(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS – An updated guideline from the American Academy of Neurology recommends that people with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation, or irregular heartbeat, take oral anticoagulants, a type of blood thinner pill, to prevent stroke. The guideline is published in the February 25, 2014, print issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The World Stroke Organization has endorsed the updated guideline.
Taking anticoagulants is especially important for people who have already had a stroke or a transient ischemic attack, which is a threatened stroke.
Irregular heartbeat is a major risk factor for stroke. "The World Health Organization has determined that atrial fibrillation is nearing epidemic proportions, affecting 0.5 percent of the population worldwide," said guideline lead author Antonio Culebras, MD, of SUNY Upstate Medical University in Syracuse, NY, and a Fellow of the American Academy of Neurology.
The uneven heart rhythm allows blood to remain in the heart's upper chambers. The blood can then form clots. These may escape the heart and travel to the brain, causing a stroke. About one in 20 people with untreated atrial fibrillation will likely have a stroke in the next year. Anticoagulants are highly effective in preventing stroke, but they also carry a risk of bleeding. They should be used only under close medical supervision.
Several new anticoagulant pills have been developed since the AAN's last guideline on this topic, which was published in 1998. The current guideline determined that the new anticoagulant pills, such as dabigatran, rivaroxaban and apixaban, are at least as effective, if not more effective than, the established treatment of warfarin and have a lower risk of bleeding in the brain. In addition, the new drugs have the added convenience of not requiring the frequent blood testing that warfarin requires.
The guideline also extends the value of this type of blood thinner to many people who are generally undertreated—such as the elderly, those with mild dementia, and those at moderate risk of falls—and whose health status was long thought to be a barrier to use.
"Of course, doctors will need to consider the individual patient's situation in making a decision whether or not to use anticoagulants, and which one to use, as the risks and benefits can vary for each person," said Culebras.
Culebras also noted that the guideline addresses special circumstances that may pertain to developing countries where new anticoagulant pills are not available or not affordable.
INFORMATION:
To learn more about stroke, please visit http://www.aan.com/patients.
The American Academy of Neurology, an association of more than 27,000 neurologists and neuroscience professionals, is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer's disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, brain injury, Parkinson's disease and epilepsy.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit http://www.aan.com or find us on Facebook, Twitter, Google+ and YouTube.
Media Contacts:
Rachel Seroka, rseroka@aan.com, (612) 928-6129
Michelle Uher, muher@aan.com, (612) 928-6120
Guideline: People with irregular heartbeat should take blood thinners to prevent stroke
2014-02-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
For older hypertension patients, an unwelcome tradeoff
2014-02-24
Medications used by many older people to control their blood pressure also increase the risk of serious fall injuries by 30% to 40% — injuries that have a similar effect on mortality and functional loss as the strokes and heart attacks the blood pressure drugs are meant to prevent — according to a new study by Yale School of Medicine researchers in the Feb. 24 issue of JAMA Internal Medicine.
Clinicians have long assumed that blood pressure medications are safe and effective in all older adults. That is probably true in healthy older adults, but the same might not be ...
Study examines acetaminophen use in pregnancy, child behavioral problems
2014-02-24
Bottom Line: Children of women who used the pain reliever acetaminophen (paracetamol) during pregnancy appear to be at higher risk for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)-like behavioral problems and hyperkinetic disorders (HKDs, a severe form of ADHD).
Author: Zeyan Liew, M.P.H., of the University of California, Los Angeles, and colleagues.
Background: Acetaminophen is the most commonly used medication for pain and fever during pregnancy. But some recent studies have suggested that acetaminophen has effects on sex and other hormones, which can in turn affect ...
Vegetarian diets associated with lower blood pressure
2014-02-24
Eating a vegetarian diet appears to be associated with lower blood pressure (BP), and the diets can also be used to reduce blood pressure.
Factors such as diet, body weight, physical activity and alcohol intake play a role in the risk of developing hypertension. Dietary modifications have been shown to be effective for preventing and managing hypertension.
The authors analyzed seven clinical trials and 32 studies published from 1900 to 2013 in which participants ate a vegetarian diet. Net differences in BP associated with eating a vegetarian diet were measured.
In ...
Medication to treat high blood pressure associated with fall injuries in elderly
2014-02-24
Medication to treat high blood pressure (BP) in older patients appears to be associated with an increased risk for serious injury from falling such as a hip fracture or head injury, especially in older patients who have been injured in previous falls.
Most people older than 70 years have high blood pressure, and blood pressure control is key to reducing risk for myocardial infarction (MI, heart attack) and stroke. Previous research has suggested that blood pressure medications may increase risk of falls and fall injuries.
Researchers examined the association between ...
Study finds differences in benefits, service at hospices based on tax status
2014-02-24
The tax status of a hospice (for-profit vs. nonprofit) affects community benefits, the population served and community outreach.
The number of for-profit hospices has increased over the past two decades with about 51 percent of hospices being for-profit in 2011 compared with about 5 percent in 1990. But little is known about how for-profit and nonprofit hospices differ in activities beyond service delivery.
The authors examined the association between hospice profit status and the provision of community benefits (charity care, research and serving as training sites), ...
Death of partner associated with increased risk of heart attack, stroke
2014-02-24
The risk of heart attack or stroke is increased in the 30 days after a partner's death.
Bereavement is recognized as a risk factor for death and is associated with cardiovascular events.
The authors compared the rate of myocardial infarction (MI, heart attack) or stroke in older patients (n=30,447, 60 to 89 years of age) whose partner died to that of individuals (n=83,588) whose partners were still alive during the same period.
Fifty patients (0.16 percent) experienced MI or stroke within 30 days of their partner's death compared with 67 (0.08 percent) of controls. ...
Panel recommends listing depression as a risk for heart disease
2014-02-24
AUDIO:
A panel of experts that includes researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis is recommending depression now be officially included as a risk factor for serious heart...
Click here for more information.
An extensive review of scientific literature indicates that depression should be added to the list of risk factors associated with heart disease. Others include obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure and smoking.
A 12-person panel of experts that ...
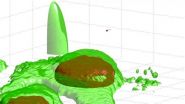
Now in 3-D: Video of virus-sized particle trying to enter cell
2014-02-24
VIDEO:
"Kiss and run " on the cell surface. This 3-D movie shows actual footage of a virus-like particle (red dot) approaching a cell (green with reddish brown nucleus), as captured by...
Click here for more information.
Tiny and swift, viruses are hard to capture on video. Now researchers at Princeton University have achieved an unprecedented look at a virus-like particle as it tries to break into and infect a cell. The technique they developed could help scientists ...
Preventive oophorectomy reduces risk of death by 77 percent for women with BRCA mutation
2014-02-24
TORONTO, ON, February 24, 2014 —Women who carry a BRCA gene mutation and opt for a preventive oophorectomy, or ovary removal surgery, have a 77 per cent lower risk of death than those who do not, according to a new study led by Women's College Hospital's Amy Finch and Dr. Steven Narod.
Research has long shown that preventive oophorectomy reduces the risks of ovarian and breast cancers in women with a BRCA gene mutation, but the best age for women to have the surgery and its impact on mortality has not been well studied. The findings by Finch and colleagues, published ...
Study shows preventive ovarian surgery in BRCA1 mutation carriers should be performed early
2014-02-24
The findings of a large international prospective study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology suggest for the first time that women with BRCA1 mutations should have preventive ovarian surgery (prophylactic oophorectomy) by age 35, as waiting until a later age appears to increase the risk of ovarian cancer before or at the time of the preventive surgery. Women with a BRCA2 mutation, however, do not appear to be at an increased risk by age 35, suggesting they may delay this procedure until later. Moreover, women with BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations who had this surgery ...