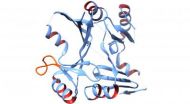
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON D.C. Feb. 16, 2014 -- A research team from Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn., is the first to decipher the 3-D structure of a protein that confers antibiotic resistance from one of the most worrisome disease agents: a strain of bacteria called methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), which can cause skin and other infections. The Vanderbilt team's findings may be an important step in combatting the MRSA public health threat over the next 5 to 10 years.
By deciphering the shape of a key S. aureus protein -- an enzyme called FosB that inactivates an antibiotic called fosfomycin -- the researchers have set the stage to devising a therapeutic method to inhibit FosB and hence improve the efficacy of the antibiotic. The team will present its work at the 58th Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society, held Feb. 15-19, 2014, in San Francisco, Calif.
"Our hope is that now that we know the 3-D shape and overall function of the FosB protein, we will be able to design inhibitors of FosB that will enable fosfomycin to function appropriately as an antibiotic," said Matthew K. Thompson, a postdoctoral researcher on the team. "When we can successfully do that, we may very well be able to combat S. aureus infections with fosfomycin."
Identifying the FosB protein's three-dimensional structure helps scientists understand that protein's particular function. In particular, the new structural images of FosB, obtained by a technique called X-ray crystallography, provide insight into the functional role of a particular part of the protein's shape called a binding loop. It appears to function like a door that opens and closes to allow the antibiotic to enter the active site of FosB.
In addition to providing new insight on the function of this S. aureus protein, the research has also produced new evidence for the role zinc might play in inhibiting FosB. This could impact restoring the efficacy of fosfomycin, leading to treatment for a variety of multi-drug-resistant pathogens.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control (CDC) and Prevention, MRSA poses a serious risk to public health. Studies show that about one in three people carry S. aureus in their nose, usually without any illness, and two in 100 people carry the methicillin-resistant version of the bacteria, though there is no data to show the total number of people who get MRSA skin infections.
INFORMATION:
The presentation "Structure and Function of the Genomically-encoded Fosfomycin Resistance Enzyme, FOSB, from Staphylococcus aureus" by Matthew K. Thompson, Michael Goodman, Mary Keithly, Neal Hammer, Paul Cook, Kevin Jafessar, Joel Harp, Eric Skaar and Richard N. Armstrong will be at 1:45 p.m. on Sunday, February 16, 2014 in Hall D in San Francisco's Moscone Convention Center.
ABSTRACT: http://tinyurl.com/kxmcerd
More Information on MRSA from the CDC:
http://www.cdc.gov/mrsa/community/index.html
ABOUT THE MEETING
Each year, the Biophysical Society Annual Meeting brings together more than 7,000 researchers working in the multidisciplinary fields representing biophysics. With more than 4,200 poster presentations, over 200 exhibits, and more than 20 symposia, the BPS Annual Meeting is the largest meeting of biophysicists in the world. Despite its size, the meeting retains its small-meeting flavor through its subgroup symposia, platform sessions, social activities, and committee programs.
The 58th Annual Meeting will be held at the Moscone Convention Center, 747 Howard Street, San Francisco, California.
PRESS REGISTRATION
The Biophysical Society invites professional journalists, freelance science writers and public information officers to attend its Annual Meeting free of charge. For press registration, contact Alisha Yocum at ayocum@biophysics.org or Jason Bardi at 240-535-4954.
QUICK LINKS
Main Meeting Page: http://tinyurl.com/mfjh37p
Program Highlights: http://tinyurl.com/mosxrof
Abstracts Search: http://tinyurl.com/lbrearu
ABOUT THE SOCIETY
The Biophysical Society, founded in 1958, is a professional, scientific Society established to encourage development and dissemination of knowledge in biophysics. The Society promotes growth in this expanding field through its annual meeting, monthly journal, and committee and outreach activities. Its 9000 members are located throughout the U.S. and the world, where they teach and conduct research in colleges, universities, laboratories, government agencies, and industry. For more information on the Society, or the 2014 Annual Meeting, visit http://www.biophysics.org
Bacterial superbug protein structure solved
3-D structure of antibiotic-resistance protein, described at 58th Biophysical Society Meeting, may lead to new tools for fighting MRSA
2014-02-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Harvesting light, the single-molecule way
2014-02-17
WASHINGTON D.C. Feb. 16, 2014 -- New insights into one of the molecular mechanisms behind light harvesting, the process that enables photosynthetic organisms to thrive, even as weather conditions change from full sunlight to deep cloud cover, will be presented at the 58th Annual Biophysical Society Meeting, taking place in San Francisco from Feb. 15-19.
At the meeting, Hsiang-Yu Yang, a graduate student, and Gabriela Schlau-Cohen, a postdoc in W.E. Moerner's research group at Stanford University, will describe how probing these natural systems at the single molecule level ...
Deep ocean needs policy, stewardship where it never existed
2014-02-17
BEAUFORT, N.C. -- Technological advances have made the extraction of deep sea mineral and precious metal deposits feasible, and the dwindling supply of land-based materials creates compelling economic incentives for deep sea industrialization. But at what cost?
“We’re really in the dark when it comes to the ecology of the deep sea," said Linwood Pendleton, director of the Ocean and Coastal Policy Program at the Nicholas Institute for Environmental Policy Solutions at Duke University. "We know a lot about a few places, but nobody is dealing with the deep sea as a whole, ...
Obesity in Samoa: A global harbinger?
2014-02-17
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — The South Pacific archipelago of Samoa and American Samoa harbors a global health mystery that may seem both remote and extreme but could foretell trends in obesity and related conditions across much of the developing world.
About three-quarters of the U.S. territory's adult population is obese, the highest rate in the world with independent Samoa quickly catching up. Rates of type 2 diabetes top one in five and a recent study found that the elevated obesity rates are present even in newborns.
This pandemic began only a few decades ...
Global perspectives on human biology and health
2014-02-17
CHICAGO --- Three anthropology professors from the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences at Northwestern University will highlight recent research in biological anthropology Sunday, Feb. 16 at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) in Chicago.
The presentations, part of the symposium "Comparative Advantage: Global Perspectives on Human Biology and Health" will be held from 1:30 to 4:30 p.m. in Crystal Ballroom A at the Hyatt Regency Chicago.
Christopher Kuzawa, professor of anthropology and faculty fellow at the Institute ...
Nanoelectronics key to advances in renewable energy
2014-02-17
TEMPE, Ariz. – Nanoscale technology looks promising as a major contributor to advancements needed to fulfill the potential of emerging sources of clean, renewable energy.
Progress in the comparatively new area of nanoelectronics in particular could be the basis for new manufacturing processes and devices to make renewable energy systems and technologies more efficient and cost-effective.
Stephen Goodnick will focus on what nanoelectronics advances could do to help push the performance of solar energy systems to the next level in his talk at the 2014 annual meeting of ...
Epigenetic regulation required to ensure correct number of chromosomes
2014-02-17
Abnormal number of chromosomes is often associated with cancer development. In a new study published in the journal Nature Structural and Molecular Biology researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have shown that a subtle epigenetic change plays an important role in the correct segregation of chromosomes.
Normally when a cell divides, the chromosomes are segregated equally to two daughter cells. However, tumour cells frequently have either too few or too many chromosomes, leading to the incorrect expression of a number of genes. When a cell is about to divide, the ...
New eye layer has possible link to glaucoma
2014-02-17
A new layer in the human cornea — discovered by researchers at The University of Nottingham
last year — plays a vital role in the structure of the tissue that controls the flow of fluid
from the eye, research has shown. The findings, published in a paper in the British
Journal of Ophthalmology, could shed new light on glaucoma, a devastating disease caused by
defective drainage of fluid from the eye and the world's second leading cause of blindness.
The latest research shows that the new layer, dubbed Dua's Layer after the academic Professor
Harminder Dua who ...
Researchers hijack cancer migration mechanism to 'move' brain tumors
2014-02-17
One factor that makes glioblastoma cancers so difficult to treat is that malignant cells from the tumors spread throughout the brain by following nerve fibers and blood vessels to invade new locations. Now, researchers have learned to hijack this migratory mechanism, turning it against the cancer by using a film of nanofibers thinner than human hair to lure tumor cells away.
Instead of invading new areas, the migrating cells latch onto the specially-designed nanofibers and follow them to a location – potentially outside the brain – where they can be captured and killed. ...
U of M study finds fertilization destabilizes global grassland ecosystems
2014-02-17
A new study led by University of Minnesota researchers demonstrates that fertilization of natural grasslands -- either intentionally or unintentionally as a side effect of global farming and industry -- is having a destabilizing effect on global grassland ecosystems. Using a network of natural grassland research sites around the world called the Nutrient Network, the study represents the first time such a large experiment has been conducted using naturally occurring sites.
Led by Yann Hautier, a Marie Curie Fellow associated with both the Department of Ecology, Evolution, ...
New study shows growing opposition to animal tests
2014-02-17
Chicago — Americans' moral opposition to animal testing
has grown significantly since 2001, according to a new study presented today at the annual
meeting of the prestigious American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) in
Chicago. Researchers from PETA and Western Governors University examined data collected
in independent surveys by the Gallup organization from 2001 to 2013, in which approximately
1,000 American adults each year were asked whether they found "medical testing on animals" to be
"morally acceptable" or "morally wrong."
The researchers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
[Press-News.org] Bacterial superbug protein structure solved3-D structure of antibiotic-resistance protein, described at 58th Biophysical Society Meeting, may lead to new tools for fighting MRSA