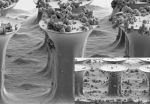
(Press-News.org) Astronomers see huge clouds of gas orbiting supermassive black holes at the centers of galaxies. Once thought to be a relatively uniform, fog-like ring, the accreting matter instead forms clumps dense enough to intermittently dim the intense radiation blazing forth as these enormous objects condense and consume matter, they report in a paper to be published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, available online now.
Video depicting the swirling clouds is posted to YouTube http://youtu.be/QA8nzRkjOEw
Evidence for the clouds comes from records collected over 16 years by NASA's Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer, a satellite in low-earth orbit equipped with instruments that measured variations in X-ray sources. Those sources include active galactic nuclei, brilliantly luminous objects powered by supermassive black holes as they gather and condense huge quantities of dust and gas.
By sifting through records for 55 active galactic nuclei Alex Markowitz, an astrophysicist at the University of California, San Diego and the Karl Remeis Observatory in Bamberg, Germany and colleagues found a dozen instances when the X-ray signal dimmed for periods of time ranging from hours to years, presumably when a cloud of dense gas passed between the source and satellite.
Mirko Krumpe of the European Southern Observatory in Garching, Germany and Robert Nikutta, of Andrés Bello University in Santiago, Chile co-authored the report, which confirms what recent models of these systems have predicted.
The clouds they observed orbit a few light-weeks to a few light-years from the center of the active galactic nuclei. One, in a spiral galaxy in the direction of the constellation Centaurus designated NGC 3783, appeared to be in the midst of being torn apart by tidal forces.
INFORMATION:
Support for this research came from NASA's Astrophysics Data Analysis Program and the European Community's Seventh Framework Program. Nikutta acknowledges support from ALMA-CONICYT. Video produced by the Scientific Visualization Studio, Goddard Spaceflight Center, NASA, based in part on visualizations created by Wolfgang Steffen, Institute of Astronomy, National Autonomous University of Mexico. More about the X-ray Timing Explorer: https://heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/xte/XTE.html
Clouds seen circling supermassive black holes
2014-02-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Better cache management could improve chip performance, cut energy use
2014-02-19
Computer chips keep getting faster because transistors keep getting smaller. But the chips themselves are as big as ever, so data moving around the chip, and between chips and main memory, has to travel just as far. As transistors get faster, the cost of moving data becomes, proportionally, a more severe limitation.
So far, chip designers have circumvented that limitation through the use of "caches" — small memory banks close to processors that store frequently used data. But the number of processors — or "cores" — per chip is also increasing, which makes cache management ...
When faced with a hard decision, people tend to blame fate
2014-02-19
Life is full of decisions. Some, like what to eat for breakfast, are relatively easy. Others, like whether to move cities for a new job, are quite a bit more difficult. Difficult decisions tend to make us feel stressed and uncomfortable – we don't want to feel responsible if the outcome is less than desirable. New research suggests that we deal with such difficult decisions by shifting responsibility for the decision to fate.
The findings are published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"Fate is a ubiquitous supernatural ...
UK failing to harness its bioenergy potential
2014-02-19
The UK could generate almost half its energy needs from biomass sources, including household waste, agricultural residues and home-grown biofuels by 2050, new research suggests.
Scientists from the Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research at The University of Manchester found that the UK could produce up to 44% of its energy by these means without the need to import.
The study, published in Energy Policy journal, highlights the country's potential abundance of biomass resources that are currently underutilised and totally overlooked by the bioenergy sector. Instead, ...
Making nanoelectronics last longer for medical devices, 'cyborgs'
2014-02-19
The debut of cyborgs who are part human and part machine may be a long way off, but researchers say they now may be getting closer. In a study published in ACS' journal Nano Letters, they report development of a coating that makes nanoelectronics much more stable in conditions mimicking those in the human body. The advance could also aid in the development of very small implanted medical devices for monitoring health and disease.
Charles Lieber and colleagues note that nanoelectronic devices with nanowire components have unique abilities to probe and interface with living ...
Gecko-inspired adhesion: Self-cleaning and reliable
2014-02-19
This news release is available in German. Geckos outclass adhesive tapes in one respect: Even after repeated contact with dirt and dust do their feet perfectly adhere to smooth surfaces. Researchers of the KIT and the Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, have now developed the first adhesive tape that does not only adhere to a surface as reliably as the toes of a gecko, but also possesses similar self-cleaning properties. Using such a tape, food packagings or bandages might be opened and closed several times. The results are published in the "Interface" journal of ...
Chemical leak in W.Va. shows gaps in research, policy
2014-02-19
The chemical leak that contaminated drinking water in the Charleston, W.Va., area last month put in sharp relief the shortcomings of the policies and research that apply to thousands of chemicals in use today. An article in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly magazine of the American Chemical Society, delves into the details of the accident that forced 300,000 residents to live on bottled water for days.
A team of C&EN reporters and editors note that the main chemical that leaked into the water supply is an obscure one called 4-methylcyclohexanemethanol, or ...
Advance in energy storage could speed up development of next-gen electronics
2014-02-19
Electronics are getting smaller all the time, but there's a limit to how tiny they can get with today's materials. Researchers now say, however, that they have developed a way to shrink capacitors — key components that store energy — even further, which could accelerate the development of more compact, high-performance next-gen devices. The study appears in the journal ACS Nano.
Takayoshi Sasaki and colleagues point out that many recent improvements have already downsized capacitors significantly. But current technology has almost reached its limit in terms of materials ...
Genetics linked to children viewing high amounts of violent media
2014-02-19
Washington, DC (February 19 2014) – The lifelong debate of nature versus nurture continues—this time in what your children watch. A recent paper published in the Journal of Communication found that a specific variation of the serotonin-transporter gene was linked to children who engaged in increased viewing of violent TV and playing of violent video games.
Sanne Nikkelen, Helen Vossen, and Patti Valkenburg of the University of Amsterdam's School of Communication Research, in collaboration with researchers at the Erasmus University Medical Centre in Rotterdam, analyzed ...
Special air filter blocks small particles called UFPs from getting inside cars
2014-02-19
While taking in the scenery during long road trips, passengers also may be taking in potentially harmful ultrafine particles (UFPs) that come into the car through outdoor air vents. Closing the vents reduces UFPs, but causes exhaled carbon dioxide to build up. Now, scientists report in the ACS journal Environmental Science & Technology that installing a newly developed high-efficiency cabin air filter (HECA) could reduce UFP exposure by 93 percent and keep carbon dioxide levels low.
Yifang Zhu and Eon Lee explain that most modern cars come with cabin air filters, but ...
Kinetic battery chargers get a boost
2014-02-19
New technology to capture the kinetic energy of our everyday movements, such as walking, and to convert it into electrical energy has come a step closer thanks to research to be published in the International Journal Biomechatronics and Biomedical Robotics.
Researchers have for many years attempted to harvest energy from our everyday movements to allow us to trickle charge electronic devices while we are walking without the need for expensive and cumbersome gadgets such as solar panels or hand-cranked chargers. Lightweight devices are limited in the voltage that they ...