.
A series of studies has shown that the way in which a person makes decisions is among the main factors that determines whether that person is protected from or vulnerable to suicide. High-risk decision-making was prevalent among many parents of individuals who committed suicide, which may serve to explain its apparent "inheritability".
Dr. Fabrice Jollant, Assistant Professor ...
2015-08-27
While most primary care physicians responding to a survey taken in late 2014 and early 2015 expressed confidence in their ability to identify potential cases of Ebola and communicate Ebola risks to their patients, only 50 to 70 percent of them gave answers that fit with CDC guidelines when asked how they would care for hypothetical patients who might have been exposed to Ebola. In addition, those who were least likely to encounter an Ebola patient - based on their location and characteristics of their patients - were most likely to choose overly intense management of patients ...
2015-08-27
Knut, the famous polar bear of the Berlin Zoological Garden (Germany) died of encephalitis, as diagnosed soon after his death. However, the cause of his disease has remained elusive until now. A team of scientists from the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE), the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (IZW) and the Charite - Universitaetsmedizin Berlin has now solved the case: The polar bear suffered from an autoimmune disease of the brain. This non-infectious illness is called "anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis", with symptoms in human patients similar ...
2015-08-27
A team of international scientists, led by astronomers from Cardiff University's School of Physics and Astronomy, has shown for the first time that galaxies can change their structure over the course of their lifetime.
By observing the sky as it is today, and peering back in time using the Hubble and Herschel telescopes, the team have shown that a large proportion of galaxies have undergone a major 'metamorphosis' since they were initially formed after the Big Bang.
By providing the first direct evidence of the extent of this transformation, the team hope to shed light ...
2015-08-27
Subject, verb, object: a triad that in spoken discourse (as well as written) can be arranged in different positions (six, in principle) although in the overwhelming majority of world languages, 86%, they occur in two forms: SVO ("Johnny eats the banana") and SOV ("Johnny the banana eats"). In particular, the latter is the most common and scientific literature supports the hypothesis that it is a basic form, perhaps the first to emerge when a new language or communication system is born. To back this up is the fact that over the course of history many languages have passed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New fossil skulls reveal insights about penguin brain evolution