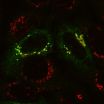
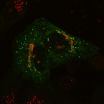
(Press-News.org) To remain healthy, the body's cells must properly manage their waste recycling centers. Problems with these compartments, known as lysosomes, lead to a number of debilitating and sometimes lethal conditions.
Reporting in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified an unusual cause of the lysosomal storage disorder called mucolipidosis III, at least in a subset of patients. This rare disorder causes skeletal and heart abnormalities and can result in a shortened lifespan. But unlike most genetic diseases that involve dysfunctional or missing proteins, the culprit is a normal protein that ends up in the wrong place.
"There is a lot of interest and study about how cells distribute proteins to the right parts of the cell," said senior author Stuart A. Kornfeld, MD, PhD, the David C. and Betty Farrell Professor of Medicine. "Our study has identified one of the few examples of a genetic disease caused by the misplacement of a protein. The protein functions just fine. It just doesn't stay in the right place."
The right place, in this case, is the Golgi apparatus, the cell's protein packaging center. The protein in question – phosphotransferase – normally resides in the Golgi, where its job is to attach address labels to proteins bound for the lysosome. There are 60 such lysosomal proteins, and all of them must be properly labeled if they are to end up in a lysosome, where they recycle waste.
Kornfeld and his colleagues, including first author Eline van Meel, PhD, postdoctoral research associate, showed that the phosphotransferase protein responsible for adding the address label starts out in the Golgi as it should, but seems to lack the signal to keep it there.
"Under normal circumstances, the phosphotransferase moves up through the Golgi, but then it's recaptured and sent back," Kornfeld said. "Our study shows that the mutant phosphotransferase moves up but is not recaptured. Ironically, the phosphotransferase that escapes the Golgi ends up in the lysosomes, where it is degraded."
Because phosphotransferase gradually wanders away from the Golgi, a low level of lysosomal enzymes end up being properly addressed, but at perhaps 20 percent of the normal amount.
"In many lysosomal storage disorders, such as Tay-Sachs or Gaucher's disease, only one out of the 60 enzymes is missing from the lysosome," Kornfeld said. "But the mislocalization of phosphotranferase causes the misdirection of all 60 lysosomal enzymes."
While the errant phosphotransferase ends up being degraded in the lysosome, the resulting misdirected lysosomal proteins end up in the bloodstream. As a result, children with this disorder have lysosomal proteins in their blood at levels 10 to 20 times higher than normal. But because some get to the lysosome at a low level, people with mucolipidosis III don't have the most severe form of the disease.
"Type III patients live into adulthood, but they're very impaired," said Kornfeld. "They have joint and heart problems and have trouble walking. In the most severe form, type II, there is zero activity of phosphotransferase. None of the 60 enzymes are properly tagged, so these patients' lysosomes are empty. Children with type II usually die by age 10."
Having implicated wayward phosphotransferase in this lysosomal storage disorder, Kornfeld and his colleagues are investigating what goes wrong that allows it to escape the Golgi.
"We think there must be some protein in the cell that recognizes phosphotransferase when it gets to the end of the Golgi, binds it and takes it back," said Kornfeld. "Now we're trying to understand how that works."
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant CA-008759-44.
Van Meel, E, Qian Y, Kornfeld SA. Mislocalization of phosphotransferase as a cause of mucolipidosis III ab. PNAS. Online Feb. 18, 2014.
Washington University School of Medicine's 2,100 employed and volunteer faculty physicians also are the medical staff of Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children's hospitals. The School of Medicine is one of the leading medical research, teaching and patient-care institutions in the nation, currently ranked sixth in the nation by U.S. News & World Report. Through its affiliations with Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children's hospitals, the School of Medicine is linked to BJC HealthCare.
Surprising culprit found in cell recycling defect
2014-02-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MD Anderson researcher uncovers some of the ancient mysteries of leprosy
2014-02-20
Research at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center is finally unearthing some of the ancient mysteries behind leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease, which has plagued mankind throughout history. The new research findings appear in the current edition of journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. According to this new hypothesis, the disease might be the oldest human-specific infection, with roots that likely stem back millions of years.
There are hundreds of thousands of new cases of leprosy worldwide each year, but the disease is rare in the United States, ...
Sustainable manufacturing system to better consider the human component
2014-02-20
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Engineers at Oregon State University have developed a new approach toward "sustainable manufacturing" that begins on the factory floor and tries to encompass the totality of manufacturing issues – including economic, environmental, and social impacts.
This approach, they say, builds on previous approaches that considered various facets of sustainability in a more individual manner. Past methods often worked backward from a finished product and rarely incorporated the complexity of human social concerns.
The findings have been published in the Journal ...
New calibration confirms LUX dark matter results
2014-02-20
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — A new high-accuracy calibration of the LUX (Large Underground Xenon) dark matter detector demonstrates the experiment's sensitivity to ultra-low energy events. The new analysis strongly confirms the result that low-mass dark matter particles were a no-show during the detector's initial run, which concluded last summer.
The first dark matter search results from LUX detector were announced last October. The detector proved to be exquisitely sensitive, but found no evidence of the dark matter particles during its first 90-day run, ruling ...
Better broccoli, enhanced anti-cancer benefits with longer shelf life
2014-02-20
URBANA, Ill. – While researching methods to increase the already well-recognized anti-cancer properties of broccoli, researchers at the University of Illinois also found a way to prolong the vegetable's shelf life.
And, according to the recently published study, the method is a natural and inexpensive way to produce broccoli that has even more health benefits and won't spoil so quickly on your refrigerator shelf.
Jack Juvik, a U of I crop sciences researcher, explained that the combined application of two compounds, both are natural products extracted from plants, increased ...
Smaller meals more times per day may curb obesity in cats
2014-02-20
URBANA, Ill. – Just as with people, feline obesity is most often linked to excessive food intake or not enough physical activity. Attempts to cut back on calories alone often result in failed weight loss or weight regain in both people and their pets.
So how do you encourage your cat to get more exercise?
Researchers from the University of Illinois interested in finding a method to maintain healthy body weight in cats, looked at a previously suggested claim that increased meal frequency could help to increase overall physical activity.
The idea is to feed cats the ...
Color vision problems become more common with age, reports Optometry and Vision Science
2014-02-20
Philadelphia, Pa. (February 20, 2014) - Abnormal color vision increases significantly with aging—affecting one-half or more of people in the oldest age groups, reports a study in Optometry and Vision Science, official journal of the American Academy of Optometry. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
While few people younger than 70 have problems with color vision, the rate increases rapidly through later decades of life, according to the new research by Marilyn E. Schneck, PhD, and colleagues of The Smith-Kettlewell ...
Roots to shoots: Hormone transport in plants deciphered
2014-02-20
Plant growth is orchestrated by a spectrum of signals from hormones within a plant. A major group of plant hormones called cytokinins originate in the roots of plants, and their journey to growth areas on the stem and in leaves stimulates plant development. Though these phytohormones have been identified in the past, the molecular mechanism responsible for their transportation within plants was previously poorly understood.
Now, a new study from a research team led by biochemist Chang-Jun Liu at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory identifies ...
New research shows the way a room is lit can affect the way you make decisions
2014-02-20
The next time you want to turn down the emotional intensity before making an important decision, you may want to dim the lights first.
A new study from the University of Toronto Scarborough shows that human emotion, whether positive or negative, is felt more intensely under bright light. Alison Jing Xu, assistant professor of management at UTSC and the Rotman School of Management, along with Aparna Labroo of Northwestern University, conducted a series of studies to examine the unusual paradox of lighting and human emotion.
"Other evidence shows that on sunny days people ...
Recurrent mouth and throat cancers less deadly when caused by virus, study shows
2014-02-20
People with late-stage cancer at the back of the mouth or throat that recurs after chemotherapy and radiation treatment are twice as likely to be alive two years later if their cancer is caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), new research led by a Johns Hopkins scientist suggests.
Previous studies have found that people with so-called HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers are more likely to survive than those whose cancers are related to smoking or whose origins are unknown.
The new study, scheduled to be presented Feb. 20 at the 2014 Multidisciplinary Head and Neck ...
Humidification of the mouth, throat during RT for head and neck cancer reduces mucositis, hospital stay
2014-02-20
Scottsdale, Ariz., February 20, 2014—Patients who received daily humidification of the mouth and throat region beginning from day one of radiation therapy treatment spent nearly 50 percent fewer days in the hospital to manage their side effects, according to research presented today at the 2014 Multidisciplinary Head and Neck Cancer Symposium.
The study was conducted by the Trans Tasman Radiation Oncology Group and evaluated 210 head and neck cancer patients in New Zealand and Australia from June 2007 through June 2011. Patients in this Phase III trial were randomized ...