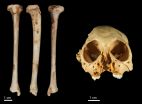
(Press-News.org) An international team of scientists have dated a species of fossil monkey found across the Caribbean to just over 1 million years old.
The discovery was made after the researchers recovered a fossil tibia (shin bone) belonging to the species of extinct monkey Antillothrix bernensis from an underwater cave in Altagracia Province, Dominican Republic. The fossil was embedded in a limestone rock that was dated using the Uranium-series technique.
In a paper published this week in the well renowned international journal, the Journal of Human Evolution, the team use three-dimensional geometric morphometrics to confirm that the fossil tibia does indeed belong to Antillothrix bernensis, a primate that we now know existed on Hispaniola relatively unchanged for over a million years. This monkey, roughly the size of a small cat, was tree-dwelling and lived largely on a diet of fruit and leaves.
Dr Helen Green of Melbourne University's School of Earth Sciences, a lead researcher involved in the dating of the limestone surrounding the fossils, said the question of the age of primate fossils from this region has puzzled scientists since the days of Darwin and Wallace.
'The presence of endemic new world monkeys on the Caribbean islands is one the great questions of bio-geography and our work on these fossils shows Antillothrix existed on Hispaniola relatively morphologically unchanged for over a million years. By establishing the age of these fossils we have changed the understanding of primate evolution in this region.' said Dr Green.
At Brooklyn College, part of the City University New York, and Northeastern Illinois University researchers, Prof. Alfred Rosenberger and Dr Siobhán Cooke have been working in the Dominican Republic since 2009, searching for rare fossil remains of endemic mammals to investigate how these animals were adapted to their unique, island environments. 'Very little was known about the native monkey from this island' said Dr Cooke, 'Prior to our discoveries in Altagracia we knew almost nothing even though this species was first described by Renato Rímoli back in 1977'.
To better understand how this primate was uniquely adapted to its environment, Dr. Melissa Tallman and her student Andrea Morrow, from the Grand Valley State University, used a specialized technique to model the three-dimensional shape of the monkey's leg bone. This helped them to reconstruct how the small primate might have moved about in its environment and allowed the comparison of relatively young examples of Antillothrix bones to the newly discovered million year old specimens.
At the University of Melbourne, Dr Helen Green and Dr Robyn Pickering worked in the state of the art Isotope Chronology Laboratory in the School of Earth Sciences, where they measured the levels of uranium, thorium and lead present in the limestone rocks today using the results to calculate an age of 1.3+-0.11 million years.
INFORMATION:
The million year old monkey: new evidence confirms the antiquity of fossil primate from the Dominica
This discovery was made possible by the collaboration between the Dominican Speleological Society, the Museo del Hombre Dominicano in Santo Domingo, and Brooklyn College, CUNY. Cave divers, Cristian Pittaro, Phillip Lehman, Dave Pratt, and Victoria Alexandrova were responsible for this incredible find within Padre Nuestro Cave. Today these caves are underwater, making them a challenging environment to search for fossils in, meaning that team work is essential.
Tropical Storm Kevin's center was several hundred miles south-southwest of Baja California when NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead and saw some associated high clouds streaming over the peninsula.
The MODIS and the AIRS instruments aboard Aqua captured visible and infrared images of Kevin on September 3 at 20:50 UTC (4:50 p.m. EDT). The visible image from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument provided look at Kevin's clouds. MODIS showed a somewhat elongated tropical storm with a fragmented band of thunderstorms wrapping into the low-level ...
Scientists studying how a heat-loving microbe transfers its DNA from one generation to the next say it could further our understanding of an extraordinary superbug.
Sulfolobus is part of the Archaea kingdom - a single-cell organism similar to bacteria - which was isolated in hot springs on the island of Hokkaido, Japan.
Some Archaea live ordinary lives in mundane environments such as lakes, seas and insect and mammal intestinal tracts, while others live extraordinary lives pushed to extremes in incredibly harsh habitats such as deep sea hydrothermal vents, volcanic ...
"Objects of granular media, such as a sandcastle, consist of millions or billions of grains. The computation time needed to produce photorealistic images amounts to hundreds to thousands of processor hours," Professor Carsten Dachsbacher of the Institute for Visualization and Data Analysis of KIT explains. Materials, such as sand, salt or sugar, consist of randomly oriented grains that are visible at a closer look only. Image synthesis, the so-called rendering, is very difficult, as the paths of millions of light rays through the grains have to be simulated. "In addition, ...
Nowadays, internet auctions play an important role in online trading. No matter whether you want to buy a hedge trimmer or an antique pocket watch - unlike purchases by a click at a fixed price, online auctions provide the atmosphere of a competition for the auction object. Whoever perceives the competition of real contenders, e.g. by avatars or photos on the screen, wishes to stay in the race - and increases his bid. This is a result of a KIT study with more than 450 test persons.
Online auctions combine shopping with entertainment, fun, and excitement. This is the ...
Action to prevent tooth decay in children, such as supervised tooth brushing and fluoride varnish schemes, are not just beneficial to children's oral health but could also result in cost savings to the NHS of hundreds of pounds per child, so says a leading dental health researcher.
Professor Elizabeth Kay, Foundation Dean of the Peninsula Dental School from Plymouth University Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, has carried out the first economic evaluation of public health measures to reduce tooth decay in children at high risk, in association with the National ...
When a jogger sets out on his evening run, the active movements of his arms and legs are accompanied by involuntary changes in the position of the head relative to the rest of the body. Yet the jogger does not experience feelings of dizziness like those induced in the passive riders of a rollercoaster, who have no control over the abrupt dips and swoops to which they are exposed. The reason for the difference lies in the vestibular organ (VO) located in the inner ear, which controls balance and posture. The VO senses ongoing self-motion and ensures that, while running, ...
Patients with cancer of the esophagus--also known as the gullet--are often given chemo- or radiotherapy, with the aim of shrinking the tumor before it is surgically removed. Increasingly positron emission tomography (PET) is being used to monitor the size of the tumor during the treatment. To date, however, no benefit for patients has ensued, as Milly Schröer-Günther and co-authors show in an original article in the current issue of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2015; 112: 545-52).
PET is an imaging technique that makes a tumor in ...
Despite continued medical advances, infectious diseases kill over 10 million people worldwide each year. The ecological complexity of many emerging disease threats--interactions among multiple hosts, multiple vectors and even multiple parasites--often complicates efforts aimed at controlling disease. Now, a new paper co-authored by a University of Colorado Boulder professor is advancing a multidisciplinary framework that could provide a better mechanistic understanding of emerging outbreaks.
In a study published today in the journal Science, researchers demonstrate how ...
In the game of wheat genetics, Jorge Dubcovsky's laboratory at UC Davis has hit a grand slam, unveiling for the fourth time in a dozen years a gene that governs wheat vernalization, the biological process requiring cold temperatures to trigger flower formation.
Identification of the newly characterized VRN-D4 gene and its three counterpart genes is crucial for understanding the vernalization process and developing improved varieties of wheat, which provides about one-fifth of the calories and proteins that we humans consume globally.
The new study, reported online in ...
Girls with autism display less repetitive and restricted behavior than boys do, according to a study by researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine.
The study also found that brain differences between boys and girls with autism help explain this discrepancy.
The study, which will be published online Sept. 3 in Molecular Autism, gives the best evidence to date that boys and girls exhibit the developmental disorder differently.
"We wanted to know which specific clinical manifestations of autism show significant gender differences, and whether patterns ...