(Press-News.org) Moderate aerobic exercise helps to preserve the structure and function of nerve cells in the retina after damage, researchers at the Emory Eye Center and the Atlanta VA Medical Center have found.
The findings, from a study of an animal model of age-related macular degeneration, are the first to suggest that aerobic exercise can have a direct effect on retinal health and vision.
The results are scheduled for publication Feb. 12 in the Journal of Neuroscience.
Senior authors are Machelle Pardue, PhD and colleague Jeffrey H. Boatright, PhD at the Atlanta VA Center for Visual and Neurocognitive Rehabilitation and Emory University School of Medicine. First author Eric Lawson earned his 2013 undergraduate degree at Emory and is now attending medical school in South Carolina.
"This research may lead to tailored exercise regimens or combination therapies in treatments of retinal degenerative diseases," Pardue says. "Possibly in the near future, ophthalmologists could be prescribing exercise as a low-cost intervention to delay vision loss."
Age-related macular degeneration, one of the leading causes of blindness in the elderly, is caused by the death of light-sensing nerve cells in the retina called photoreceptors. Although several studies in animals and humans point to the protective effects of exercise in neurodegenerative diseases or injury, less was known about how exercise affects vision.
Working with Pardue and Boatright, Lawson ran mice on a treadmill for two weeks before and after exposing the animals to bright light that causes retinal degeneration. They found that treadmill training preserved photoreceptors and retinal cell function in the mice.
The researchers trained mice to run on a treadmill for one hour per day, five days per week, for two weeks. After the animals were exposed to toxic bright light — a commonly used model of retinal degeneration — they exercised for two more weeks. The exercised animals had nearly twice the number of photoreceptor cells of animals that spent the equivalent amount of time on a stationary treadmill, and their retinal cells were more responsive to light.
"One point to emphasize is that the exercise the animals engaged in is really comparable to a brisk walk," Pardue says. "One previous study that examined the effects of exercise on vision in humans had examined a select group of long distance runners. Our results suggest it's possible to attain these effects with more moderate exercise."
The researchers were able to show that the effects of exercise come partly from a growth factor called BDNF, which was thought to be involved in the beneficial effects of exercise in other studies. Exercised mice had higher levels of BDNF in the blood, brain and retina, while chemically blocking BDNF receptors effectively eliminated the protective effects of aerobic exercise, they demonstrated.
Pardue and Boatright are testing whether other exercise regimens are even more protective and whether exercise is beneficial in models of other retinal diseases such as glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy.
INFORMATION:
Exercise may slow retinal degeneration
2014-02-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Smoking cessation may improve mental health
2014-02-12
Health professionals who treat people with psychiatric problems often overlook their patients' smoking habits, assuming it's best to tackle depression, anxiety or substance abuse problems first. However, new research at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis shows that people who struggle with mood problems or addiction can safely quit smoking and that kicking the habit is associated with improved mental health.
The study is published online in the journal Psychological Medicine.
"Clinicians tend to treat the depression, alcohol dependence or drug problem ...
Man's best friend equally adapted to high altitudes of Tibet
2014-02-12
As humans have expanded into new environments and civilizations, man's best friend, dogs, have been faithful companions at their sides. Now, with DNA sequencing technology readily available to examine the dog genome, scientists are gaining new insights into canine evolution.
In a new study published in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution, author Dong-Dong Wu, et. al., explored the genetic basis of high-altitude adaptation of Tibetan Mastiffs, which were originally domesticated from the Chinese native dogs of the plains. The authors examined genome-wide mutations ...
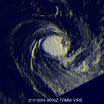
NASA still sees some high thunderstorms in Tropical Cyclone Fobane
2014-02-12
VIDEO:
This TRMM flyover is a simulated 3-D view of Fobane that shows a few powerful thunderstorms near the center were reaching heights of over 14km (~8.7 miles) on Feb. 11....
Click here for more information.
Tropical Cyclone Fobane was located southeast of Reunion Island in the southwest Indian Ocean when the TRMM satellite passed over and captured rainfall and cloud data on the storm. TRMM saw that despite Fobane weakening, there was still some punch left in a few of the thunderstorms ...
Tech products can turn uncool when they become too popular
2014-02-12
In the tech world, coolness takes more than just good looks. Technology users must consider a product attractive, original and edgy before they label those products as cool, according to researchers.
That coolness can turn tepid if the product appears to be losing its edginess, they also found.
"Everyone says they know what 'cool' is, but we wanted to get at the core of what 'cool' actually is, because there's a different connotation to what cool actually means in the tech world," said S. Shyam Sundar, Distinguished Professor of Communications, Penn State, and co-director ...
NIH-funded researchers use antibody treatment to protect humanized mice from HIV
2014-02-12
NIH-funded scientists have shown that boosting the production of certain broadly neutralizing antibodies can protect humanized mice from both intravenous and vaginal infection with HIV. Humanized mice have immune systems genetically modified to resemble those of humans, making it possible for them to become HIV-infected.
Led by David Baltimore, Ph.D., of the California Institute of Technology, the investigators inserted the genes encoding the NIH-discovered broadly HIV neutralizing antibody VRC01 into a vector, a virus that infects mice but does not cause disease. In ...
New evidence shows how chronic stress predisposes brain to mental disorders
2014-02-12
University of California, Berkeley, researchers have shown that chronic stress generates long-term changes in the brain that may explain why people suffering chronic stress are prone to mental problems such as anxiety and mood disorders later in life.
Their findings could lead to new therapies to reduce the risk of developing mental illness after stressful events.
Doctors know that people with stress-related illnesses, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), have abnormalities in the brain, including differences in the amount of gray matter versus white matter. ...
Slim pickings for 2 weight-loss drugs?
2014-02-12
LEBANON, NH (Feb. 10, 2014) – Options are limited in America's battle of the bulge. While diet and exercise can help in the short term, they are frustratingly ineffective in the long run.
And, even the search for a magic weight-loss pill is falling short, said Drs. Steven Woloshin and Lisa Schwartz of The Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy & Clinical Practice in the Feb. 10 issue of JAMA Internal Medicine.
Many medications for weight loss have been proposed or are under development. The Federal Drug Administration has approved few drugs for long-term weight loss, ...
UTMB study examines hospital readmission rates after inpatient rehabilitation
2014-02-12
Nearly 12 percent of Medicare patients who receive inpatient rehabilitation following discharge from acute-care hospitalization are readmitted to the hospital within 30 days after discharge from the rehabilitation facility according to new research published in the Feb. 12 issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association. Before now, there was a lack of research on the frequency and causes of patients returning to hospital after rehabilitation.
The new research reports 30-day hospital readmission rates across rehabilitation impairment categories and examines ...
New UK study shows potential for targeting aggressive breast cancers
2014-02-12
LEXINGTON, Ky. (Feb. 10, 2014) — A new study led by University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center researcher Peter Zhou shows that targeting Twist, a nuclear protein that is an accelerant of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) program in human cells, may provide an effective approach for treating triple-negative breast cancer.
Triple-negative breast cancer has an activated EMT program, which is a process that provides cells with the increased plasticity (or flexibility) to adapt to stressed environments during embryonic development, wound healing, tissue fibrosis ...
Penn Medicine: Cognitive development 'growth charts' may help diagnose and treat psychosis-risk kids
2014-02-12
PHILADELPHIA -- Penn Medicine researchers have developed a better way to assess and diagnose psychosis in young children. By "growth charting" cognitive development alongside the presentation of psychotic symptoms, they have demonstrated that the most significant lags in cognitive development correlate with the most severe cases of psychosis. Their findings are published online this month in JAMA Psychiatry.
"We know that disorders such as schizophrenia come with a functional decline as well as a concurrent cognitive decline," says Ruben Gur, PhD, director of the Brain ...