(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of East Anglia have made an important advance in understanding genetic changes associated with terminal prostate cancer.
Findings published today in the British Journal of Cancer, and funded by the Association for International Cancer Research (AICR), show how a genetic mutation in untreated patients is linked to aggressive cancer later in life. It was previously thought that the mutation only occurred in response to therapy.
The research highlights why relapses could occur in some men following hormone therapy. And it could help identify those patients that will develop fatal prostate cancer much earlier for life-extending therapy.
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men in the UK, with more than 40,000 new cases diagnosed every year. Treatment options for patients diagnosed with early stage prostate cancer vary from "watchful waiting" to hormone-withdrawal therapy, radiotherapy or surgery.
Additional tests for indicators of aggressive cancer are necessary to help categorise patients so that those with a low-risk of the disease spreading can avoid unnecessary treatment, and those diagnosed with a high-risk can be targeted for more aggressive first line therapy.
Hormone-withdrawal therapy often results in a dramatic remission, however the disease invariably relapses with a resistant form of the cancer. A third of these are due to an increase in copy number of a particular gene called the 'androgen receptor'. The gene is on the X-Chromosome and so there is normally only one copy of this gene present in men. Prostate cancer thrives on male hormones, and one way that they develop to grow better is to increase the number of copies of the androgen receptor gene. This also enables the cancer to resist therapy.
Lead researchers Dr Jeremy Clark and Prof Colin Cooper from UEA's school of Biological Sciences carried out the research at the Institute of Cancer Research, London, and at UEA.
Dr Clark said: "By the age of 60, the majority of men will have signs of prostate cancer. However, only a small proportion of men will die of the disease. The question is - which of these cancers are dangerous and which are not? Deciding which cancers are going to progress and kill the patient is key to effective patient treatment."
"Prostate cancer thrives on male hormones, and cutting the supply of hormones to the cancer is a main avenue of therapy. Prostate cancer only kills the patient when it becomes immune to these therapies. A third of these killer cancers are immune to therapy because they have boosted the number of male hormone receptor (AR) genes in their DNA. This gene boosting, also known as amplification, has been thought to be a response of the tumour to the hormone reduction therapy itself.
"Our research has shown that an early form of this hormone-gene boosting is present in a number of prostate cancers that have never been treated with hormone reduction therapy. We think that it is these cancers that will grow and kill the patient.
"This discovery can be used to identify these killer cancers in patients much earlier than is currently possible. Patients could then be selected for more aggressive therapy before the cancer has developed full immunity."
The research team looked at biomarkers from almost 600 patients prior to hormone-withdrawal therapy. But the method of identification used was labour intensive and time consuming. Developing ways of identifying patients for early therapeutic intervention will be key to implementing this discovery in the clinic. The research team are currently looking at more rapid ways of identifying patients that will develop aggressive cancer.
INFORMATION:
'Focal amplification of the androgen receptor gene in hormone-naïve human prostate cancer' is published in the British Journal of Cancer.
Prostate cancer advance could improve treatment options
2014-02-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mountains, models, salt, sand, and cycles
2014-02-12
Boulder, Colo., USA – Topics in this current batch of Geology articles posted ahead of print include the puzzle of parallel mountain chains; 25 years on the East Pacific Rise; unique episodes in Earth's history; turbidity currents; computer models; Wilson cycles; salt structure beneath the sea bed; the North Scotia Ridge; El Hierro, Canary Islands; sand-sized sub-spherical silica grains; bank pull or bar push; kaolinitic paleosols; Earth's youngest, hottest rocks; 3-D thermo-mechanical numerical models; and the Bohemian Massif.
Open Access Papers:
1. Sublithospheric ...
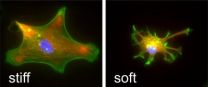
Filling me softly
2014-02-12
Surgical implants are widely used in modern medicine but their effectiveness is often compromised by how our bodies react to them. Now, scientists at the University of Cambridge have discovered that implant stiffness is a major cause of this so-called foreign body reaction.
This is the first time that stiffness of implant materials has been shown to be involved in foreign body reactions. The findings – published in the journal Biomaterials – could lead to major improvements in surgical implants and the quality of life of patients whose lives depend on them.
Foreign ...
The physics of curly hair
2014-02-12
CAMBRIDGE, Mass-- The heroes and villains in animated films tend to be on opposite ends of the moral spectrum. But they're often similar in their hair, which is usually extremely rigid or — if it moves at all — is straight and swings to and fro. It's rare to see an animated character with bouncy, curly hair, since computer animators don't have a simple mathematical means for describing it.
However, change may be coming soon to a theater near you: In a paper appearing in the Feb. 13 issue of Physical Review Letters, researchers at MIT and the Université Pierre et Marie ...
Test for persistent Lyme infection using live ticks shown safe in clinical study
2014-02-12
In a first-of-its-kind study for Lyme disease, researchers have used live, disease-free ticks to see if Lyme disease bacteria can be detected in people who continue to experience symptoms such as fatigue or arthritis after completing antibiotic therapy. The technique, called xenodiagnosis, attempts to find evidence of a disease-causing microbe indirectly, through use of the natural disease-carrier—in this case, ticks. It was well tolerated by the volunteers, but investigators could not find evidence of Lyme disease bacteria in most of the cases where enough ticks were collected ...
U-M scientists & colleagues investigate the fiber of our being
2014-02-12
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — We are all aware of the health benefits of dietary fiber. But what is dietary fiber and how do we metabolize it?
Research at the University of Michigan Medical School, the University of York's Structural Biology Laboratory, and institutions in Canada and Sweden, has begun to uncover how our gut bacteria metabolize the complex dietary carbohydrates found in fruits and vegetables.
Trillions of bacteria live in human intestines - there are about ten times more bacterial cells in the average person's body than human ones. Known as "microbiota", these ...
NASA satellite sees Tropical Cyclone Fobane spinning down
2014-02-12
Tropical Cyclone Fobane continues to be battered with increasing vertical wind shear as it moves southward through the Southern Indian Ocean. NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead and saw the bulk of precipitation and bands of thunderstorms were south of the center.
On Feb. 12 at 0900 UTC/4 a.m. EST, Tropical Cyclone Fobane had maximum sustained winds near 45 knots/51.7 mph/83.3 kph. Fobane was centered near 27.6 south latitude and 64.7 east longitude, about 596 nautical miles southeast of Port Louis, Mauritius. Fobane is moving to the south-southwest at 11 knots/12.6 ...
Study highlights long-term effects of childhood obesity on late-life health
2014-02-12
Childhood obesity rates have nearly tripled in the previous 30 years and researchers are asking the important question of how this epidemic will impact the future health of these obese children and public health in general. A University of Colorado Cancer Center article recently published in the journal Gerontology shows that even in cases in which obese children later lose weight, the health effects of childhood obesity may be long-lasting and profound.
"There were two things going on here. First, the earlier you are exposed to obesity, the earlier we may see the onset ...
Study: IOC should ban lead shot to help wildlife, water
2014-02-12
With the world watching the Sochi Winter Olympics including the biathlon shooting events, now is the time for the International Olympic Committee (IOC) to ban the use of lead shot to prevent wildlife poisoning and health threats to surface and groundwater, says a new paper co-authored this month by a University of Guelph biologist.
Thousands of tons of lead shot discharged every year during training by Olympic shooters pose a threat to birds and mammals and to water resources, says Vernon Thomas, professor emeritus in the Department of Integrative Biology.
His paper ...
Plastic shopping bags make a fine diesel fuel, researchers report
2014-02-12
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Plastic shopping bags, an abundant source of litter on land and at sea, can be converted into diesel, natural gas and other useful petroleum products, researchers report.
The conversion produces significantly more energy than it requires and results in transportation fuels – diesel, for example – that can be blended with existing ultra-low-sulfur diesels and biodiesels. Other products, such as natural gas, naphtha (a solvent), gasoline, waxes and lubricating oils such as engine oil and hydraulic oil also can be obtained from shopping bags.
A report ...
LA BioMed researchers report on promising new therapy for devastating genetic disorder
2014-02-12
LOS ANGELES – (Feb. 12, 2014) – A promising new therapy has – for the first time – reduced damage to the brain that can be caused by Sanfilippo B (MPS IIIB), a rare and devastating genetic disease, Los Angeles Biomedical Research Institute (LA BioMed) researchers will report today in a presentation at the Lysosomal Disease Network's 10th Annual WORLD Symposium™.
Sanfilippo B syndrome is a lysosomal storage disease belonging to the group of mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS) that is characterized by severe and rapid intellectual deterioration. LA BioMed pioneered the research ...