(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
A comparative analysis shows that stethoscope diaphragms are more contaminated than the physician's own thenar eminence (group of muscles in the palm of the hand) following a physical examination.
Click here for more information.
Rochester, MN, February 27, 2014 – Although healthcare workers' hands are the main source of bacterial transmission in hospitals, physicians' stethoscopes appear to play a role. To explore this question, investigators at the University of Geneva Hospitals assessed the level of bacterial contamination on physicians' hands and stethoscopes following a single physical examination. The study appears in the March issue of Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
"By considering that stethoscopes are used repeatedly over the course of a day, come directly into contact with patients' skin, and may harbor several thousands of bacteria (including MRSA) collected during a previous physical examination, we consider them as potentially significant vectors of transmission," commented lead investigator Didier Pittet, MD, MS, Director of the Infection Control Program and WHO Collaborating Centre on Patient Safety, University of Geneva Hospitals. "From infection control and patient safety perspectives, the stethoscope should be regarded as an extension of the physician's hands and be disinfected after every patient contact."
In this study, 71 patients were examined by one of three physicians using sterile gloves and a sterile stethoscope. After they completed the examination, two parts of the stethoscope (the tube and diaphragm) and four regions of the physician's hands (back, fingertips, and thenar and hypothenar eminences) were measured for the total number of bacteria present.
The stethoscope's diaphragm was more contaminated than all regions of the physician's hand except the fingertips. Further, the tube of the stethoscope was more heavily contaminated than the back of the physician's hand. Similar results were observed when contamination was due to methicillin-resistant S.aureus (MRSA) after examining MRSA-colonized patients.
This work is the first to compare directly the level of contamination of physicians' hands and stethoscopes. Stethoscope contamination is not trivial and is comparable to the contamination of healthcare workers' fingertips, the hand region most implicated in microbial cross-transmission. Physicians must be aware of the need to disinfect their stethoscope after each use.
INFORMATION:
Physicians' stethoscopes more contaminated than palms of their hands
Results of new study published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings
2014-02-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study reveals mechanisms cancer cells use to establish metastatic brain tumors
2014-02-27
NEW YORK, NY, February 27, 2014 — New research from Memorial Sloan Kettering provides fresh insight into the biologic mechanisms that individual cancer cells use to metastasize to the brain. Published in the February 27 issue of Cell, the study found that tumor cells that reach the brain — and successfully grow into new tumors — hug capillaries and express specific proteins that overcome the brain's natural defense against metastatic invasion.
Metastasis, the process that allows some cancer cells to break off from their tumor of origin and take root in a different tissue, ...
Methane leaks from palm oil wastewater are a climate concern, CU-Boulder study says
2014-02-27
In recent years, palm oil production has come under fire from environmentalists concerned about the deforestation of land in the tropics to make way for new palm plantations. Now there is a new reason to be concerned about palm oil's environmental impact, according to researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder.
An analysis published Feb. 26 in the journal Nature Climate Change shows that the wastewater produced during the processing of palm oil is a significant source of heat-trapping methane in the atmosphere. But the researchers also present a possible solution: ...
Famed Milwaukee County Zoo orangutan's death caused by strange infection
2014-02-27
MADISON – Mahal, the young orangutan who became a star of the Milwaukee County Zoo and an emblem of survival for a dwindling species, led an extraordinary life.
It turns out, the young ape died an extraordinary death, too.
Rejected by his biological mother at the Cheyenne Mountain Zoo in Colorado Springs, Colo., and eventually flown to Milwaukee aboard a private jet to live with a surrogate mother, Mahal became one of the Milwaukee County Zoo's star attractions. His unexpected death at age 5 in late December 2012 was a shock to the community that came to know him through ...
Scientists describe deadly immune 'storm' caused by emergent flu infections
2014-02-27
LA JOLLA, CA—February 26, 2014—Scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have mapped key elements of a severe immune overreaction—a "cytokine storm"—that can both sicken and kill patients who are infected with certain strains of flu virus.
Their findings, published in this week's online Early Edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, also clarify the workings of a potent new class of anti-inflammatory compounds that prevent this immune overreaction in animal models.
"We show that with this type of drug, we can quiet the storm enough to ...
Livestock found ganging up on pandas at the bamboo buffet
2014-02-27
VIDEO:
A panda in the Wolong Nature Reserve munches on bamboo -- which comprises 99 percent of the endangered species' diet in the wild.
Click here for more information.
Pandas, it turns out, aren't celebrating the Year of the Horse.
Livestock, particularly horses, have been identified as a significant threat to panda survival. The reason: They're beating the pandas to the bamboo buffet. A paper by Michigan State University panda habitat experts published in this week's Journal ...
Making treatment of rare blood disorder more affordable and effective
2014-02-27
PHILADELPHIA — A University of Pennsylvania research team has defined a possible new way to fight a disease that is currently treatable only with the most expensive drug available for sale in the United States. In a study published this month in Blood, the Penn team describes the strategy, based on the oldest part of the human immune system – called "complement" -- that could turn out to be less costly and more effective for the majority of patients with a rare blood disorder.
Complement is a network of more than 50 proteins in the blood and on cell surfaces that quietly ...
International study shows majority of children unaware of cigarette warning labels
2014-02-27
College Park, Md. -- An international study of children's perceptions of cigarette package warning labels found that the majority of children are unaware that they exist. Children in countries where larger warning labels are used, and which include a compelling graphic image of the negative health impacts of smoking, were more likely to be aware of and understand the health risks of tobacco products.
The study, led by Dina Borzekowski, Ed.D, in the University of Maryland School of Public Health (UMD SPH), and Joanna Cohen, PhD, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public ...
AGU: A 'shark's eye' view: Witnessing the life of a top predator
2014-02-27
HONOLULU – Instruments strapped onto and ingested by sharks are revealing novel insights into how one of the most feared and least understood ocean predators swims, eats and lives.
For the first time, researchers at the University of Hawaii and the University of Tokyo outfitted sharks with sophisticated sensors and video recorders to measure and see where they are going, how they are getting there, and what they are doing once they reach their destinations. (Go to http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UHDOAmXRw-0&feature=youtu.be for video).
Scientists are also piloting ...
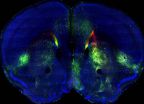
Mouse brain atlas maps neural networks to reveal how brain regions interact
2014-02-27
Different brain regions must communicate with each other to control complex thoughts and behaviors, but relatively little is known about how these areas organize into broad neuronal networks. In a study published by Cell Press February 27th in the journal Cell, researchers developed a mouse whole-brain atlas that reveals hundreds of neuronal pathways in a brain structure called the cerebral cortex. The online, open access, interactive image database, called the Mouse Connectome Project, provides an invaluable resource for researchers interested in studying the anatomy and ...
Study uncovers why autism is more common in males
2014-02-27
Males are at greater risk for neurodevelopmental disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), than females, but the underlying reasons have been unclear. A large cohort study published by Cell Press on February 27th in the American Journal of Human Genetics provides compelling evidence in support of the "female protective model," which proposes that females require more extreme genetic mutations than do males to push them over the diagnostic threshold for neurodevelopmental disorders.
"This is the first study that convincingly demonstrates a difference at the molecular ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Physicians' stethoscopes more contaminated than palms of their handsResults of new study published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings