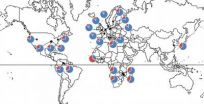
(Press-News.org) People living in cold, northern latitudes have bacteria in their guts that may predispose them to obesity, according to a new study by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, and the University of Arizona, Tucson.
The researchers' analysis of the gut microbes of more than a thousand people from around the world showed that those living in northern latitudes had more gut bacteria that have been linked to obesity than did people living farther south.
The meta-analysis of six earlier studies by UC Berkeley graduate student Taichi Suzuki and evolutionary biology professor Michael Worobey of the University of Arizona appeared this week in the online journal Biology Letters.
"People think obesity is a bad thing, but maybe in the past getting more fat and more energy from the diet might have been important to survival in cold places. Our gut microbes today might be influenced by our ancestors," said Suzuki, noting that one theory is that obesity-linked bacteria are better at extracting energy from food. "This suggests that what we call 'healthy microbiota' may differ in different geographic regions."
"This observation is pretty cool, but it is not clear why we are seeing the relationship we do with latitude," Worobey said. "There is something amazing and weird going on with microbiomes."
To Worobey, the results are fascinating from an evolutionary biology perspective. "Maybe changes to your gut community of bacteria are important for allowing populations to adapt to different environmental conditions in lots of animals, including humans," he said.
Suzuki proposed the study while rotating through Worobey's lab during his first year as a graduate student at the University of Arizona. Studies of gut microbes have become a hot research area among scientists because the proportion of different types of bacteria and Archaea in the gut seems to be correlated with diseases ranging from diabetes and obesity to cancer. In particular, the group of bacteria called Firmicutes seems to dominate in the intestines of obese people – and obese mice – while a group called Bacteroidetes dominates in slimmer people and mice.
Suzuki reasoned that, since animals and humans in the north tend to be larger in size – an observation called Bergmann's rule – then perhaps their gut microbiota would contain a greater proportion of Firmicutes than Bacteriodetes. While at the University of Arizona, and since moving to UC Berkeley, Suzuki has been studying how rodents adapt to living at different latitudes.
"It was almost as a lark," Woroby said. "Taichi thought that if Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes are linked to obesity, why not look at large scale trends in humans. When he came back with results that really showed there was something to it, it was quite a surprise."
Suzuki used data published in six previous studies, totaling 1,020 people from 23 populations in Africa, Europe, North and South America and Asia. The data on gut microbiomes were essentially censuses of the types and numbers of bacteria and Archaea in people's intestinal track.
He found that the proportion of Firmicutes increased with latitude and the proportion of Bacteriodetes decreased with latitude, regardless of sex, age, or detection methods. African Americans showed the same patterns as Europeans and North Americans, not the pattern of Africans living in tropical areas.
"Bergmann's rule – that body size increases with latitude for many animals – is a good one and presumed to be an adaptation for dealing with cold environments," said Suzuki's advisor Michael Nachman, professor of integrative biology and director of UC Berkeley's Museum of Vertebrate Zoology. "Whether gut microbes also help explain Bergmann's rule will require experimental tests, but Taichi's discovery adds an intriguing and completely overlooked piece of the puzzle to this otherwise well-studied evolutionary pattern."
INFORMATION: END
Geographic variation of human gut microbes tied to obesity
People in northern latitudes have greater proportion of obesity-related bacteria in gut
2014-02-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
What do women want? It depends on the time of the month
2014-02-14
If she loves you and then she loves you not, don't blame the petals of that daisy. Blame evolution.
UCLA researchers analyzed dozens of published and unpublished studies on how women's preferences for mates change throughout the menstrual cycle. Their findings suggest that ovulating women have evolved to prefer mates who display sexy traits – such as a masculine body type and facial features, dominant behavior and certain scents – but not traits typically desired in long-term mates.
So, desires for those masculine characteristics, which are thought to have been ...
Another reason to not mix work and family: Money makes parenting less meaningful
2014-02-14
Austin – February 14, 2014 - Money and parenting don't mix. That's according to new research that suggests that merely thinking about money diminishes the meaning people derive from parenting. The study is one among a growing number that identifies when, why, and how parenthood is associated with happiness or misery.
"The relationship between parenthood and well-being is not one and the same for all parents," says Kostadin Kushlev of the University of British Columbia. While this may seems like an obvious claim, social scientists until now have yet to identify the psychological ...
In-hospital formula use deters breastfeeding
2014-02-14
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — When mothers feed their newborns formula in the hospital, they are less likely to fully breastfeed their babies in the second month of life and more likely to quit breastfeeding early, even if they had hoped to breastfeed longer, UC Davis researchers have found.
"We are a step closer to showing that giving formula in the hospital can cause problems by reducing how much women breastfeed later," says Caroline Chantry, lead author and professor of clinical pediatrics at UC Davis Medical Center. "Despite being highly motivated to breastfeed their babies, ...
Superbright and fast X-rays image single layer of proteins
2014-02-14
RICHLAND, Wash. -- In biology, a protein's shape is key to understanding how it causes disease or toxicity. Researchers who use X-rays to takes snapshots of proteins need a billion copies of the same protein stacked and packed into a neat crystal. Now, scientists using exceptionally bright and fast X-rays can take a picture that rivals conventional methods with a sheet of proteins just one protein molecule thick.
Using a type of laser known as XFEL, the technique opens the door to learning the structural details of almost 25 percent of known proteins, many of which have ...
Head, neck injuries may increase stroke risk among trauma patients younger than 50
2014-02-14
Suffering an injury to the head or neck increases ischemic stroke risk three-fold among trauma patients younger than 50, according to research presented at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2014.
"These findings are important because strokes after trauma might be preventable," said Christine Fox, M.D., M.A.S., lead author and assistant professor of neurology at the University of California San Francisco.
Researchers studied the health records of 1.3 million patients younger than 50 years who had been treated in emergency trauma rooms. ...
Hispanic stroke patients less likely to receive clot-busting drugs in
2014-02-14
Hispanic stroke patients admitted to hospitals in the border states of California, Arizona, New Mexico and Texas were less likely than non-Hispanics in the same border states to receive clot-busting drugs and more likely to die, according to research presented at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2014.
Researchers analyzed stroke care for Hispanic and non-Hispanic patients according to demographics and clinical characteristics in states bordering Mexico and states not on the Mexican border. They found:
Of the nearly 35,000 Hispanic stroke ...
Stroke survivors often return to driving without being evaluated for ability
2014-02-14
Stroke survivors often resume driving without being formally evaluated for ability — though stroke can cause deficits that can impair driving, according to research presented at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2014.
Researchers surveyed 162 stroke survivors a year after their strokes and found:
More than 51 percent returned to driving — many a month after suffering a stroke.
Only 5.6 percent received a formal driving evaluation.
Eleven percent of those who returned to driving reported their strokes had greatly impacted their abilities ...
What makes the newborn immune system in the lungs different and vulnerable?
2014-02-14
Newborns are more susceptible to infections, presumably because of their immature and inexperienced immune systems. The most common dangerous condition in newborns and infants are lower respiratory tract infections caused by viruses, especially respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). A study published on February 13th in PLOS Pathogens shows how the immune system in the lungs during early life differs from the one in older children and adults.
Ideally, newborns could be protected against RSV by vaccination, but it is known that the immune system in early life is less responsive ...
Intensive dialysis in pregnant women with kidney failure benefits mother and baby
2014-02-14
Washington, DC (February 13, 2014) — Intensive dialysis treatments in pregnant women with kidney failure lead to a higher proportion of live births than standard dialysis care, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (JASN). The findings suggest that more frequent and longer dialysis sessions should be considered for dialysis patients of childbearing age who want to become pregnant or who are already pregnant.
When young women develop advanced kidney disease, pregnancy becomes dangerous and often impossible ...
Wealthy neighborhoods fuel materialistic desires, study says
2014-02-14
SAN FRANCISCO -- Where you live could affect whether or not you spend compulsively, according to new research from San Francisco State University published today in the Journal of Consumer Culture.
Individuals who live in wealthy neighborhoods are more likely to have materialistic values and poor spending habits, the study says, particularly if they are young, living in urban areas and relatively poor compared with their surroundings. The study is the first to show a connection between neighborhood socioeconomic status and materialism.
The reason for the link, said ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
Adults with concurrent hearing and vision loss report barriers and challenges in navigating complex, everyday environments
Breast cancer stage at diagnosis differs sharply across rural US regions
Concrete sensor manufacturer Wavelogix receives $500,000 grant from National Science Foundation
California communities’ recovery time between wildfire smoke events is shrinking
Augmented reality job coaching boosts performance by 79% for people with disabilities
Medical debt associated with deferring dental, medical, and mental health care
AAI appoints Anand Balasubramani as Chief Scientific Programs Officer
Prior authorization may hinder access to lifesaving heart failure medications
Scholars propose transparency, credit and accountability as key principles in scientific authorship guidelines
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
[Press-News.org] Geographic variation of human gut microbes tied to obesityPeople in northern latitudes have greater proportion of obesity-related bacteria in gut