(Press-News.org) The zone of overlap between two popular, closely related backyard birds is moving northward at a rate that matches warming winter temperatures, according to a study by researchers from the Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Villanova University, and Cornell University. The research will be published online in Current Biology on Thursday, March 6, 2014.
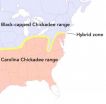
In a narrow strip that runs across the eastern U.S., Carolina Chickadees from the south meet and interbreed with Black-capped Chickadees from the north. The new study finds that this hybrid zone has moved northward at a rate of 0.7 mile per year over the last decade. That's fast enough that the researchers had to add an extra study site partway through their project in order to keep up.
"A lot of the time climate change doesn't really seem tangible," said lead author Scott Taylor, a postdoctoral researcher at the Cornell Lab of Ornithology. "But here are these common little backyard birds we all grew up with, and we're seeing them moving northward on relatively short time scales."
In Pennsylvania, where the study was conducted, the hybrid zone is just 21 miles across on average. Hybrid chickadees have lower breeding success and survival than either of the pure species. This keeps the contact zone small and well defined, making it a convenient reference point for scientists aiming to track environmental changes.
"Hybridization is kind of a brick wall between these two species," said Robert Curry, a professor of biology at Villanova University, who led the field component of the study. "Carolina Chickadees can't blithely disperse north without running into black-caps and creating hybrids. That makes it possible to keep an eye on the hybrid zone and see exactly how the ranges are shifting."
The researchers drew on field studies, genetic analyses, and crowdsourced bird sightings. First, detailed observations and banding data from sites arrayed across the hybrid zone provided a basic record of how quickly the zone moved. Next, genetic analyses revealed in unprecedented detail the degree to which hybrids shared the DNA of both parent species. And then crowdsourced data drawn from eBird, a citizen-science project run by the Cornell Lab, allowed the researchers to expand the scale of the study and match bird observations with winter temperatures.
The researchers analyzed blood samples from 167 chickadees—83 collected in 2000–2002 and 84 in 2010–2012. Using next-generation genetic sequencing, they looked at more than 1,400 fragments of the birds’ genomes to see how much was Black-capped Chickadee DNA and how much was Carolina.
The site that had been in the middle of the hybrid zone at the start of the study was almost pure Carolina Chickadees by the end. The next site to the north, which Curry and his students had originally picked as a stronghold of Black-capped Chickadees, had become dominated by hybrids.
Female Carolina Chickadees seem to be leading the charge, Curry said. Field observations show that females move on average about 0.6 mile between where they're born and where they settle down. That's about twice as far as males and almost exactly as fast as the hybrid zone is moving.
As a final step, the researchers overlaid temperature records on eBird sightings of hybrid chickadees. They found a very close match: hybrids occurred only in areas where the average winter low temperature was between 14 and 20 degrees Fahrenheit. They also used eBird records to estimate where the hybrid zone had been a decade earlier, and found the same relationship with temperature existed then, too. The only difference was that those temperatures had shifted to the north by about seven miles since 2000.
Chickadees—there are seven species in North America—are fixtures in most of the backyards of the continent. These tiny, fluffy birds with bold black-and-white faces are favorite year-round visitors to bird feeders, somehow surviving cold winters despite weighing less than half an ounce.
To the untrained eye the Carolina Chickadee of the southeastern U.S. is almost identical to the more northern Black-capped Chickadee—although the Carolina has a shorter tail, less white on its shoulders, and a song of four notes instead of two notes. Genetic research indicates the two have been distinct species for at least 2.5 million years.
"The rapidity with which these changes are happening is a big deal," Taylor said. "If we can see it happening with chickadees, which are pretty mobile, we should think more closely about what's happening to other species. Small mammals, insects, and definitely plants are probably feeling these same pressures—they're just not as able to move in response."
INFORMATION:
In addition to Taylor and Curry, the authors include Thomas White of Cornell University, Valentina Ferretti of Villanova University, and Wesley Hochachka and Irby Lovette of the Cornell Lab.
Warming temperatures are pushing 2 chickadee species -- and their hybrids -- northward
DNA sleuthing confirms chickadee 'hybrid zone' marching northward as climate warms
2014-03-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Obese adolescents not getting enough sleep?
2014-03-06
Cincinnati, OH, March 6, 2014 -- Lack of sleep and obesity have been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases in adults and young children. However, the association is not as clear in adolescents, an age group that is known to lack adequate sleep and have an overweight and obesity prevalence rate of 30% in the US. In a new study scheduled for publication in The Journal of Pediatrics, researchers found that cardiometabolic risk in obese adolescents may be predicted by typical sleep patterns.
Heidi B. IglayReger, PhD, and colleagues from ...
Establishing standards where none exist; Harvard researchers define 'good' stem cells
2014-03-06
After more than a decade of incremental – and paradigm shifting, advances in stem cell biology, almost anyone with a basic understanding of life sciences knows that stem cells are the basic form of cell from which all specialized cells, and eventually organs and body parts, derive.
But what makes a "good" stem cell, one that can reliably be used in drug development, and for disease study? Researchers have made enormous strides in understanding the process of cellular reprogramming, and how and why stem cells commit to becoming various types of adult cells. But until now, ...
Dr. Brenna Anderson contributes to expert series on GAS in pregnancy
2014-03-06
Ignaz Semmelweiss made one of the most important contributions to modern medicine when he instituted hand washing in an obstetric clinic in Austria in 1847, decreasing mortality there from more than ten percent to two percent. Unfortunately, infections can still occur in pregnancy and during delivery and can have associated mortality rates of up to 30 to 50 percent if not treated quickly and properly.
Brenna Anderson, MD, director of the Women's Infectious Diseases Consultative Service at Women & Infants of Rhode Island and an associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology ...
Study identifies gene important to breast development and breast cancer
2014-03-06
Significance: Understanding more about how the different types of cells in breast tissue develop improves our knowledge of breast cancer. TAZ represents a potential new target for drug therapies to treat aggressive types of breast cancer.
Background: In cancer, normal cells can become unpredictable or aggressive and thus difficult to treat with anti-cancer drugs. This is especially true in breast cancer. By identifying the genes responsible for this change in cells from breast tissue, researchers hope to identify a way to stop or reverse it.
In breast tissue, there ...
Are you smarter than a 5-year-old? Preschoolers can do algebra
2014-03-06
Millions of high school and college algebra students are united in a shared agony over solving for x and y, and for those to whom the answers don't come easily, it gets worse: Most preschoolers and kindergarteners can do some algebra before even entering a math class.
In a recently published study in the journal Developmental Science, lead author and post-doctoral fellow Melissa Kibbe and Lisa Feigenson, associate professor of psychological and brain sciences at Johns Hopkins University's Krieger School of Arts and Sciences, find that most preschoolers and kindergarteners, ...
Access to social workers could keep veterans out of criminal justice system, MU researchers find
2014-03-06
COLUMBIA, Mo. –Approximately one in six veterans struggles with substance abuse, and 20 percent show signs of mental health issues or cognitive impairments, previous research has shown. These risk factors, combined with a lack of resources, could be contributing to an increase of veterans entering the criminal justice system, according to a report by the Center for Mental Health Services. Now, University of Missouri researchers have investigated ways social workers can address veterans' needs and keep them out of jail.
"Social workers are equipped to provide support to ...
Save money and the planet: Turn your old milk jugs into 3-D printer filament
2014-03-06
Making your own stuff with a 3D printer is vastly cheaper than what you'd pay for manufactured goods, even factoring in the cost of buying the plastic filament.
Yet, you can drive the cost down even more by making your own filament from old milk jugs. And, while you are patting yourself on the back for saving 99 cents on the dollar, there's a bonus: you can feel warm and fuzzy about preserving the environment.
A study led by Joshua Pearce of Michigan Technological University has shown that making your own plastic 3D printer filament from milk jugs uses less energy—often ...
First-ever 3-D image created of the structure beneath Sierra Negra volcano
2014-03-06
The Galápagos Islands are home to some of the most active volcanoes in the world, with more than 50 eruptions in the last 200 years. Yet until recently, scientists knew far more about the history of finches, tortoises, and iguanas than of the volcanoes on which these unusual fauna had evolved.
Now research out of the University of Rochester is providing a better picture of the subterranean plumbing system that feeds the Galápagos volcanoes, as well as a major difference with another Pacific Island chain—the Hawaiian Islands. The findings have been published in the Journal ...
Sickle cell trait: Neglected opportunities in the era of genomic medicine
2014-03-06
(Boston)--While acknowledging the potential of genomics to prevent and treat disease, researchers from Boston Medical Center (BMC) and Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) believe it is long past due to use current scientific data and technical advances to reduce the burden of sickle cell disease (SCD), one of the most common serious single gene disorders. The work, reported as a Viewpoint in this week's Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), highlights the gaps in knowledge and care in terms of SCD and the need to address this issue expeditiously. ...
Physician bias does not affect hypertension treatment for minority patients, says CU
2014-03-06
Doctors' unconscious biases favor whites but do not affect high blood pressure treatment for their minority patients, according to a University of Colorado Boulder study, even though a previous study by the same research group found that doctors' biases are reflected in lower ratings by African-American patients.
The new research, led by Irene Blair, an associate professor in CU-Boulder's Department of Psychology and Neuroscience, is published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine.
"We know that minorities have to face bias and discrimination in many different ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
[Press-News.org] Warming temperatures are pushing 2 chickadee species -- and their hybrids -- northwardDNA sleuthing confirms chickadee 'hybrid zone' marching northward as climate warms