(Press-News.org) This news release is available in German.
The research team of Annette Rompel from the Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, University of Vienna explore the mechanisms behind the "browning reaction" during the spoilage of mushrooms. The researchers were able to demonstrate that the enzyme responsible is already formed prior to fungal spoiling. The detailed study is published online in the well renowned journals, Phytochemistry and Acta Crystallographica.
Understanding the mechanism of enzyme tyrosinase pigmentation is currently of both medical as well as technological interest. The copper-containing enzyme is present in animals and humans and is essential for the protective pathway against UV radiation, it also simultaneously provides the elucidation and potential means with which to prevent the spoilage of food. Mushrooms were selected for the study due to their low cost and ready availability. In addition they are also a valuable target for researchers, largely because of their high enzyme content, fungi are ideal sources for potential studies of tyrosinase. The mushrooms therefore serve as a model organism for the study of the pathway involved in food spoilage.
Elucidation of an inactive precursor
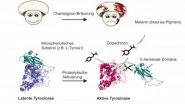
Since 2012, it has become established that six different tyrosinases (PPO1 to 6) exist within the mushroom, two of which (PPO3 and PPO4) occur in larger quantities. The enzyme responsible for the mechanism of food spoilage is formed within eukaryotes (organisms that have a nucleus) as an inactive precursor during the developmental phase of an organism. This precursor is then activated via specific chemical cleavage. At this cleavage site, the protein segment covering part of the enzyme active site is removed and the substrates (tyrosine and other monophenols) can be accessed and take part in key chemical reactions.
New Method of Isolation and unique reagent leads to success
None of the previously established methods of isolation present in the literature could be successfully applied for PPO4. For the first time, at the Institute for Biophysical Chemistry of the University of Vienna, a method was developed that allows for the one stage isolation of latent tyrosinase from their natural source. The enzyme characterization was undertaken at the Department of Chemistry with close cooperation with the Institute of Mass Spectrometry lead by Andreas Rizzi, both within the University of Vienna. After sufficiently large quantities were extracted from pure PPO4, the researchers were able to identify and optimize appropriate crystallization conditions which produced well formed protein crystals. This was only possible with the use of a relatively unusual co-crystallization reagent, a polyoxometalate of the Anderson type.
Integral for medicine and biotechnology
The PhD student Stephan Mauracher worked at the University of Vienna, taking an essential part in this project as part of the University Initiative termed "Functional Molecules". Following this research it has been made possible to purify the enzyme in sufficient quantities for characterization. Ulrich Kortz, working at the Jacobs University of Bremen was responsible for synthesizing the polyoxometalate used and was a key proponent of its usage as an additive for protein crystallization.
The research project was then continued as FWF Initiative. "This research has allowed for the crystallization and three-dimensional structure of PPO4 to be resolved", says Anette Rompel.
INFORMATION:
Publication in Phytochemistry:
S. G. Mauracher, C. Molitor, C. Michael, M. Kragl, A. Rizzi and A. Rompel: High level proteinpurification allows the unambiguous polypeptide determination of latent isoform PPO4 of mushroom tyrosinase. Phytochemistry 99 (2014) 14-25.
Publication in Acta Crystallographica Section F – Structural Biology and Crystallization Communication:
S. G. Mauracher, C. Molitor, R. Al-Oweini, U. Kortz and A. Rompel: Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of latent isoform PPO4 mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) tyrosinase. Acta Cryst. F70 (2014) 263-266.
Publication in Acta Crystallographica Section D – Biological Crystallography:
S. G. Mauracher, C. Molitor, R. Al-Oweini, U. Kortz and A Rompel: Latent and active abPPO4 mushroom tyrosinase cocrystallized with hexatungstotellurate(VI) in a single crystal. Acta Cryst. Sect. D70 (August 29, 2014) 2301-2315.
Scientific contact
Univ.-Prof. Dr. Annette Rompel
Institute of Biophysical Chemistry
Chemistry Faculty
University of Vienna
T +43-1-4277-525 02
annette.rompel@univie.ac.at
http://www.bpc.univie.ac.at
Press contact
Mag. Alexandra Frey
Press Office of the University of Vienna
Research and teaching
T +43-1-4277-175 33
M +43-664-602 77-175 33
alexandra.frey@univie.ac.at
The University of Vienna, founded in 1365, is one of the oldest and largest universities in Europe. About 9,500 employees, 6,700 of who are academic employees, work at 15 faculties and four centres. This makes the University of Vienna Austria's largest research and education institution. About 92,000 national and international students are currently enrolled at the University of Vienna. With more than 180 degree programmes, the University offers the most diverse range of studies in Austria. The University of Vienna is also a major provider of continuing education. In 2015, the Alma Mater Rudolphina Vindobonensis celebrates its 650th Anniversary. http://www.univie.ac.at
Why do mushrooms turn brown?
Chemists explore the mechanisms behind food spoilage
2014-09-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Growth factors found in breast milk may protect against necrotizing enterocolitis
2014-09-09
Philadelphia, PA, September 9, 2014 – Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a devastating gastrointestinal illness affecting up to 10% of premature infants, with a 30% mortality rate, and formula feeding has been identified as a risk factor for NEC. A study published in The American Journal of Pathology found that growth factors present in human breast milk, but not in formula, may explain the protection against intestinal damage. Further, supplementing the diet of newborn NEC-affected rodents with these growth factors promotes epithelial cell survival.
"NEC is a highly ...
A weekly text message could encourage healthier food choices, new study shows
2014-09-09
Many people are unaware that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration's mandated nutrition labels are based on a 2,000-calorie-a-day diet, but a simple weekly text message reminder can greatly improve that awareness, according to a new study from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
While not an outright recommendation, the 2,000-calorie benchmark is what the FDA considers a reasonable daily calorie intake for many adults. More importantly, nutrition labels on food products sold in the U.S. are based on it.
The key to translating nutrition labels and ...
The saplings go their own way
2014-09-09
This news release is available in German. Leipzig. In tropical rainforests, most young trees grow spatially independent from their parent trees. This means that it is not possible to predict where seedlings will take root, and less specialised species therefore have an advantage even in the species-rich rainforests of the tropics. This is the finding of a study, conducted by researchers at the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ), the University of California and the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute, the results of which were published recently in ...
Study sheds light on asthma and respiratory viruses
2014-09-09
People with asthma often have a hard time dealing with respiratory viruses such as the flu or the common cold, and researchers have struggled to explain why.
In a new study that compared people with and without asthma, the answer is becoming clearer. The researchers found no difference in the key immune response to viruses in the lungs and breathing passages. The work, at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, suggests that a fundamental antiviral defense mechanism is intact in asthma. This means that another aspect of the immune system must explain the ...
Weakness in malaria parasite fats could see new treatments
2014-09-09
A new study has revealed a weak spot in the complex life cycle of malaria, which could be exploited to prevent the spread of the deadly disease.
It found female malaria parasites put on fat differently to male ones.
"The study opens potential new ways to combat malaria," said Associate Professor Alexander Maier, from The Australian National University Research School of Biology.
"Malaria parasites show resistance to all current anti-malarial drugs. We are losing our weapons against this very important disease. But by studying lipid molecules – fats – rather than ...
Eating is addictive but sugar and fat are not like drugs, study says
2014-09-09
People can become addicted to eating for its own sake but not to consuming specific foods such as those high in sugar or fat, research suggests.
An international team of scientists has found no strong evidence for people being addicted to the chemical substances in certain foods.
The brain does not respond to nutrients in the same way as it does to addictive drugs such as heroin or cocaine, the researchers say.
Instead, people can develop a psychological compulsion to eat, driven by the positive feelings that the brain associates with eating.
This is a behavioural ...
New methods enhance the quality of myocardial perfusion imaging
2014-09-09
New methods that enhance the quality of myocardial perfusion imaging were developed in a recent study completed at the University of Eastern Finland. In her PhD study, Tuija Kangasmaa, Lic. Phil., invented a method which makes it possible to reduce the imaging time by up to 50%, making the scan session easier for the patient. Furthermore, the study also created two additional methods which correct errors resulting from patient movement during the scan. The methods were validated and they have already been taken into use in hospitals all over the world.
Coronary artery ...
New infrared marker for bio-imaging
2014-09-09
Far-red shifted fluorescent tissue markers make it possible to visualize structures and processes with advanced bio-imaging. This permits new insights into organisms and creates the potential for a wide range of applications – from more exact delineation of tumor and metastasis through to tracking drug responses within whole-body imaging.
The team of scientists headed by Dr. Ulrike Schoetz, Dr. Nikolas Deliolanis, Dr. Wolfgang Beisker, Professor Horst Zitzelsberger und Randolph Caldwell from the Helmholtz Zentrum München have succeeded in developing novel fluorescent ...
Xenon gas protects the brain after head injury
2014-09-09
Treatment with xenon gas after a head injury reduces the extent of brain damage, according to a study in mice.
Head injury is the leading cause of death and disability in people aged under 45 in developed countries, mostly resulting from falls and road accidents. The primary injury caused by the initial mechanical force is followed by a secondary injury which develops in the hours and days afterwards. This secondary injury is largely responsible for patients' mental and physical disabilities, but there are currently no drug treatments that can be given after the accident ...
Winter is coming: British weather set to become more unsettled
2014-09-09
Britain hit by extremely unsettled winter weather
Three all-time high and two all-time low NAO values recorded in the last decade showing huge contrast in conditions
Month of December shows biggest variation in weather.
British winters are becoming increasingly volatile due to extreme variations in pressure over the North Atlantic according to scientists from the University of Sheffield.
The new research, published today (9 September 2014) in the International Journal of Climatology, shows that weather patterns over the UK have become distinctly more unstable, resulting ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
[Press-News.org] Why do mushrooms turn brown?Chemists explore the mechanisms behind food spoilage