(Press-News.org) Cancer patients could one day experience fewer side effects from chemotherapy following a discovery that opens the door for more targeted treatments.
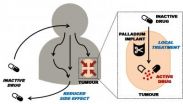
Researchers have identified a possible way of treating tumours that would see doctors place harmless metal implants at the cancer site.
The discovery could make treatment more targeted than existing therapies, avoiding unwanted side effects, such as hair loss, tiredness and nausea. These occur when chemotherapy drugs carried in the blood kill healthy cells as well as cancer cells.
The scientists found that they could alter the chemical composition of commonly used chemotherapy drugs so that they only become active when they come into contact with a metal called palladium.
Researchers hope that by implanting small devices coated with palladium into patients' tumours, the drugs would become activated only where they are needed, causing minimal damage to the rest of the body.
The scientists reported their discovery today in the journal Nature Communications but the approach will first need to be tested in animals before it can be studied in patients.
The research was led by scientists from the Edinburgh Cancer Research UK Centre at the MRC Institute of Genetics and Molecular Medicine, the University of Edinburgh.
Dr Asier Unciti-Broceta, who led the study, said: "It will be several years before we're able to start treating patients but we're hopeful that this approach will lead to better tolerated cancer therapies in the future."
INFORMATION: END
Metal implants may cut chemotherapy side effects, study suggests
2014-02-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Deutsche eMark (DEM) - Could be second cryptocurrency coin after Bitcoin
2014-02-13
Deutsche eMark is an open source peer-to-peer digital Internet currency. Deutsche eMark stands for fast and secure payments to anyone around the world, who has an eMark Wallet. Therefore no banks are required and the fees are low and simple to understand. Today price on Cryptsy Exchange is 0.00012, but experts says, that it could fast reach 0.002 DEM/BTC.
Sleep apnea common among stroke-related brainstem injuries
2014-02-13
People whose brainstems are affected by their stroke have a significantly higher prevalence of sleep apnea than those who have stroke-related injury elsewhere in the brain, according to research presented at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2014.
Sleep apnea is marked by interrupted breathing during sleep and can lead to serious health problems including heart disease and stroke.
"This is the largest population-based study to address the issue of the location of the brain injury and its relationship to sleep apnea in post-stroke patients," ...
ADHD drugs not linked to increased stroke risk among children
2014-02-13
Children who take medication to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) don't appear to be at increased stroke risk, according to a study presented at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2014.
In a study of 2.5 million 2- to 19-year-olds over a 14-year period, researchers compared stimulant medication usage in children diagnosed with ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke to stimulant usage in children without stroke.
Researchers found no association between stroke risk and the use of ADHD stimulant medications at the time of stroke ...
Worm infections in developing countries: Veterinary drugs improve the health of school children
2014-02-13
This news release is available in German.
Hookworms and whipworms are detrimental to health. Children in many developing countries in particular are prone to regular infection via contaminated soil due to a lack of latrines and clean water. Whipworm eggs enter the body via the gastrointestinal tract and evolve over several devel-opment stages. To contain the health risks of worm infections, the WHO recommends annual de-worm treatment for children and at-risk groups (such as field hands and miners). However, the recommended standard treatment appears to have little ...
New research uncovers debilitating effects of disease on toy dog breeds
2014-02-13
A new study from the University of Surrey, published today in the journal PLOS One, has identified the specific effect Chiari malformation has on the shape of a dog's skull and brain. This condition has become prevalent as a result of selective breeding and affects many toy dog breeds which have been bred to look more doll-like, including Griffon Bruxellois, Cavalier King Charles Spaniels, Chihuahuas and their crosses.
Researchers took brain, skull and vertebrae measurements of 155 Griffon Bruxellois and compared dogs affected by the condition, with normal Griffons. ...
Jawed vertebrates get a face
2014-02-13
This week in the leading journal Nature, a team of French and Swedish researchers present new fossil evidence for the origin of one of the most important and emotionally significant parts of our anatomy: the face. They show how a series of fossils, with a 410 million year old armoured fish called Romundina at its centre, documents the step-by-step assembly of the face during the evolutionary transition from jawless to jawed vertebrates.
Vertebrates (backboned animals) come in two basic models: jawless and jawed. Today, the only jawless vertebrates are lampreys and hagfishes, ...
Quality of acupuncture needles is less than perfect and must improve
2014-02-13
The quality of acupuncture needles is high, but should still be universally improved to avoid potential problems, such as pain and skin reactions, finds research published online in Acupuncture in Medicine (AiM).
Despite improvements to the manufacturing process, surface irregularities and bent tips have not been completely eliminated, say the researchers.
In China, traditional Chinese medicine including acupuncture, accounts for 40% of all medical treatment, while in the West, acupuncture is one of the most frequently used complementary therapies.
An estimated 1.4 ...
Tobacco industry claims 'plain' packs won't work based on weak evidence
2014-02-13
Tobacco companies lack strong, relevant evidence to support their claims that standardised (plain) packaging of tobacco products in the UK won't work, finds research published in the online journal BMJ Open.
The aim of plain packaging, with no logos, brand imagery, symbols, or promotional text, is to restrict the already limited opportunities that transnational tobacco companies have to market their products, and deter people from starting smoking.
Australia adopted plain packaging for tobacco products in 2012, the same year that the Department of Health in England ...
Hospitals not always prepared for full costs of implementing electronic patient records
2014-02-13
Hospitals don't always take into account the full costs of implementing new electronic health record systems and should be better prepared if they are to maximise the benefits, finds research published online in the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association (JAMIA).
Electronic health record (EHR) systems can improve the safety, quality, and efficiency of healthcare in hospitals, and their adoption is a priority for the UK and US governments.
But despite their promise and the existence of EHRs in UK primary care for several decades, UK hospitals have been ...
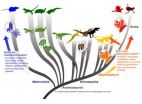
Revision to rules for color in dinosaurs suggests connection between color and physiology
2014-02-13
New research that revises the rules allowing scientists to decipher color in dinosaurs may also provide a tool for understanding the evolutionary emergence of flight and changes in dinosaur physiology prior to its origin.
In a survey comparing the hair, skin, fuzz and feathers of living terrestrial vertebrates and fossil specimens, a research team from The University of Texas at Austin, the University of Akron, the China University of Geosciences and four other Chinese institutions found evidence for evolutionary shifts in the rules that govern the relationship between ...