(Press-News.org) Colchicine, a drug that's used to treat gout, has the beneficial side effect of lowering the risk of heart attack in patients taking it. Conversely, taxol, a drug for treating cancer, has the opposite effect; raising the risk of heart failure.
What both these drugs have in common is that they act on microtubules – a network of fibers inside heart cells that provide internal structural support. Previous studies, including evidence from human patients and experimental models of heart failure, have suggested a link between heart failure and increased density of microtubules, but the mechanisms underlying the link were not clear.
"While it was known that changes in microtubules are linked to the progression of heart failure, no one understood how this was happening," says Long-Sheng Song, M.D., associate professor of internal medicine at the University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine. "Our study provides the first compelling evidence showing how increased microtubule density drives heart failure."
The new study, published online Feb. 11 in the journal Circulation, reveals that colchicine, which decreases the density of microtubules, protects normal heart muscle function and increases survival in mice with heart failure, while taxol, which increases microtubule density, accelerates heart muscle damage during heart failure.
Specifically, the UI team, led by Song and first study author Caimei Zhang, Ph.D., found that increasing microtubule density causes a specialized protein called junctophilin-2 (JP2) to be shuttled to the wrong cellular destination. This abnormal redistribution of JP2 leads to loss of normal heart cell function and ultimately heart failure.
"Changes in microtubule density directly affect where junctophilin-2 is located within the cell," Song explains. "If junctophilin-2 is not in its proper destination, then the cell cannot function properly, which leads to the development and progression of heart failure."
Location, location, location
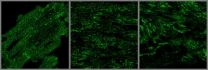
JP2 protein is critical to the normal organization of an important component of heart muscle membrane network called Transverse-tubules or T-tubules. These T-tubules are essential for transmitting the electrical and chemical signals that make a heart beat.
The UI study shows that increased density of microtubules results in abnormal localization of JP2 away from the T-tubule sites to the periphery of the heart cell. The researchers show that this abnormal distribution pattern is also seen in animal models of heart failure and in failing human heart muscle.
Using a mouse model of heart failure, the UI researchers found that decreasing microtubule density with the gout drug colchicine prevents the abnormal redistribution of JP2, prevents disruption of T-tubules, and protects the mice from heart failure.
"The findings suggest that colchicine could be considered as a treatment for patients with heart failure," says Song. "The study also suggests that future approaches targeting junctophilin-2 directly might be a potential strategy for treating heart failure."
INFORMATION:
In addition to Song and Zhang, the research team included UI researchers
Biyi Chen, M.D., Ph.D.; Ang Guo, Ph.D.; Yanqi Zhu, M.D., Ph.D.; Shan Gao, M.D., Ph.D.; William Kutschke, M.S.; Robert M. Weiss, M.D.; Frances L. Johnson, M.D.; and Mark E. Anderson, M.D., Ph.D. Researcher from the Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Iowa City, Iowa; Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.; Anhui Medical University in China; University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, Wash.; and Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, also were part of the team.
The research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (HL090905, HL092235, HL079031, HL622494, HL70250, HL113001, HL085686), and the American Heart Association.
Misplaced protein causes heart failure
Study shows how changes in the organized cell membrane network of heart muscle leads to heart failure
2014-03-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
IUPUI researchers use computers to 'see' neurons to better understand brain function
2014-03-06
INDIANAPOLIS— A study conducted by local high school students and faculty from the Department of Computer and Information Science in the School of Science at Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis reveals new information about the motor circuits of the brain that may one day help those developing therapies to treat conditions such as stroke, schizophrenia, spinal cord injury or Alzheimer's disease.
"MRI and CAT scans of the human brain can tell us many things about the structure of this most complicated of organs, formed of trillions of neurons and the synapses ...
Complications following surgery predict costly readmissions
2014-03-06
The presence – or absence – of complications following surgery is a strong indicator of which patients are likely to be readmitted to the hospital in the 30 days following their procedure, according to a study published today in JAMA Surgery. Predicting which patients are most likely to experience complications using a simple online tool may allow healthcare professionals to flag patients at high risk of readmission in real time and alter care to reduce expensive trips back to the hospital.
The study examined more than 142,000 patients who had non-cardiac surgery using ...
Listening to whispers at the water cooler
2014-03-06
Just as she was about to retire, Lily Ledbetter, a production supervisor at an Alabama tire plant, learned that her employers had financially discriminated against her throughout her career. She filed suit for pay discrimination, losing due to a statute of limitations on equal-pay suits. As a result, President Barack Obama signed the Lily Ledbetter Fair Pay Act into law in 2009, drawing attention to the effects of pay secrecy on the workplace.
Now Prof. Peter Bamberger of Tel Aviv University's Recanati School of Business and Dr. Elena Belogolovsky of Cornell University's ...
Strong teams attract crowds for international cricket
2014-03-06
The strength of the team — not the promise of a close contest — is the biggest draw to crowds in international cricket, new research has found.
The findings from the study, published in the journal Applied Economics, appear to contradict previous research which suggested that attendance is largely determined by how closely matched the two teams are during a game.
Economists Dr Abhinav Sacheti and Professor David Paton from Nottingham University Business School, in collaboration with Dr Ian Gregory-Smith from the University of Sheffield, analysed the number of spectators ...
MIT team proposes storing extra rocket fuel in space for future missions
2014-03-06
Future lunar missions may be fueled by gas stations in space, according to MIT engineers: A spacecraft might dock at a propellant depot, somewhere between the Earth and the moon, and pick up extra rocket fuel before making its way to the lunar surface.
Orbiting way stations could reduce the fuel a spacecraft needs to carry from Earth — and with less fuel onboard, a rocket could launch heavier payloads, such as large scientific experiments.
Over the last few decades, scientists have proposed various designs, such as building a fuel-manufacturing station on the moon ...
Researchers identify target for shutting down growth of prostate cancer cells
2014-03-06
DALLAS – March 4, 2014 – Scientists at UT Southwestern Medical Center have identified an important step toward potentially shutting down the growth of prostate cancer cells.
Dr. Ralf Kittler, Assistant Professor of Pharmacology, studies ERG, a protein that facilitates the transformation of normal prostate cells into cancer cells. His lab found that an enzyme called USP9X protects ERG from degradation and subsequently found that a molecule called WP1130 can block USP9X and lead to the destruction of ERG.
"We now have a target that we could potentially exploit to develop ...
Thirty percent of adults with attention deficit disorder report childhood physical abuse
2014-03-06
Thirty percent of adults with Attention Deficit Disorder or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADD/ADHD) report they were physically abused before they turned 18. This compares to seven per cent of those without ADD/ADHD who were physically abused before 18. The results were in a study published in this week's online Journal of Aggression, Maltreatment, and Trauma.
"This strong association between abuse and ADD/ADHD was not explained by differences in demographic characteristics or other early adversities experienced by those who had been abused," says lead author ...
Pharmaceutical companies' DC marketing efforts increase to nearly $98 million
2014-03-06
WASHINGTON, DC (March 6, 2014)— Drug companies spent $97.5 million marketing pharmaceuticals in the District of Columbia in 2012, with $30.5 million (31.3%) of that spending taking the form of payments and gifts to physicians, hospitals, and other healthcare providers, according to a report by researchers at the George Washington University School of Public Health and Health Services (SPHHS).
These expenditures represent the first year-on-year spending increase by drug companies since 2007. Between 2007 and 2011, spending declined each year to a low of $84 million in ...
IT security for the daily life: Withdrawing money at cash machines with 'Google Glass'
2014-03-06
This news release is available in German.
Taking photos with a wink, checking one's calendar with a glance of the right eye, reading text messages — the multinational cooperation Google wants to make it possible with Google Glass. But what IT experts celebrate as a new milestone makes privacy groups skeptical. So far, few people have access to the prototype to test how it can be used in daily life. "Thanks to the Max Planck Institute for Informatics we are one of the few universities in Germany that can do research with Google Glass", says Dominique Schröder, assistant ...
Study: Classroom focus on social and emotional skills can lead to academic gains
2014-03-06
VIDEO:
This video shows: "Efficacy of the Responsive Classroom Approach:
Results from a Three Year, Longitudinal Randomized Controlled Trial. "
Published Online First in:
American Educational Research Journal
March 6, 2014
Authors:
Sarah Rimm-Kaufman, Ross A. Larsen, Alison...
Click here for more information.
WASHINGTON, D.C., March 6, 2014 ─ Classroom programs designed to improve elementary school students' social and emotional skills can also ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] Misplaced protein causes heart failureStudy shows how changes in the organized cell membrane network of heart muscle leads to heart failure