(Press-News.org) Daejeon, Republic of Korea, February 17, 2014 – Walking around the streets searching for a place to eat will be no hassle when a head-mounted display (HMD) becomes affordable and ubiquitous. Researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) developed K-Glass, a wearable, hands-free HMD that enables users to find restaurants while checking out their menus. If the user of K-Glass walks up to a restaurant and looks at the name of the restaurant, today's menu and a 3D image of food pop up. The Glass can even show the number of tables available inside the restaurant. K-Glass makes this possible because of its built-in augmented reality (AR) processor.
Unlike virtual reality which replaces the real world with a computer-simulated environment, AR incorporates digital data generated by the computer into the reality of a user. With the computer-made sensory inputs such as sound, video, graphics or GPS data, the user's real and physical world becomes live and interactive. Augmentation takes place in real-time and in semantic context with surrounding environments, such as a menu list overlain on the signboard of a restaurant when the user passes by it, not an airplane flight schedule, which is irrelevant information, displayed.
Most commonly, location-based or computer-vision services are used in order to generate AR effects. Location-based services activate motion sensors to identify the user's surroundings, whereas computer-vision uses algorithms such as facial, pattern, and optical character recognition, or object and motion tracking to distinguish images and objects. Many of the current HMDs deliver augmented reality experiences employing location-based services by scanning the markers or barcodes printed on the back of objects. The AR system tracks the codes or markers to identify objects and then align them with virtual reality. However, this AR algorithm is difficult to use for the objects or spaces which do not have barcodes, QR codes, or markers, particularly those in outdoor environments and thus cannot be recognized.
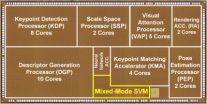
To solve this problem, Hoi-Jun Yoo, Professor of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and his team developed, for the first time in the world, an AR chip that works just like human vision. This processor is based on the Visual Attention Model (VAM) that duplicates the ability of human brain to process visual data. VAM, almost unconsciously or automatically, disentangles the most salient and relevant information about the environment in which human vision operates, thereby eliminating unnecessary data unless they must be processed. In return, the processor can dramatically speed up the computation of complex AR algorithms.
The AR processor has a data processing network similar to that of a human brain's central nervous system. When the human brain perceives visual data, different sets of neurons, all connected, work concurrently on each fragment of a decision-making process; one group's work is relayed to other group of neurons for the next round of the process, which continues until a set of decider neurons determines the character of the data. Likewise, the artificial neural network allows parallel data processing, alleviating data congestion and reducing power consumption significantly.
KAIST's AR processor, which is produced using the 65 nm (nanometers) manufacturing process with the area of 32 mm2, delivers 1.22 TOPS (tera-operations per second) peak performance when running at 250 MHz and consumes 778 miliWatts on a 1.2V power supply. The ultra-low power processor shows 1.57 TOPS/W high efficiency rate of energy consumption under the real-time operation of 30fps/720p video camera, a 76% improvement in power conservation over other devices. The HMDs, available on the market including the Project Glass whose battery lasts only for two hours, have revealed so far poor performance. Professor Yoo said, "Our processor can work for long hours without sacrificing K-Glass's high performance, an ideal mobile gadget or wearable computer, which users can wear for almost the whole day."
He further commented:
"HMDs will become the next mobile device, eventually taking over smartphones. Their markets have been growing fast, and it's really a matter of time before mobile users will eventually embrace an optical see-through HMD as part of their daily use. Through augmented reality, we will have richer, deeper, and more powerful reality in all aspects of our life from education, business, and entertainment to art and culture."
The KAIST team presented a research paper at the International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) held on February 9-13, 2014 in San Francisco, CA, which is entitled "1.22TOPS and 1.52mW/MHz Augmented Reality Multi-Core Processor with Neural Network NoC for HMD Applications."
YouTube video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fzQpSORKYr8&list=TLrzHjmO535jH3qTBrgVGED3MAA74i2-WX (K-Glass with Augmented Reality)
INFORMATION:
For further inquires:
Hoi-Jun Yoo
Professor of Electrical Engineering, KAIST
Tel: +82-42-350-3468
Email: hjyoo@ee.kaist.ac.kr
http://ssl.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST developed low-powered, high-speed head-mounted display with augment reality chip
2014-02-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gender and genes play an important role in delayed language development
2014-02-18
Boys are at greater risk for delayed language development than girls, according to a new study using data from the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study. The researchers also found that reading and writing difficulties in the family gave an increased risk.
"We show for the first time that reading and writing difficulties in the family can be the main reason why a child has a speech delay that first begins between three to five years of age," says Eivind Ystrøm, senior researcher at the Norwegian Institute of Public Health.
Ystrøm was supervisor of Imac Maria Zambrana, ...
Researchers identify new way to control stone fruit disease
2014-02-18
Researchers at the University of Kent and East Malling Research have identified a new way of controlling a fungal disease that can have a devastating impact on the UK's valuable cherry and plum crops.
Brown rot disease – caused by the agent Monilinia laxa – attacks stone fruit as well as causing blossom wilt and twig canker. Traditionally, this has been controlled through the use of fungicide treatments, but in some cases these are now becoming ineffective.
Now researchers from the two organisations have identified a new strategy for controlling the disease, using biological ...
In search of lost genes
2014-02-18
How do new genes arise? Current research shows that so-called "orphan genes" may appear as if by magic as a result of mutations in segments of DNA that previously had no function. Orphan genes were first discovered in the fruit fly but are found in all organisms, including man. Strikingly, up to 30 per cent of the total number of genes in an organism may be orphans and these genes may rapidly acquire functions. Scientists from the Institute of Population Genetics of the University of Veterinary Medicine, Vienna (Vetmeduni) have now investigated the fate of orphan genes. ...
HIV drug used to reverse effects of virus that causes cervical cancer
2014-02-18
A commonly-used HIV drug has been shown to kill-off the human papilloma virus (HPV) that leads to cervical cancer in a world-first clinical trial led by The University of Manchester with Kenyatta National Hospital (KNH) in Nairobi.
Drs Ian and Lynne Hampson, from the University's Institute of Cancer Sciences and Dr Innocent Orora Maranga, Consultant in Obstetrics and Gynaecology at KNH in Nairobi examined Kenyan women diagnosed with HPV positive early stage cervical cancer who were treated with the antiviral HIV drug lopinavir in Kenya.
The study looked at 40 women ...
Leeds researchers build world's most powerful terahertz laser chip
2014-02-18
A paper in the Institution of Engineering and Technology's (IET) journal Electronics Letters reports that the Leeds team has exceeded a 1 Watt output power from a quantum cascade terahertz laser.
The new record more than doubles landmarks set by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and subsequently by a team from Vienna last year.
Terahertz waves, which lie in the part of the electromagnetic spectrum between infrared and microwaves, can penetrate materials that block visible light and have a wide range of possible uses including chemical analysis, security ...
The conditions for a society to become a democracy are analyzed
2014-02-18
This news release is available in Spanish. In view of the changes that have taken place in Europe,JuleGoikoetxea, a lecturer at the UPV/EHU's Faculty of Social Sciences and Communication, has been conducting research into "the conditions needed for a people to become a democracy or sustain its democratisation process over time."The study has been published in the specialised journal Nationalities Papers.
According to Goikoetxea, nation is not synonymous with demos: "The nation is the will, socially and historically articulated, that a group has in order to be a political ...
Researchers shed new light on the genetic history of the European beaver
2014-02-18
An international team of scientists has used detailed analysis of ancient and modern DNA to show that the distribution and lack of genetic diversity among modern European beavers is due largely to human hunting.
The research, which was led by University of York researcher Professor Michi Hofreiter, provides important new insights into the genetic history of the Eurasian beaver Castor fiber. Crucially, it shows the European beaver has been strongly affected by expanding human populations for many thousands of years.
The researchers say that centuries of hunting, rather ...
Surprising survey: Most small businesses remain silent rather than report employee theft
2014-02-18
In a recent survey of small businesses, a University of Cincinnati criminal justice researcher has found that only 16 percent of those that have experienced theft by employees actually reported that theft to the police.
That's even though 64 percent of the small businesses surveyed reported experiencing employee theft.
These are some of the findings in a survey of small businesses that examined the incidence of employee theft, how often it was reported, the types of goods taken by employees, the types of employees most likely to commit theft, and the reasons the business ...
Einstein's conversion from a static to an expanding universe
2014-02-18
Until 1931, physicist Albert Einstein believed that the universe was static. An urban legend attributes this change of perspective to when American astronomer Edwin Hubble showed Einstein his observations of redshift in the light emitted by far away nebulae—today known as galaxies. But the reality is more complex. The change in Einstein's viewpoint, in fact, resulted from a tortuous thought process. Now, in an article published in EPJ H, Harry Nussbaumer from the Institute of Astronomy at ETH Zurich, Switzerland, explains how Einstein changed his mind following many encounters ...
Daily walk of just 3km can reduce risk of hospitalization for respiratory problems
2014-02-18
New research in Respirology shows that suffers of Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can reduce their risk of being hospitalized with severe attacks, by maintaining an exercise regime of walking between three to six kilometers a day.
COPD, a term which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, results in breathing difficulties due to long-term lung damage. Severe symptoms (eCOPD), caused by a sudden loss of lung function, can be life threatening.
543 COPD patients were recruited from five Spanish respiratory clinics and their exercise levels were calculated ...