(Press-News.org) Young women who smoke and have been smoking a pack a day for a decade or more have a significantly increased risk of developing the most common type of breast cancer. That is the finding of an analysis published early online in Cancer, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society. The study indicates that an increased risk of breast cancer may be another health risk incurred by young women who smoke.
The majority of recent studies evaluating the relationship between smoking and breast cancer risk among young women have found that smoking is linked with an increased risk; however, few studies have evaluated risks according to different subtypes of breast cancer.
To investigate, Christopher Li, MD, PhD, of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, and his colleagues conducted a population-based study consisting of 778 patients with estrogen receptor positive breast cancer and 182 patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Estrogen receptor positive breast cancer is the most common subtype of breast cancer, while triple-negative breast cancer is less common but tends to be more aggressive. Patients in the study were 20 to 44 years old and were diagnosed from 2004-2010 in the Seattle-Puget Sound metropolitan area. The study also included 938 cancer-free controls.
The researchers found that young women who were current or recent smokers and had been smoking a pack a day for at least 10 years had a 60 percent increased risk of estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. In contrast, smoking was not related to a woman's risk of triple-negative breast cancer.
"The health hazards associated with smoking are numerous and well known. This study adds to our knowledge in suggesting that with respect to breast cancer, smoking may increase the risk of the most common molecular subtype of breast cancer but not influence risk of one of the rarer, more aggressive subtypes," said Dr. Li.
INFORMATION: END
Smoking linked with increased risk of most common type of breast cancer
2014-02-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
No strength in numbers
2014-02-10
Urban legislators have long lamented that they do not get their fair share of bills passed in state governments, often blaming rural and suburban interests for blocking their efforts. Now a new study confirms one of those suspicions but surprisingly refutes the other.
The analysis—of 1,736 bills in 13 states over 120 years—found that big-city legislation was passed at dramatically lower rates than bills for smaller places.
However, rural and suburban colleagues should not be blamed for the dismal track record, conclude co-authors Gerald Gamm of the University of Rochester ...
Virtual avatars may impact real-world behavior
2014-02-10
How you represent yourself in the virtual world of video games may affect how you behave toward others in the real world, according to new research published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"Our results indicate that just five minutes of role-play in virtual environments as either a hero or villain can easily cause people to reward or punish anonymous strangers," says lead researcher Gunwoo Yoon of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
As Yoon and co-author Patrick Vargas note, virtual environments afford people ...
Huntington disease prevention trial shows creatine safe, suggests slowing of progression
2014-02-08
The first clinical trial of a drug intended to delay the onset of symptoms of Huntington disease (HD) reveals that high-dose treatment with the nutritional supplement creatine was safe and well tolerated by most study participants. In addition, neuroimaging showed a treatment-associated slowing of regional brain atrophy, evidence that creatine might slow the progression of presymptomatic HD. The Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) study also utilized a novel design that allowed participants – all of whom were at genetic risk for the neurodegenerative disorder – to enroll ...
Stroke trigger more deadly for African-Americans
2014-02-08
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — Infection is a stronger trigger of stroke death in African- Americans than in whites, a University of Michigan study shows.
African-Americans were 39 times more likely to die of a stroke if they were exposed to an infection in the previous month when compared to other time periods while whites were four times more likely and Hispanics were five times more likely to die of stroke after an infection, according to the findings that appear online Feb. 7 in Neurology.
The most frequent infections were urinary, skin, and respiratory tract infections ...
Women fare worse than men following stroke
2014-02-08
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – Feb. 7, 2014 – The good news: More people survive stroke now than 10 years ago due to improved treatment and prevention.
The bad news: Women who survive stroke have a worse quality of life than men, according to a study published in the Feb. 7 online issue of the journal Neurology.
Researchers at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center compared the quality of life in men and women who had a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA). A total of 1,370 patients ages 56 to 77 from the AVAIL registry – a national, multicenter, longitudinal registry of ischemic ...
New application of physics tools used in biology
2014-02-08
A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory physicist and his colleagues have found a new application for the tools and mathematics typically used in physics to help solve problems in biology.
Specifically, the team used statistical mechanics and mathematical modeling to shed light on something known as epigenetic memory -- how an organism can create a biological memory of some variable condition, such as quality of nutrition or temperature.
"The work highlights the interdisciplinary nature of modern molecular biology, in particular, how the tools and models from mathematics ...
Social or stinky? New study reveals how animal defenses evolve
2014-02-08
When people see a skunk, the reaction usually is "Eww," but when they see a group of meerkats peering around, they often think "Aww."
Why some animals use noxious scents while others live in social groups to defend themselves against predators is the question that biologists Tim Caro of the University of California, Davis and Theodore Stankowich of California State University, Long Beach and sought to answer through a comprehensive analysis of predator-prey interactions among carnivorous mammals and birds of prey.
Their findings appear in the online edition of the ...
Endocrine Society calls for large-scale studies to evaluate testosterone therapy risks
2014-02-08
Chevy Chase, MD—According to a statement issued today by the Endocrine Society, the risks and benefits of testosterone therapy for older men with declining levels of the hormone need to be fully evaluated.
The statement comes in response to recent studies that have raised concerns about the safety of testosterone therapy in older men with a history of heart disease. Two retrospective analyses and one randomized trial supported by the Veterans Health Care System, and the National Institutes of Health found a higher rate of cardiovascular events in men who received testosterone ...
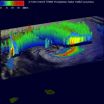
NASA spots very heavy rainfall rates in Tropical Cyclone Edilson
2014-02-08
Imagine receiving as much as 7 inches of rain in one hour. That's about what NASA's TRMM satellite spotted falling in one area within Tropical Cyclone Edilson as it moved over the Southern Indian Ocean.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite is managed by both NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency called JAXA. TRMM can read the rate in which rain is falling on Earth while in its orbit high above.
The TRMM satellite had an excellent early morning look at Edilson on February 7, 2014 at 0237 UTC/06:28 local time when it passed directly above ...
Diaphragm pacing in spinal cord injury successful in weaning patients from ventilators
2014-02-08
CLEVELAND – A new study published in the Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery finds that diaphragm pacing (DP) stimulation in spinal cord-injured patients is successful not only in weaning patients from mechanical ventilators but also in bridging patients to independent respiration, where they could breathe on their own without the aid of a ventilator or stimulation.
The stimulation is provided by the Diaphragm Pacing System (DPS), a technology providing electrical stimulation to nerves running through the diaphragm, the major muscle involved in breathing. When stimulated, ...