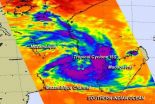
(Press-News.org) NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Cyclone 15S as it formed in the Mozambique Channel on Feb. 18 and the AIRS instrument aboard gathered infrared data on its cloud top temperatures and potential.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical cyclone 15S on Feb. 18 at 10:53 a.m. EST. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument captured infrared data on the tropical system that showed the highest cloud tops and strongest thunderstorms were in a band that stretched from the east to the south of the center. Cloud top temperatures were near -63F/-52C, indicating high, powerful thunderstorms with potential for heavy rainfall. The eastern-most edge was over western Madagascar and the southwestern extent reached Mozambique on the African mainland.
On February 18 at 1500 UTC/10 a.m. EST, Tropical Cyclone 15S had maximum sustained winds near 35 knots/40 mph/62 kph, making it a tropical storm. 15S was centered near 18.3 south and 40.3 east, about 375 nautical miles/431.5 miles/694.5 km west of Antananarivo, Madagascar. It was moving to the south at 5 knots/5.7 mph/9.2 kph and is expected to strengthen to hurricane-force over the next couple of days. It is generating 10 foot high waves in the Mozambique Channel.
Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center expect 15S to drift south through the Mozambique Channel over the next couple of days and emerge in the Southern Indian Ocean in cooler waters.
INFORMATION:
NASA sees Tropical Cyclone 15S form in the Mozambique Channel
2014-02-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Agricultural productivity loss as a result of soil and crop damage from flooding
2014-02-18
URBANA, Ill. – The Cache River Basin, which once drained more than 614,100 acres across six southern Illinois counties, has changed substantively since the ancient Ohio River receded. The basin contains a slow-moving, meandering river; fertile soils and productive farmlands; deep sand and gravel deposits; sloughs and uplands; and one of the most unique and diverse natural habitats in Illinois and the nation.
According to a recent University of Illinois study, the region's agricultural lands dodged a bullet due to the timing of the great flood of April 2011 when the Ohio ...
GW spirituality and health pioneer publishes paper on development of the field
2014-02-18
WASHINGTON (Feb. 18, 2014) — While spirituality played a significant role in health care for centuries, technological advances in the 20th century overshadowed this more human side of medicine. Christina Puchalski, M.D.'94, RESD'97, founder and director of the George Washington University (GW) Institute for Spirituality and Health and professor of medicine at the GW School of Medicine and Health Sciences (SMHS), and co-authors published a commentary in Academic Medicine on the history of spirituality and health, the movement to reclaim medicine's spiritual roots, and the ...
Neuropsychological assessment more efficient than MRI for tracking disease progression
2014-02-18
Amsterdam, NL, February 18, 2014 – Investigators at the University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands, have shown that progression of disease in memory clinic patients can be tracked efficiently with 45 minutes of neuropsychological testing. MRI measures of brain atrophy were shown to be less reliable to pick up changes in the same patients.
This finding has important implications for the design of clinical trials of new anti-Alzheimer drugs. If neuropsychological assessment is used as the outcome measure or "gold standard," fewer patients would be needed to conduct such ...
Artificial cells and salad dressing
2014-02-18
RIVERSIDE, Calif. (http://www.ucr.edu) — A University of California, Riverside assistant professor of engineering is among a group of researchers that have made important discoveries regarding the behavior of a synthetic molecular oscillator, which could serve as a timekeeping device to control artificial cells.
Elisa Franco, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering at UC Riverside's Bourns College of Engineering, and the other researchers developed methods to screen thousands of copies of this oscillator using small droplets. They found, surprisingly, that the ...
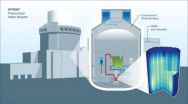
CASL, Westinghouse simulate neutron behavior in AP1000 reactor core
2014-02-18
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Feb. 18, 2014 — Scientists and engineers developing more accurate approaches to analyzing nuclear power reactors have successfully tested a new suite of computer codes that closely model "neutronics" — the behavior of neutrons in a reactor core.
Technical staff at Westinghouse Electric Company, LLC, supported by the research team at the Consortium for Advanced Simulation of Light Water Reactors (CASL), used the Virtual Environment for Reactor Applications core simulator (VERA-CS) to analyze its AP1000 advanced pressurized water reactor (PWR). The testing ...
SDSC/UC San Diego researchers hone in on Alzheimer's disease
2014-02-18
Researchers studying peptides using the Gordon supercomputer at the San Diego Supercomputer Center (SDSC) at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) have found new ways to elucidate the creation of the toxic oligomers associated with Alzheimer's disease.
Igor Tsigelny, a research scientist with SDSC, the UCSD Moores Cancer Center, and the Department of Neurosciences, focused on the small peptide called amyloid-beta, which pairs up with itself to form dimers and oligomers.
The scientists surveyed all the possible ways to look at the dynamics of conformational ...
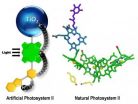
Artificial leaf jumps developmental hurdle
2014-02-18
In a recent early online edition of Nature Chemistry, ASU scientists, along with colleagues at Argonne National Laboratory, have reported advances toward perfecting a functional artificial leaf.
Designing an artificial leaf that uses solar energy to convert water cheaply and efficiently into hydrogen and oxygen is one of the goals of BISfuel – the Energy Frontier Research Center, funded by the Department of Energy, in the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry at Arizona State University.
Hydrogen is an important fuel in itself and serves as an indispensible ...
Wistar scientists develop gene test to accurately classify brain tumors
2014-02-18
cientists at The Wistar Institute have developed a mathematical method for classifying forms of glioblastoma, an aggressive and deadly type of brain cancer, through variations in the way these tumor cells "read" genes. Their system was capable of predicting the subclasses of glioblastoma tumors with 92 percent accuracy. With further testing, this system could enable physicians to accurately predict which forms of therapy would benefit their patients the most.
Their research was performed in collaboration with Donald M. O'Rourke, M.D., a neurosurgeon at the University ...
COXEN model picks the best drug for ovarian cancer
2014-02-18
There are three common drugs for advanced ovarian cancer: paclitaxel, cyclophosphamide, and topotecan. Like a shell game, if you pick the right drug a patient is likely to respond. And, unfortunately, picking the wrong drug can lead to treatment failure. As reported in this month's issue of the journal PLoS ONE, a University of Colorado Cancer Center and University of Virginia study used a sophisticated model of ovarian cancer genetics to match the right tumor with the right drug. Patients who were matched in this way lived an average 21 months longer than patients who ...
A battery small enough to be injected, energetic enough to track salmon
2014-02-18
RICHLAND, Wash. – Scientists have created a microbattery that packs twice the energy compared to current microbatteries used to monitor the movements of salmon through rivers in the Pacific Northwest and around the world.
The battery, a cylinder just slightly larger than a long grain of rice, is certainly not the world's smallest battery, as engineers have created batteries far tinier than the width of a human hair. But those smaller batteries don't hold enough energy to power acoustic fish tags. The new battery is small enough to be injected into an organism and holds ...