(Press-News.org) This news release is available in German.
Proteins like the so-called heat shock protein Hsp90 play an important role in almost all processes within human cells. They help other proteins fold into their three-dimensional structure or return damaged proteins back into their proper shape.
Recently, there has been increasing evidence indicating that the heat shock protein HSP90 may also be involved in the folding processes of the tau protein. Deposits of tau proteins in brain cells are typical for Alzheimer's disease and are held responsible for decaying nerve cells.
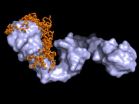
However, while dissolved tau proteins look more like long, stretched chains, HSP90 binds predominantly proteins that have already been prefolded. This contradiction has now been resolved by an international team headed by Dr. Tobias Madl, leader of the BioSysNet Working Group and TUM Junior Fellow at the Technische Universität München and leader of the Emmy-Noether Group Structural Biology of Signal Transduction at the Institute of Structural Biology at the Helmholz Zentrum München, as well as Prof. Stefan Rüdiger from the Dutch University of Utrecht.
Detective work
Using a combination of very different techniques like magnetic resonance spectroscopy, small-angle X-ray scattering and computer modeling, they successfully determined structure and dynamics of the interactions between the two biomolecules: For Hsp90 the tau protein looks like a prefolded larger protein. Furthermore they were able to deduce how Hsp90 influences the aggregation of tau proteins with one another.
"Deposits of tau proteins can cause Alzheimer's disease. We have discovered the protein regions in which the proteins interact. This is a novel and important starting point for influencing structural formation and for developing future therapies for Alzheimer's disease," says Madl.
In addition to Alzheimer's disease, further neuro-degenerative diseases are caused by protein aggregation. Chaperones also play a role in the development of cancer and cystic fibrosis. These scientific insights thus provide an important basis for better understanding the disease mechanisms.
INFORMATION:
The research was funded by the European Community, the German Research Foundation (DFG), the Dutch Organization for Scientific Research (NWO), the Austrian Academy of Sciences, the Portugese Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia and the National Institutes of Health (USA), as well as the Bavarian Ministry of Science and Research. The small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) experiments were conducted in the outstation of the EMBL at DESY in Hamburg. The computer modeling was done at the Leibniz Supercomputing Center of the Bavarian Academy of Sciences.
Publication:
Karagoz, G. E. et al., Hsp90-Tau Complex Reveals Molecular Basis for Specificity in Chaperone Action. Cell, 156, (5), 963-974 Doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.01.037
Dangerous mistaken identity
Chaperone binds protein responsible for Alzheimer's disease
2014-02-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Diabetes and obesity more common in socioeconomically deprived regions
2014-02-28
Living in a socioeconomically deprived region is a risk factor for being affected by diabetes mellitus and obesity. This holds true regardless of the individual social status of the inhabitants. This is the conclusion reached by scientists from the Institute of Health Economics and Health Care Management (IGM) at the Helmholtz Zentrum München (HMGU) and the Department of Epidemiology and Health Monitoring at the Robert Koch Institute (RKI) in Berlin. "Regional factors, such as the population's average income, unemployment or quality of the living environment can affect ...
Unearthing key function of plant hormone
2014-02-28
This news release is available in German.
Plants, like animals, employ hormones as messengers, which coordinate growth and regulate how they react to the environment. One of these plant hormones, auxin, regulates nearly all aspects of plant behavior and development, for example phototropism, root growth and fruit growth. Depending on the context, auxin elicits a range of responses such as cell polarization or division. In this week's edition of Science (DOI:10.1126/science.1245125), a team of researchers including Jiri Friml from IST Austria and led by Zhenbiao ...
Scientists discover the specific types of macrophages that affect Crohn's disease severity
2014-02-28
For those coping with Crohn's disease, a new research report published in the Journal of Leukocyte Biology offers hope for the development of new and more effective drugs. In the report, scientists show for the first time, precisely what type of immune cells are involved in driving the inflammation process in the disease. With this knowledge, new compounds can be identified which reduce the activity of these cells or lessen their inflammatory effects.
"By increasing the knowledge on the different macrophage subsets in the intestine and their blood counterparts, we hope ...
York physicists pave the way for more energy efficient technology
2014-02-28
An international team of scientists led by physicists from the University of York has paved the way for a new class of magnetic materials and devices with improved performance and power efficiency.
Magnetic materials are currently used to store almost all digital information. However, with information processing and storage now making up a significant fraction of the world's energy consumption, continuing improvements in energy efficiency will require new technologies and materials.
A promising development is all-optical thermally induced magnetic switching (TIMS), which ...
Emergency alert in the cell
2014-02-28
When an organism is exposed to life-threatening conditions, it sounds the alarm and a cellular emergency program, the heat shock response, is initiated. However, the name "heat shock response" is misleading. In the beginning of the 1960s, this form of stress response was first observed. Scientists exposed fruit flies to high temperatures and discovered a complex emergency program designated to save single cells and thus the organism itself. Today researchers know that this program is also triggered by other dangers such as radiation or toxic substances. The terminology, ...
Twitter 'big data' can be used to monitor HIV and drug-related behavior, UCLA study shows
2014-02-28
Real-time social media like Twitter could be used to track HIV incidence and drug-related behaviors with the aim of detecting and potentially preventing outbreaks, a new UCLA-led study shows.
The study, published in the peer-reviewed journal Preventive Medicine, suggests it may be possible to predict sexual risk and drug use behaviors by monitoring tweets, mapping where those messages come from and linking them with data on the geographical distribution of HIV cases. The use of various drugs had been associated in previous studies with HIV sexual risk behaviors and ...
Competition breeds new fish species, study finds
2014-02-28
Competition may play an important role during the evolution of new species, but empirical evidence for this is scarce, despite being implicit in Charles Darwin's work and support from theoretical studies.
Dr Martin Genner from Bristol's School of Biological Sciences and colleagues used population genetics and experimental evidence to demonstrate a role for competition that leads to the differentiation of new species within the highly diverse cichlid fishes of Lake Tanganyika in East Africa.
They found that the cichlid fish Telmatochromis temporalis shows two genetically ...
Rise in New York foreclosures means many could benefit from bankruptcy
2014-02-28
Rise in New York foreclosures means many could benefit from bankruptcy
Article provided by Michael A. Fakhoury, Esq., P.C.
Visit us at http://www.fakhourylaw.com
According to a report from the chief administrator of courts in New York, the number of foreclosurefilings in 2013 exceeded the totals for 2012 and 2011 combined. In some areas, the problem has been particularly pronounced.
A report from the Times Herald-Record indicated that foreclosure filings approximately doubled in Orange and Ulster counties from 2012 to 2013. RealtyTrac, a company that tracks foreclosures, ...
Divorce and tax audits an unfortunately common combination
2014-02-28
Divorce and tax audits an unfortunately common combination
Article provided by Kenney & Kenney
Visit us at http://www.kenney-law.com
Two dreaded legal actions often occur in the early months of the year; winter is a popular time to divorce and most people are required to file a tax return before April. Unfortunately, certain actions that take place during divorce proceedings may also make it more likely to receive a tax audit. In addition, many divorcing couples have questions about how their divorce will affect their taxes. When do they file as single? Who ...
Study finds medical errors third-leading cause of death in US
2014-02-28
Study finds medical errors third-leading cause of death in US
Article provided by Nix Law Group, PLLC
Visit us at http://www.oklahomainjurylaw.com/
If you were asked to name the top causes of death in the United States, you might answer heart disease, cancer or perhaps stroke. Although you would have been correct in naming some of the top causes of death, if you were asked to name other leading causes, you probably never would have identified medical errors. However, a recent study has found that such errors are among the leading reasons why people die each year.
Medical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Dangerous mistaken identityChaperone binds protein responsible for Alzheimer's disease