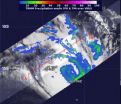
(Press-News.org) Some towering thunderstorms were spotted in Tropical Cyclone Fobane as NASA's TRMM satellite passed over the Southern Indian Ocean on February 10. Fobane was formerly Tropical Cyclone 14S and when it strengthened into a tropical storm it was renamed.
NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency manages the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite known as TRMM. TRMM has the capability to measure rainfall rates from space and data that can be used to determine the heights of thunderstorms that make up a storm. When TRMM passed over Tropical Cyclone Fobane on February 10 at 0228 UTC/Feb. 9 at 9:28 p.m. EST, it spotted some thunderstorms up to 14 km/8.6 miles, where rainfall rates were near 35 mm/1.3 inches near the center of circulation.
On February 10 at 0900 UTC/4 a.m. EST, Tropical Cyclone Fobane, known on La Reunion island as Tropical Cyclone 11/20132014, was located near 22.5 south latitude and 72.6 east longitude, about 973 nautical miles/1,120 miles/1,802 km east of St, Denis, La Reunion. Fobane's maximum sustained winds were near 55 knots/63.2 mph/101.9 kph and the storm was weakening. It was moving to the southwest at 21 knots/24.1 mph/ 38.8 kph.
Fobane has moved into an area of moderate to strong vertical wind shear, according to the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. That wind shear is not expected to let up and Fobane is moving into cooler waters, so the storm is expected to continue to weaken.
Fobane is expected to continue moving in a southerly direction over open waters over the next several days as it passes far to the southeast of La Reunion Island.
INFORMATION:
NASA's TRMM satellite eyes rainfall in Tropical Cyclone Fobane
2014-02-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cars, computers, TVs spark obesity in developing countries
2014-02-11
The spread of obesity and type-2 diabetes could become epidemic in low-income countries, as more individuals are able to own higher priced items such as TVs, computers and cars. The findings of an international study, led by Simon Fraser University health sciences professor Scott Lear, are published today in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Lear headed an international research team that analyzed data on more than 150,000 adults from 17 countries, ranging from high and middle income to low-income nations.
Researchers, who questioned participants about ownership ...
Recycling of 'chauffeur protein' helps regulate fat production
2014-02-11
Studying a cycle of protein interactions needed to make fat, Johns Hopkins researchers say they have discovered a biological switch that regulates a protein that causes fatty liver disease in mice. Their findings, they report, may help develop drugs to decrease excessive fat production and its associated conditions in people, including fatty liver disease and diabetes.
A summary of the research appeared online on Jan. 29 in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
"We've learned how the body finely tunes levels of a protein called SCAP that is required to turn on fat production ...
Long distance signals protect brain from viral infections
2014-02-11
The brain contains a defense system that prevents at least two unrelated viruses—and possibly many more—from invading the brain at large. The research is published online ahead of print in the Journal of Virology.
"Our work points to the remarkable ability of the immune system, even within the brain, to protect us against opportunistic viruses," says Anthony van den Pol of Yale University, an author on the study.
The research explains a long-standing mystery. The olfactory mucosa in the nose can serve as a conduit for a number of viruses to enter the brain including ...
Mayo Clinic identifies a key cellular pathway in prostate cancer
2014-02-11
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Mayo Clinic researchers have shed light on a new mechanism by which prostate cancer develops in men. Central to development of nearly all prostate cancer cases are malfunctions in the androgen receptor — the cellular component that binds to male hormones. The research team has shown that SPOP, a protein that is most frequently mutated in human prostate cancers, is a key regulator of androgen receptor activity that prevents uncontrolled growth of cells in the prostate and thus helps prevent cancer. The findings appear in the journal Cell Reports.
"By ...
Flowing water on Mars appears likely but hard to prove
2014-02-11
Martian experts have known since 2011 that mysterious, possibly water-related streaks appear and disappear on the planet's surface. Georgia Institute of Technology Ph.D. candidate Lujendra Ojha discovered them while an undergraduate at the University of Arizona. These features were given the descriptive name of recurring slope lineae (RSL) because of their shape, annual reappearance and occurrence generally on steep slopes such as crater walls. Ojha has been taking a closer look at this phenomenon, searching for minerals that RSL might leave in their wake, to try to understand ...
With their amazing necks, ants don't need 'high hopes' to do heavy lifting
2014-02-11
COLUMBUS, Ohio—High hopes may help move a rubber tree plant (as the old song goes), but the real secret to the ant's legendary strength may lie in its tiny neck joint.
In the Journal of Biomechanics, researchers report that the neck joint of a common American field ant can withstand pressures up to 5,000 times the ant's weight.
"Ants are impressive mechanical systems—astounding, really," said Carlos Castro, assistant professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at The Ohio State University. "Before we started, we made a somewhat conservative estimate that they ...
Chips that listen to bacteria
2014-02-11
VIDEO:
The development of colony biofilms by Pseudomonas aeruginosa is affected by redox-active compounds called phenazines. A phenazine-null mutant forms a hyperwrinkled colony with prominent spokes, while wild-type colonies are more...
Click here for more information.
New York, NY—February 10, 2014—In a study published today in Nature Communications, a research team led by Ken Shepard, professor of electrical engineering and biomedical engineering at Columbia Engineering, ...
Manga comics may help promote fruit consumption among youth
2014-02-11
AUDIO:
May May Leung, Ph.D., R.D., discusses how a recent pilot study in Brooklyn, N.Y., with minority students found that exposure to manga comics (Japanese comic art) promoting fruit intake significantly...
Click here for more information.
PHILADELPHIA, PA, February 10, 2014 – A recent pilot study in Brooklyn, New York, with minority students found that exposure to Manga comics (Japanese comic art) promoting fruit intake significantly improved healthy snack selection. As ...
Political values influence people's response to health disparities messages
2014-02-11
PHILADELPHIA (February 10, 2014) – Policymakers and advocates discussing health disparities in the United States would be wise to consider the political affiliation of their audience, suggests a new study published in the Journal of Health Communication: International Perspectives (2014).
"Understanding Public Resistance to Messages about Health Disparities" was written by Sarah E. Gollust, University of Minnesota School of Public Health; and Joseph N. Cappella, Annenberg School for Communication, University of Pennsylvania. The study examines how political ...
TGen study uncovers possible genetic markers in breast cancer that spreads to the brain
2014-02-11
PHOENIX, Ariz. — Feb. 10, 2014 — The Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen) has uncovered possible genetic origins of breast cancer that spreads to the brain, according to a first-of-its-kind study published in the scientific journal PLOS ONE.
The compendium of genetic targets uncovered by TGen now can be used to identify potential new methods of diagnosis and new drug therapies for the estimated 45,000 patients in the U.S. each year whose cancer spreads from the breast to the brain.
The 3-year study is significant since these patients currently have few treatments ...