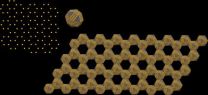
(Press-News.org) A new breed of ultra thin super-material has the potential to cause a technological revolution. "Artificial graphene" should lead to faster, smaller and lighter electronic and optical devices of all kinds, including higher performance photovoltaic cells, lasers or LED lighting.
For the first time, scientists are able to produce and have analysed artificial graphene from traditional semiconductor materials. Such is the scientific importance of this breakthrough these findings were published recently in one of the world's leading physics journals, Physical Review X. A researcher from the University of Luxembourg played an important role in this highly innovative work.
Graphene (derived from graphite) is a one atom thick honeycomb lattice of carbon atoms. This strong, flexible, conducting and transparent material has huge scientific and technological potential. Only discovered in 2004, there is a major global push to understand its potential uses. Artificial graphene has the same honeycomb structure, but in this case, instead of carbon atoms, nanometer-thick semiconductor crystals are used. Changing the size, shape and chemical nature of the nano-crystals, makes it possible to tailor the material to each specific task.
The University of Luxembourg is heavily involved in cross-border, multidisciplinary research projects. In this case it partnered with the Institute for Electronics, Microelectronics, and Nanotechnology (IEMN) in Lille, France, the Debye Institute for Nanomaterials Science and the Institute for Theoretical Physics of the University of Utrecht, Netherlands and the Max Planck Institute for the Physics of Complex Systems in Dresden, Germany.
University of Luxembourg researcher Dr. Efterpi Kalesaki is the first author of the article appearing in the Physical Review X. Dr. Kalesaki said: "these self-assembled semi-conducting nano-crystals with a honeycomb structure are emerging as a new class of systems with great potential." Prof Ludger Wirtz, head of the Theoretical Solid-State Physics group at the University of Luxembourg, added: "artificial graphene opens the door to a wide variety of materials with variable nano-geometry and 'tunable' properties."
INFORMATION:
The full scientific article can be viewed here: http://prx.aps.org/abstract/PRX/v4/i1/e011010
About the Physics and Materials Science Research Unit
The Physics and Materials Science Research Unit of the University of Luxembourg focuses on condensed matter physics. Its activities cover the whole field from the electronic structure of crystals to the thermodynamics of soft matter. Experimental and theoretical groups join forces to understand and develop materials.
Physicists produce a potentially revolutionary material
Global recognition for a novel form of artificial graphene
2014-02-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Penn study: Topiramate reduces heavy drinking in patients seeking to cut down on alcohol consumption
2014-02-14
PHILADELPHIA – Heavy drinking is common in the United States and takes a personal and societal toll, with an annual estimated cost of $223.5 billion due to losses in workplace productivity, health care and criminal justice expenses. Data shows that 23 percent of individuals age 12 or older reported drinking five or more drinks on one occasion in the previous month, and almost seven percent reported doing so on at least five days per month. Despite this, few heavy drinkers seek out treatment—especially those who do not meet the clinical criteria for an alcohol use disorder, ...
Rice's carbon nanotube fibers outperform copper
2014-02-14
On a pound-per-pound basis, carbon nanotube-based fibers invented at Rice University have greater capacity to carry electrical current than copper cables of the same mass, according to new research.
While individual nanotubes are capable of transmitting nearly 1,000 times more current than copper, the same tubes coalesced into a fiber using other technologies fail long before reaching that capacity.
But a series of tests at Rice showed the wet-spun carbon nanotube fiber still handily beat copper, carrying up to four times as much current as a copper wire of the same ...
Tinnitus study signals advance in understanding link between loud sounds exposure and hearing loss
2014-02-14
A research team investigating tinnitus, from the University of Leicester, has revealed new insights into the link between the exposure to loud sounds and hearing loss.
Their study, published this week in Neuroscience, helps to understand how damage to myelin – a protection sheet around cells - alters the transmission of auditory signals occurring during hearing loss.
The three-year study was derived from a PhD studentship funded by Action on Hearing Loss. It was led by Dr Martine Hamann, Lecturer in Neurosciences at the University's Department of Cell Physiology and ...
Pregnancy study leads to fewer high birth weight babies
2014-02-14
The world's biggest study offering healthy eating and exercise advice to pregnant women who are overweight or obese has shown a significant reduction in the number of babies born over 4kg (8.8 pounds) in weight.
The LIMIT Study, led by researchers from the University of Adelaide's Robinson Institute and the Women's and Children's Hospital, involved more than 2200 pregnant women from 2008-2011.
In the first major results from the LIMIT Study, published this week in the British Medical Journal, the researchers say that providing advice and assistance to adopt a healthy ...
A strategy that narrows academic achievement gap by 63 percent
2014-02-14
Americans don't like to talk about social class. But new research from Northwestern and Stanford universities suggests that, at least in college and university settings, they should do just that.
An upcoming article in "Psychological Science" describes a novel one-hour intervention that closed by 63 percent the persistent academic achievement gap between first-generation college students and continuing-generation students. (Continuing-generation students are defined as those with at least one parent with a four-year college degree.)
The key to the one-time intervention's ...
BU researcher to present at AAAS 2014 annual meeting in Chicago
2014-02-14
BOSTON – Dr. Raquell Holmes, an assistant research professor at Boston University's Center for Computational Science, will be a featured presenter at the 2014 annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in Chicago, February 15, 2014. Dr. Holmes will participate in a panel session titled, "Improvisation for Scientists: Making a Human Connection" on February 16, 2014 at 9:15 am.
Efforts to "communicate science" have been a rallying cry from governmental agencies, elected officials and citizens in need of accurate and accessible information ...
Even fact will not change first impressions
2014-02-14
February 14, 2014 - Knowledge is power, yet new research suggests that a person's appearance alone can trump knowledge. First impressions are so powerful that they can override what we are told about people. A new study found that even when told whether a person was gay or straight, participants generally identified the person's sexual orientation based on how they looked – even if it contradicted the facts presented to them.
"We judge books by their covers, and we can't help but do it," says Nicholas Rule of the University of Toronto. "With effort, we can overcome this ...
Blacks, Hispanics, older people not benefitting equally from better colon cancer treatment
2014-02-14
ATLANTA – February 14, 2014—While new and better treatments have improved the odds of survival for patients diagnosed late stage colorectal cancer, that progress has been largely confined to non-Hispanic whites and Asians and those under age 65, according to a new study. American Cancer Society researchers led by Helmneh Sineshaw, M.D., MPH, find there have been no significant increases in survival rates for Hispanics and non-Hispanic blacks with metastatic colon cancer. The study, appearing in the January issue of Cancer Causes and Control, concludes that the findings ...
Crab nebula of life
2014-02-14
Crabs -- those sometimes pesky, hard-shelled beachcombers -- are a highly diverse animal, with some 7,000 species found in oceans, lakes and on land, varying in size from the diminutive pea crab (millimeters) to the giant 4 meter-wide Japanese spider crab.
Chu, et.al., have constructed the most complete and extensive dataset to date. Their recalibrated crab gene tree using DNA and mitochondrial sequences from 140 species and 58 crab families provides some new important insights into the timing and diversity of crab evolution.
The research team's estimates confirm the ...
Metabolism gives a boost to understanding plant and animal nutrient evolution
2014-02-14
For the ancient ancestors of plants and animals, a partnership with other microbes was once formed during an endosymbiotic event to give rise to eukaryotes. Plants and animals, over billions of years of trial and error, made efficient use of different energy sources in the environment, namely carbon dioxide and oxygen.
In the advanced online edition of Molecular Biology and Evolution, authors Maurino, et. al., explore the evolution of a family of enzymes, called 2-hydroxy acid oxidase, or 2-HAOX, that break down fats in both plant and animals. They wanted to test and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
[Press-News.org] Physicists produce a potentially revolutionary materialGlobal recognition for a novel form of artificial graphene