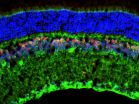
(Press-News.org) NEW YORK, NY (August 31, 2015) -- Vision researchers at Columbia University Medical Center have discovered a gene that causes myopia, but only in people who spend a lot of time in childhood reading or doing other "nearwork."
Using a database of approximately 14,000 people, the researchers found that those with a certain variant of the gene - called APLP2 - were five times more likely to develop myopia in their teens if they had read an hour or more each day in their childhood. Those who carried the APLP2 risk variant but spent less time reading had no additional risk of developing myopia.
"We have known for decades that myopia is caused by genes and their interactions with environmental factors like reading and nearwork, but we have not had hard proof. This is the first known evidence of gene-environment interaction in myopia," says the study's lead investigator, Andrei Tkatchenko, MD, PhD, of CUMC. The research was published August 27 in PLOS Genetics.
Although it's not yet known how genetic variation at the APLP2 gene causes myopia, Dr. Tkatchenko and his colleagues think the risk variant may increase the amount of APLP2 protein produced in the eye, which in turn may cause the eye to undergo excessive elongation.
They found that mice exposed to a visual environment that mimics reading were less likely to develop myopia when little APLP2 protein was present in the eye.
"By reducing the level of APLP2 in the eye, you can reduce susceptibility to environmentally induced myopia. This gives us an opportunity to develop a therapy to prevent myopia in everyone, regardless of the APLP2 variant they carry," Dr. Tkatchenko says.
Developing such a therapy, however, could take years, as researchers don't yet know how APLP2 levels could be reduced in people. And the therapy would be most effective in young children, before the eye has started to elongate and become myopic.
"Once the eye has elongated, you cannot shrink it, so we would need to identify kids with genetic risk factors as they enter school," Dr. Tkatchenko says. That's not yet possible because there are probably hundreds of genes that can cause myopia, and so far, only 25 candidates have been identified. The high-risk variant of APLP2 is relatively uncommon, occurring in about 1 percent of the population.
Though a drug or gene therapy to prevent myopia may be years away, Dr. Tkatchenko says spending time outdoors is the best way to reduce kids' risk of developing myopia.
"We pretty much know all the environmental risk factors: time spent reading increases the risk, while time spent outdoors reduces it," Dr. Tkatchenko says.
Myopia rates have shot up in recent years due to changes in these environmental factors. In the U.S., 44 percent of adults are now nearsighted, up from 25 percent 30 years ago. And in some parts of Asia, 80 percent of young adults are now myopic.
"The critical period for myopia development is during elementary and middle school, so when kids are in school, make sure they also spend at least two hours outdoors each day," Dr. Tkatchenko says.
Preventing myopia not only reduces the need for vision correction, but also prevents potentially blinding eye conditions later in life.
"People say, 'What's so terrible about myopia? You just have to get glasses,'" Dr. Tkatchenko says, "But myopia increases the risk of developing cataracts, glaucoma, and retinal detachment later in life. All of these can lead to blindness.
"Even in people with mild myopia there is a significant risk, but it's especially high in people who need five or more diopters of vision correction (about 20/400 vision). That's why it's important to study myopia."
INFORMATION:
The paper is titled "APLP2 regulates refractive error and myopia development in mice and humans." The authors are: Andrei V. Tkatchenko, Tatiana V. Tkatchenko, Jeremy A. Guggenheim (Cardiff University), Virginie J. M. Verhoeven (Erasmus Medical Center), Pirro G. Hysi (King's College London School of Medicine), Robert Wojciechowski (Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and NIH), Pawan Kumar Singh (Wayne State University), Ashok Kumar (Wayne State University), Gopal Thinakaran (University of Chicago), Consortium for Refractive Error and Myopia, and Cathy Williams (University of Bristol).
The work was supported by the National Eye Institute of NIH (grants R21EY018902 and R01EY023839), research grants from the Midwest Eye-Banks, and the generous donations from the Acquavella Family Foundation and Joseph Connors.
The CUMC investigators report no conflicts of interest.
Columbia University Medical Center provides international leadership in basic, preclinical, and clinical research; medical and health sciences education; and patient care. The medical center trains future leaders and includes the dedicated work of many physicians, scientists, public health professionals, dentists, and nurses at the College of Physicians and Surgeons, the Mailman School of Public Health, the College of Dental Medicine, the School of Nursing, the biomedical departments of the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, and allied research centers and institutions. Columbia University Medical Center is home to the largest medical research enterprise in New York City and State and one of the largest faculty medical practices in the Northeast. For more information, visit cumc.columbia.edu or columbiadoctors.org.
An in-depth dialect study from NC State University researchers shows that some students from rural Appalachia feel that their dialects put them at a disadvantage in a college classroom, even in the South.
The Journal of Higher Education study raises important questions about language as a type of diversity that isn't always celebrated on campus, says lead author Stephany Dunstan, a linguist and associate director of assessment at NC State.
In their interviews, some rural Appalachian students recalled times when they spoke up in class only to be met with snickers for ...
You've probably never noticed, but the human eye includes an unavoidable blind spot. That's because the optic nerve that sends visual signals to the brain must pass through the retina, which creates a hole in that light-sensitive layer of tissue. When images project to that precise location, we miss them. Now researchers reporting in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on August 31 have some good news: this blind spot can be effectively "shrunk" with training, despite the fact that the hole in our visual field cannot be.
The findings raise the possibility that similar ...
A higher resting heart rate and lower heart rate variability in older adults at high risk of heart disease are associated with poorer ability to function in daily life as well as future decline, according to a new research in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
"It has been hypothesized that heart rate and heart rate variability are markers of frailty, an increased vulnerability to stressors and functional decline," writes Dr. Behnam Sabayan, Department of Gerontology and Geriatrics, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, the Netherlands, with coauthors. "However, ...
Lyme disease is becoming increasingly common in Canada, and Canadians with Lyme disease symptoms may seek diagnoses from laboratories in the United States, although many of the results will be false-positives, according to a commentary in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
"Patients with chronic subjective symptoms without a diagnosis can be vulnerable and desperate for an answer as to the cause of their illness," writes Dr. Dan Gregson, divisions of Medical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, departments of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, and Medicine, ...
(Philadelphia, PA) - Early intervention facilitated by a digital health application for reporting symptoms of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) provides key benefits for patients, according to the results of a Temple-led, two-year clinical study.
COPD is a serious chronic respiratory disease that is often characterized by flare-ups, called acute exacerbations, in which the patient may experience increased coughing, mucus, shortness of breath, wheezing, and a feeling of tightness in their chest. If exacerbation symptoms are not detected and treated in a timely ...
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) -- In addition to restricting when and where tobacco is used at work, UC Davis Health System research shows that employers can do something else to reduce smoking: raise wages.
Published in the August issue of the Annals of Epidemiology, the study found that a 10 percent increase in wages leads to about a 5 percent drop in smoking rates among workers who are male or who have high school educations or less and improves their overall chances of quitting smoking from 17 to 20 percent.
"Our findings are especially important as inflation-adjusted wages ...
Amsterdam, NL, August 31, 2015 - About 50% of patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) experience freezing of gait (FOG), an inability to move forward while walking. This can affect not only mobility but also balance. In a new study published in Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience, researchers report that repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) can reduce FOG and improve other motor skills in PD patients.
In a study conducted by researchers at the Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, 17 PD patients experiencing FOG were treated with either ...
BOSTON - Clinicians at Boston Medical Center (BMC) showed that expanding the number of sites offering office-based opioid treatment with buprenorphine (OBOT B) utilizing addiction nurse care managers, trainings and technical support resulted in more physicians becoming waivered to prescribe buprenorphine and more patients accessing treatment at sites across Massachusetts. This model, highlighted online in the Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, demonstrates the efficacy of this medication-assisted treatment modality as a sustainable way to treat greater numbers of patients ...
NASA's Aqua satellite and NOAA's GOES-East satellites provided views of Hurricane Jimena that showed it maintained a large eye and powerful thunderstorms around it. On August 31, Jimena continued moving through the Eastern Pacific as a major hurricane.
An infrared image from NOAA's GOES-West satellite on August 31 at 8:00 a.m. EDT revealed that Hurricane Jimena's wide-eye continued to be cloud free. The GOES image also showed thick bands of powerful thunderstorms circling the eye.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard Aqua gathers infrared data ...
A bill to improve the nutritional value of fast food restaurant meals marketed to children--like McDonald's Happy Meals--could have a wide enough impact to reduce calories, fat, and sodium, according to a new study led by researchers at NYU Langone Medical Center.
The study, which will publish in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine online on August 31, includes collaboration from NYU College of Global Public Health, NYU Wagner Graduate School of Public Service, and NYU Steinhardt School of Culture, Education, and Human Development.
The "Healthy Happy Meals" ...