(Press-News.org) Tropical Cyclone Lusi has spawned warnings and watches in the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, and New Zealand as it moves through the South Pacific Ocean. NASA's Terra and Aqua satellites provided visible and infrared views of the storm that revealed it has become better organized.
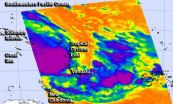
NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Cyclone Lusi over Vanuatu on March 9 at 23:30 UTC. The image showed towering thunderstorms surrounded the center and northwestern quadrants of the storm.
The next day at 02:17 UTC, NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Lusi and captured infrared data on the storm that showed the thunderstorms rose high into the troposphere. The strongest thunderstorms had cloud top temperatures as cold as -63F/-52C. Multispectral satellite imagery showed that Lusi continued to consolidate and strong thunderstorms continue to develop. Those thunderstorms are wrapping into the center of circulation.
NASA and JAXA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite provided a microwave look at Lusi at 05:31 UTC/1:31 a.m. EST and showed the system continues to consolidate. TRMM data showed bands of strong thunderstorms had wrapped tightly around the center, and that the bulk of the deep convection is within the storm's northwestern quadrant.
Lusi has spawned several watches and warnings. In the Solomon Islands a tropical cyclone watch is in effect for Temotu, Makira, Rennell and Bellona, as well as the southern Guadalcanal and Malaita provinces.
In Vanuatu, gale force winds were expected to continue to affect Torba, Sanma, Penama and Malampa Provinces on March 10 and 11 as the storm pushes south. The Vanuatu Meteorological Service expects very rough seas and heavy swells throughout Vanuatu. They noted that heavy rainfall and flooding are also expected over low lying areas and areas close to river banks on March 10. For further updates from the Vanuatu Meteorological Services, visit: http://www.meteo.gov.vu.
Farther south, New Zealand is already anticipating effects from Lusi. The Met Service of New Zealand noted in their discussion on March 10, that once Lusi moves closer "it could bring a spell of wet and windy weather especially to parts of northern New Zealand by the weekend." For further updates from the New Zealand Met Service, visit: http://www.metservice.com/.
On March 10 at 0900 UTC/5 a.m. EST, Tropical Cyclone Lusi had maximum sustained winds near 45 knots/51.7 mph/84.4 kph. It was centered near 15.0 south latitude and 166.7 east longitude, about 433 nautical miles/498.3 miles/801.9 km north of Noumea, New Caledonia. Lusi was moving to the west-southwest at 4 knots/4.6 mph/7.4 kph.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center expects Lusi to run into cooler waters and increasing vertical wind shear that will help weaken the storm and transition it into an extra-tropical storm.
INFORMATION:
NASA satellites eye troublesome Tropical Cyclone Lusi
2014-03-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
US cocaine use cut by half, while marijuana consumption jumps, study finds
2014-03-10
The use of cocaine dropped sharply across the United States from 2006 to 2010, while the amount of marijuana consumed increased significantly during the same period, according to a new report.
Studying illegal drug use nationally from 2000 to 2010, researchers found the amount of marijuana consumed by Americans increased by more than 30 percent from 2006 to 2010, while cocaine consumption fell by about half. Meanwhile, heroin use was fairly stable throughout the decade.
Methamphetamine consumption dramatically increased during the first half of the decade and then declined, ...
Scientists build thinnest-possible LEDs to be stronger, more energy efficient
2014-03-10
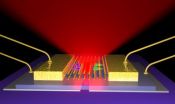
Most modern electronics, from flat-screen TVs and smartphones to wearable technologies and computer monitors, use tiny light-emitting diodes, or LEDs. These LEDs are based off of semiconductors that emit light with the movement of electrons. As devices get smaller and faster, there is more demand for such semiconductors that are tinier, stronger and more energy efficient.
University of Washington scientists have built the thinnest-known LED that can be used as a source of light energy in electronics. The LED is based off of two-dimensional, flexible semiconductors, making ...
A signal to spread: Wistar scientists identify potent driver of metastasis
2014-03-10
An international team of researchers led by scientists at The Wistar Institute have discovered and defined LIMD2, a protein that can drive metastasis, the process where tumors spread throughout the body.
Their study, published in the March issue of the journal Cancer Research, defines the structure of LIMD2 and correlates the protein in metastatic bladder, melanoma, breast, and thyroid tumors. Wistar scientists have also developed and patented a monoclonal antibody that may one day be used as a prognostic test to see if tumors have LIMD2, and plans are underway to create ...
Malnourished children are better fed when mothers have network of peers
2014-03-10
URBANA, Ill. – Women in rural India who participate in a vocational training program learn more than just life skills. A recent University of Illinois study found that mothers who participated in a program designed to educate and empower women gained a network of peers that led to increased bargaining strength in the home, and significantly improved their children's consumption of rice and dairy.
"Prior to participating in Mahila Samakhya, which loosely translates to women of equal value, most of the participants reported regularly communicating with fewer than five ...
New research shows elevated mercury from in-ground wastewater disposal
2014-03-10
As towns across Cape Cod struggle with problems stemming from septic systems, a recent study by a Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) scientist focuses on one specific toxic by-product: mercury. In a study of local groundwater, biogeochemist Carl Lamborg found microbial action on wastewater transforms it into more mobile, more toxic forms of the element.
His findings were published in Environmental Science and Technology in November 2013.
Mercury (Hg) is a toxic trace metal. Wastewater contains small amounts of it, but Lamborg found the chemical processes that ...
What's new in autism spectrum disorder? Harvard Review of Psychiatry presents research update
2014-03-10
Philadelphia, Pa. (March 10, 2014) – Recent years have seen exciting progress in key areas of research on autism spectrum disorders (ASD): from possible genetic causes, to effective treatments for common symptoms and clinical problems, to promoting success for young people with ASD entering college. Updates on these and other advances in ASD research are presented in the March special issue of Harvard Review of Psychiatry. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
"Autism is one of the most challenging disorders to ...
Phosphorylation of tau protein in rats subjected to cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury
2014-03-10
Transient brain ischemia has been shown to induce hyperphosphorylation of the microtu-bule-associated protein tau. To further determine the mechanisms underlying these processes, Dr, Bo Song and co-workers from School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University in China found for the first time that the interaction of tau with glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3β and protein phosphatase 2A is altered during transient brain ischemia. In addition, the researchers found that the neuroprotective function of lithium chloride may depend partly on the altered phosphorylation of tau, ...
Pretreatment with SSTF prevents hippocampal neuronal apoptosis due to cerebral infarction
2014-03-10
Focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion may lead to neuronal loss in the hippocampus, which is regarded as one of the basic pathological mechanisms underlying cognitive impairment. The neuronal apoptosis plays an important role in cerebral infarction, determining the number of loss of neurons and infarct volume. Growing evidence has suggested that Chinese herbs can inhibit hippocampal apoptosis caused by ischemia-reperfusion. Prof. Shumin Zhao and team from Chengde Medical College in China pretreated rats with scutellaria baicalensis stem-leaf total flavonoid (SSTF) intragastrically ...
Agroforestry can ensure food security and mitigate the effects of climate change in Africa
2014-03-10
Agroforestry can help to achieve climate change mitigation and adaptation while at the same time providing livelihoods for poor smallholder farmers in Africa.
Scientists at the World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF) say agroforestry - which is an integrated land use management technique that incorporates trees and shrubs with crops and livestock on farms - could be a win-win solution to the seemingly difficult choice between reforestation and agricultural land use, because it increases the storage of carbon and may also enhance agricultural productivity.
In a special issue ...
Smokers' brains biased against negative images of smoking
2014-03-10
This news release is available in French. What if the use of a product influenced your perception of it, making you even more susceptible to its positive aspects and altering your understanding of its drawbacks? This is precisely what happens with cigarettes in chronic smokers, according to a recent study by the Institut universitaire en santé mentale de Montréal and Université de Montréal.
The study showed that chronic smokers have altered emotional reactions when they are exposed to negative and positive images associated with tobacco. "We observed a bias depending ...