(Press-News.org) Stars, diamonds, circles.
Rather than your average bowl of Lucky Charms, these are three-dimensional cell cultures generated by an exciting new digital microfluidics platform, the results of which have been published in Nature Communications this week by researchers at the University of Toronto. The tool, which can be used to study cells in cost-efficient, three-dimensional microgels, may hold the key to personalized medicine applications in the future.
"We already know that the microenvironment can greatly influence cell fate," says Irwin A. Eydelnant, recent doctoral graduate from IBBME and first author of the publication. "The important part of this study is that we've developed a tool that will allow us to investigate the sensitivity of cells to their 3D environment."
"Everyone wants to do three-dimensional (3D) cell culture," explains Aaron Wheeler, Professor and Canada Research Chair in Bioanalytical Chemistry at the Institute of Biomaterials & Biomedical Engineering (IBBME), the Department of Chemistry, and the Donnelly Centre for Cellular and Biomolecular Research (DCCBR) at the University of Toronto. "Cells grown in this manner share much more in common with living systems than the standard two-dimensional (2D) cell culture format," says Wheeler, corresponding author of the study.
More naturalistic, 3D cell cultures are a challenge to grow. "The reagents are expensive, the materials are inconvenient for automation, and 3D matrices break down upon repeated handling," explains Wheeler, who was named an Inventor of the Year by the University of Toronto in 2012.
Eydelnant was able to address these difficulties by adapting a digital microfluidics platform first created in the Wheeler lab. Cells, caught up in a hydrogel material, are gently flowed across a small field that, on a screen, looks much like a tiny chessboard. The cells are strategically manipulated by a small electric field across a cutout shape on the top plate of the system, made from indium in oxide, and become fixed.
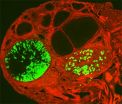
"When we grew kidney cells in these microgels, the cultures formed hollow sphere structures resembling primitive kidneys within four or five days," Eydelnant claims.
The tool allows a great deal of flexibility in terms of the number of different kinds of cells that can be incorporated into the shapes, as well as the shapes and size of the microenvironments: whimsical, like the stars, diamond and circles of Lucky Charms, or designed to mimic living 3D niches, offering researchers a glimpse into how these factors all affect cell fate decisions.
What's more, according to Eydelnant, the platform permits researchers to run, "32 experiments at the same time, automatically, and all on something the size of a credit card."
"[This new] system allows for hands-free assembly of sub-microlitre, three-dimensional microgels. Each gel is individually addressable, fluid exchange is gentler than macro-scale alternatives, and reagent use is reduced more than 100-fold," Wheeler says.
"We believe that this new tool will make 3D cell culture a more attractive and accessible format for cell biology research," he adds.
Although the researchers can foresee numerous possible applications for this platform, the team is "particularly excited" about its potential for personalized medicine.
Wheeler argues, "We may be able to collect small tissue samples from patients, distribute them into 3D gels on digital microfluidic devices, and screen for conditions to identify individually tailored therapies. This is in the 'dream' stages for now, but we think the methods described here will be useful for these types of applications in the future."
INFORMATION:
ABOUT IBBME
The Institute of Biomaterials and Biomedical Engineering (IBBME) is a cutting-edge interdisciplinary unit situated between three Faculties at the University of Toronto: Applied Science & Engineering, Dentistry and Medicine. The Institute pursues research in four areas: neural, sensory systems and rehabilitation engineering; biomaterials, tissue engineering and regenerative medicine; molecular imaging and biomedical nanotechnology; medical devices and clinical technologies. END
3D microgels 'on-demand' offer new potential for cell research
2014-02-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Keck Medicine of USC scientists uncover 2 micro mechanisms that regulate immune system
2014-02-26
A Keck Medicine of USC-led team of microbiologists has identified previously unknown interactions between critical proteins in the human immune response system, uncovering two independent regulatory mechanisms that keep the body's immune response in check. Their findings appear in the February 2014 edition of Cell Host & Microbe, the top peer-reviewed scientific journal that focuses on the study of cell-pathogen interaction.
"The body's response to infection consists of a complex network of biological processes set off by the intrusion of disease-causing microbes," said ...
Study: Mailing free tests to patients' homes boosts colon cancer screening rates
2014-02-26
PORTLAND, Ore. February 26, 2014 -- Colon cancer screening rates increased by nearly 40 percent when free stool tests were mailed to patients' homes, according to results of a pilot study published today in the journal BMC Cancer.
The study, funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), included 869 patients who received their health care from community health centers in the Portland, Ore. metropolitan area. The clinics serve many Latino patients who live below the poverty level. About half of them have no health insurance.
"We are very happy that so many of the ...
Attitude during pregnancy affects weight gain
2014-02-26
Overweight or obese women with the mentality that they are "eating for two" are more likely to experience excessive weight gain while pregnant, according to researchers at Penn State College of Medicine.
Cynthia Chuang, associate professor of medicine and public health sciences, studied the attitudes and habits of women who gained appropriate weight and those who exceeded guidelines. Overweight is defined as having a body mass index of 25 to 29; obese is having a BMI greater than 29. In 2009 the Institute of Medicine recommends that women of normal weight gain 25 to ...
Suicide among apparently well-functioning young men
2014-02-26
Suicide among young men is a major public health concern in many countries, despite great efforts to find effective prevention strategies. By interviewing close relatives and friends of apparently well-functioning young men who unexpectedly took their own life, Norwegian researchers found there had been no signs of serious mental disorder. This contradicts previous research which suggests that depression or other mental illness is an important risk factor in suicide.
In Norway, there is still scant scientific evidence of effective prevention strategies, and suicide rates ...
Whales, ships more common through Bering Strait
2014-02-26
AUDIO:
Humpback whale sounds were recorded in Bering Strait in October 2012.
Click here for more information.
The Arctic is home to a growing number of whales and ships, and to populations of sub-Arctic whales that are expanding their territory into newly ice-free Arctic waters.
A study of the narrow passage of the Bering Strait uses underwater microphones to track the whales by their sounds. Three years of recordings reveal more detections of both Arctic and sub-Arctic whales ...
NPL scientists blend synthetic air to measure climate change
2014-02-26
Scientists at the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) have produced a synthetic air reference standard which can be used to accurately measure levels of carbon dioxide and methane in the atmosphere. This will greatly help scientists contribute to our understanding of climate change.
A paper published in Analytical Chemistry describes how researchers at NPL have created a synthetic gas standard for the first time, which is comparable to the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) scale and can be quickly produced in a laboratory and distributed, meeting growing demand.
The ...
Self-administration of flu vaccine with a patch may be feasible, study suggests
2014-02-26
The annual ritual of visiting a doctor's office or health clinic to receive a flu shot may soon be outdated, thanks to the findings of a new study published in the journal Vaccine.
The research, which involved nearly 100 people recruited in the metropolitan Atlanta area, found that test subjects could successfully apply a prototype vaccine patch to themselves. That suggests the self-administration of vaccines with microneedle patches may one day be feasible, potentially reducing administration costs and relieving an annual burden on health care professionals.
The ...
New blood analysis predicts risk of death
2014-02-26
The general state of a person's metabolism can be diversely illustrated with a new scientific blood analysis. With the aid of the analysis biomarkers predicting short-term mortality have now been discovered.
If a person belongs to a risk group based on these biomarker concentrations, he/she has a multifold risk of dying in the next five years compared to the general population. The study is based on blood samples of over 17,000 Finnish and Estonian people.
Mortality was related to four biomarkers in the blood: levels of two proteins (albumin and alpha-1 acidic glycoprotein), ...
Self-rated physical fitness in midlife an indicator of dementia risk
2014-02-26
How would you rate your own physical fitness? Is it good, satisfactory or maybe even poor? Surprisingly, your answer may reveal your future risk of getting dementia.
A recent collaborative study from Finland, involving the follow-up of 3,559 adults for 30 years, has found that a simple question about self-rated physical fitness in midlife may reveal individuals who are at an increased risk of developing dementia. Those who reported poor self-rated physical fitness in midlife, at the mean age of 50 years, were four times more likely to get dementia during the next three ...
Different eggs in adolescent girls and adult women
2014-02-26
Are the eggs produced by adolescent girls the same as the ones produced by adult women? A recent study published in Human Molecular Genetics by Professor Kui Liu from the University of Gothenburg in Sweden shows compelling evidence that there are two completely distinct types of eggs in the mammalian ovary – "the first wave" and "the adult wave".
Professor Liu's team used two genetically modified mouse models to show that the first wave of eggs, which starts immediately after birth, contributes to the onset of puberty and provides fertilizable eggs into the transition ...